Team:TU-Munich/Results/GM-Moss
From 2013.igem.org
IngmarPolte (Talk | contribs) (→The PhyscoFilter for Fluorescein) |
IngmarPolte (Talk | contribs) (→The PhyscoFilter for Fluorescein) |
||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
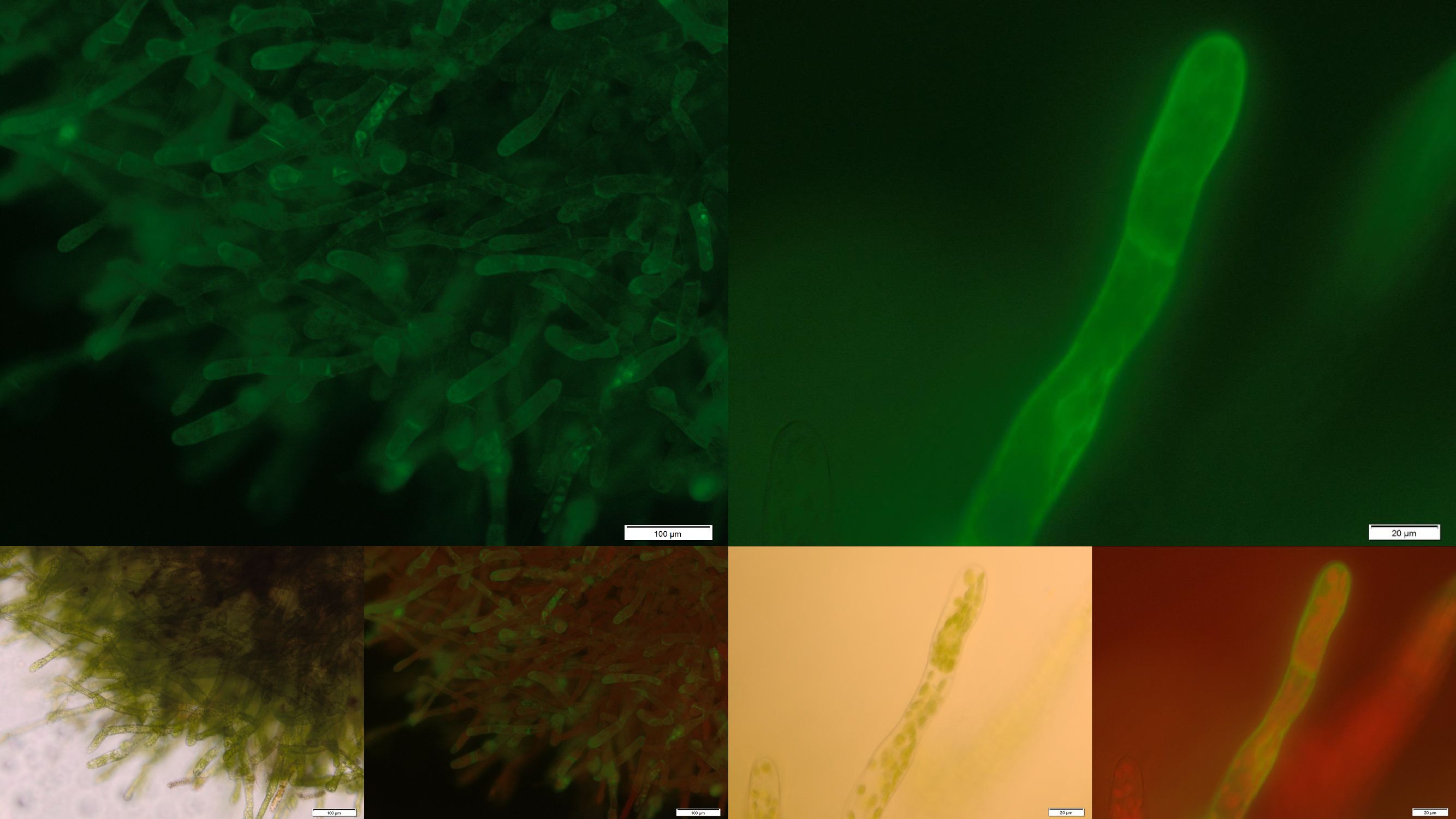
[[File:Localization_membrane_FluA.jpg|thumb|center|920px|'''Figure 4:''' Successfully selected moss with membrane-anchored FluA. You can clearly see the GFP fluorescence of the membrane-anchored FluA in the edges of the moss cells. Upper images: GFP-fluorescence; lower two left: brightfield; lower two right: GFP-fluorescence plus chloroplast autofluorescence.]] | [[File:Localization_membrane_FluA.jpg|thumb|center|920px|'''Figure 4:''' Successfully selected moss with membrane-anchored FluA. You can clearly see the GFP fluorescence of the membrane-anchored FluA in the edges of the moss cells. Upper images: GFP-fluorescence; lower two left: brightfield; lower two right: GFP-fluorescence plus chloroplast autofluorescence.]] | ||
(receptor bound BioAccumulation using <partinfo>BBa_K1159003</partinfo>) | (receptor bound BioAccumulation using <partinfo>BBa_K1159003</partinfo>) | ||
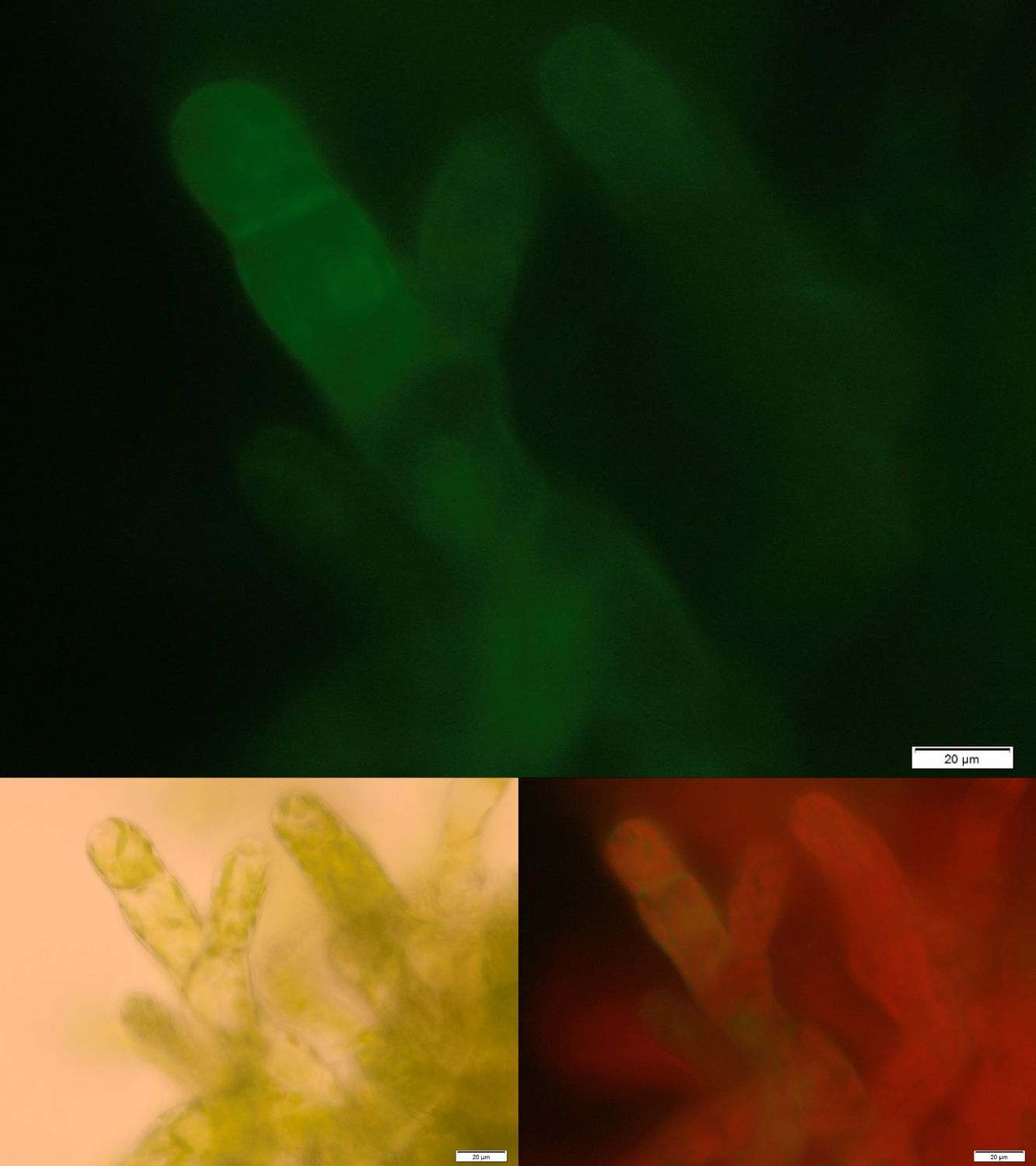
| + | In order to prove the suitability of surface immobilized binding molecules in general and of aniticalins in particular we decided to transform our moss with a genetic construct containing [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1159003 FluA], an Anticalin with a high affinity towards fluorescein, fused at the C-terminus to the N-terminus of our developed [http://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K1159315 trans membrane receptor]. Especially in the upper and lower fluorescence images on the right a compared to the cytoplasm increased membrane associated GFP fluorescence can be seen. This fluorescence indicates that our used secretion signal and trans membrane domain work properly and lead to the desired membrane localization. | ||
==References:== | ==References:== | ||
Revision as of 23:53, 28 October 2013
Characterization of transgenic plants
The PhyscoFilter for Erythromycin
In order to check the activity of the erythromycine esterase B we pursued two different approaches: on the one hand we produced the enzyme recombinant in Escherichia coli and purified it. The purified protein was used for in vitro activity tests determining the depletion rates. The reaction was stopped at predetermined times by addition of three volumes acetonitrile and freezing in liquid nitrogen. On the other hand we added the substrate erythromycin at a concentration of 0.2 g L-1 to 3 mL of a polyclonal suspension of transgenic moss plants expressing the erythromycin esterase B in the cytoplasm. After 24 h of incubation at normal growth conditions 100 µL of the supernatant were used for further analysis.
Both samples were analyzed by liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry (UPLC/MS/MS). The samples were measured at a Waters Xevo TQ-S using a Waters Acquity BEH C18 2,1 x 100mm column (1.7 µm, 130 Å pore size) and the following method: Solvent A: 0.1 % formic acid in water, B: 0.1 % formic acid in ACN and a linear gradient of 99 % A 0.5 min isocratic to 99 % B in 6 min. Column temperature 40 °C, flux 0.4 mL min-1, maximal pressure 703 bar. The tuning was executed with solutions consisting of the pure educt at concentrations of approximately 0.1 mgL-1.
In part A of figure seven the liquid chromatography chromatogram and the associated molecular mass for pure erythromycin as a standard is shown highlighted in red at a retention time of 3.65 min and a mass of ~734.3 g mol-1.
Part B of figure seven shows the corresponding LCMS spectra of purified erythromycin esterase B incubated for 0 min and 5 min with erythromycin. After 0 min of incubation the red highlighted peak with a retention time of 3.68 min and a mass of ~734.3 g mol-1 shows the initial presence of the substrate. However even merely mixing the substrate and enzyme was sufficient to degrade a small amount of substrate which is shown by the emerging peaks at 4.19 and 4.30 min retention time. The chromatogram of the sample taken after five minutes of incubation no longer shows the characteristic substrate peak at 3.68 min indicating that the whole amount of substrate was successfully degraded by the purified enzyme.
Part C of figure seven shows the corresponding LCMS spectra of the in vivo degradation experiment with transgenic moss expressing erythromycin esterase B in the cytoplasm. After 24 h of incubation at normal growth conditions the chromatogram of the sample containing the wild type moss as a negative control exclusively shows the characteristic peak for the substrate highlighted in red. The chromatogram of the sample in which the transgenic moss was utilized in contrast shows the clear degradation of the substrate because only the peaks at retention times of 4.19 and 4.30 min appear representing the degradation product as explained for part B of this figure.
To summarize this experiment demonstrates that our transgenic moss successfully degraded the environmental pollutant erythromycin!
The PhyscoFilter for Diclofenac and Ethinylestradiol
The PhyscoFilter for Microcystin

The PhyscoFilter for Fluorescein
(receptor bound BioAccumulation using <partinfo>BBa_K1159003</partinfo>) In order to prove the suitability of surface immobilized binding molecules in general and of aniticalins in particular we decided to transform our moss with a genetic construct containing [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1159003 FluA], an Anticalin with a high affinity towards fluorescein, fused at the C-terminus to the N-terminus of our developed [http://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K1159315 trans membrane receptor]. Especially in the upper and lower fluorescence images on the right a compared to the cytoplasm increased membrane associated GFP fluorescence can be seen. This fluorescence indicates that our used secretion signal and trans membrane domain work properly and lead to the desired membrane localization.
References:
- http://www.plant-biotech.net/paper/CurrGenet_2003_hohe.pdf Hohe, A., T. Egener, J. Lucht, H. Holtorf, C. Reinhard, G. Schween, R. Reski (2004): An improved and highly standardised transformation procedure allows efficient production of single and multiple targeted gene knockouts in a moss, Physcomitrella patens. Current Genet. 44, 339-347.
 "
"




AutoAnnotator:
Follow us:
Address:
iGEM Team TU-Munich
Emil-Erlenmeyer-Forum 5
85354 Freising, Germany
Email: igem@wzw.tum.de
Phone: +49 8161 71-4351