Team:Evry/Sensor
From 2013.igem.org
| Line 140: | Line 140: | ||
<div align='center'><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/1/12/ColiSensor.png" width="75%"/></div> | <div align='center'><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/1/12/ColiSensor.png" width="75%"/></div> | ||
| + | |||
<p align="center"> | <p align="center"> | ||
<b>Fig. 2</b> Diagram of our genetic iron sensor. Iron binds the Ferric Uptake Regulator (Fur) to form a complex with high affinity for the Fur box in the promoter, here shown as the aceB promoter. Once the iron-Fur complex is bound to the promoter, it represses transcription of the target gene GFP. GFP expression is thus negatively correlated with iron availability. | <b>Fig. 2</b> Diagram of our genetic iron sensor. Iron binds the Ferric Uptake Regulator (Fur) to form a complex with high affinity for the Fur box in the promoter, here shown as the aceB promoter. Once the iron-Fur complex is bound to the promoter, it represses transcription of the target gene GFP. GFP expression is thus negatively correlated with iron availability. | ||
| Line 145: | Line 146: | ||
<p> | <p> | ||
| - | We characterised our construction | + | We characterised our construction growing our bacteria in different iron concentrations (0.1 µM, 1 µM and 10 µM). Using 96-wells plate reader, we measured O.D. (600 nm) and GFP intensity (530 nm) each 10 minutes of the bacterial growth. |
</p> | </p> | ||
| - | + | <div align='center'><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/9/96/Tecan.jpg" width="75%"/></div> | |
Revision as of 20:28, 28 October 2013
Iron Sensor

Construction of the iron-responsive biosensors
E. coli's genome is composed of many Fur binding site. Based on a genome study, we identified 4 promoters which are controled by the FUR protein.
- AceB promoter - (BBa_K1163102)
- Fes promoter - (BBa_K1163108)
- FepA promoter - (BBa_K1163105)
- yncE promoter - (BBa_K1163111)
Using PCR on E. coli genome, we extracted these four promoters. We constructed iron-responsive biosensors by combining 3 genetic parts: an E. coli promoter with a Ferric Uptake Regulator (Fur) binding site, a fluorescent reporter (sfGFP), and a transcriptional terminator (see Figure 1 below). Promoter-reporter fusions were made with flanking restriction sites that are compatible with Biobrick-based cloning.


Fig. 1 Construction of an iron-responsive genetic element by fusing a Fur-regulated promoter with a reporter gene.
We put all the parts together using Golden Gate assembly method. In order to combine our part in the right way, we designed specific overhang as shown in the table 1.
| Name | Figure | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
E. coli promoter with Fur binding site |

|
iron-Fur complex binds promoter to repress expression |
|
sfGFP |

|
Fluorescent reporter gene |
|
Terminator |

|
terminator to stop transcription |
|
Plasmid |

|
Biobrick-compatible plasmid backbone |
Table 1 Genetic elements used to make iron-responsive sensors.
These biosensors respond to ambient iron by using the Fur system to repress the reporter gene placed downstream the promoter.
Caracterisation of the iron-responsive biosensors
As shown in figure 2, in our construction, sfGFP is placed downstream the Fur binding site. It means that in iron starvation sfGFP should be expressed and in high concentration of iron it should be repressed.
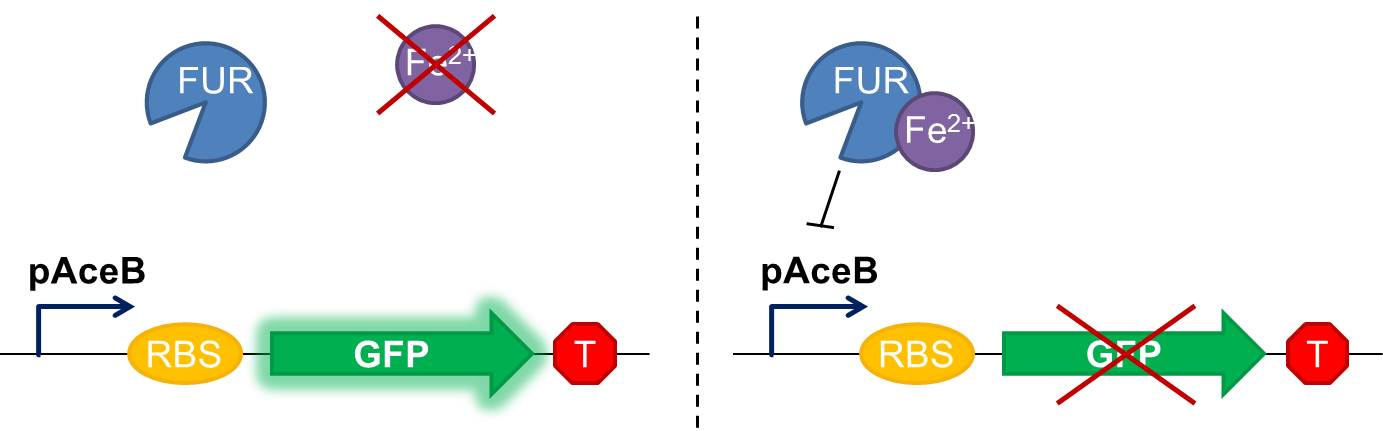
Fig. 2 Diagram of our genetic iron sensor. Iron binds the Ferric Uptake Regulator (Fur) to form a complex with high affinity for the Fur box in the promoter, here shown as the aceB promoter. Once the iron-Fur complex is bound to the promoter, it represses transcription of the target gene GFP. GFP expression is thus negatively correlated with iron availability.
We characterised our construction growing our bacteria in different iron concentrations (0.1 µM, 1 µM and 10 µM). Using 96-wells plate reader, we measured O.D. (600 nm) and GFP intensity (530 nm) each 10 minutes of the bacterial growth.

 "
"













