Team:Linkoping Sweden/Notebook
From 2013.igem.org
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
A common problem in todays society is allergies. To be able to quickly detect the precence of an antigen we are developing a biosensor. The sensor is created by letting genetically modified E.Coli produce a complex consisting of an antibody and a fluorescent protein. When this complex comes in contact with a certain antigen attached to another fluorescent protein, it will emit light. This light will be discovered by a detector and translated into an electrical signal. Using this method, very small amounts of an antigen can be measured and ampified. | A common problem in todays society is allergies. To be able to quickly detect the precence of an antigen we are developing a biosensor. The sensor is created by letting genetically modified E.Coli produce a complex consisting of an antibody and a fluorescent protein. When this complex comes in contact with a certain antigen attached to another fluorescent protein, it will emit light. This light will be discovered by a detector and translated into an electrical signal. Using this method, very small amounts of an antigen can be measured and ampified. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''September 11''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Great success today as we managed to create our first biobrick! The band in the red circle on the gel shows us that we got the antibody, promoter and luciferase together to create a new biobrick. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Gele biobrick AK.png]] | ||
---- | ---- | ||
Revision as of 18:07, 18 September 2013














Construction of a living detection system or biosensor of allergens using Luciferase
A common problem in todays society is allergies. To be able to quickly detect the precence of an antigen we are developing a biosensor. The sensor is created by letting genetically modified E.Coli produce a complex consisting of an antibody and a fluorescent protein. When this complex comes in contact with a certain antigen attached to another fluorescent protein, it will emit light. This light will be discovered by a detector and translated into an electrical signal. Using this method, very small amounts of an antigen can be measured and ampified.
September 11
Great success today as we managed to create our first biobrick! The band in the red circle on the gel shows us that we got the antibody, promoter and luciferase together to create a new biobrick.
August 17
After adding enzymes to cut our Luciferase part from the plasmid, we did a gelelectrophoresis. In this way, we can controll that the enzymes cut at the right places in the plasmid, resulting in a fragment about 3000 baspairs long for Luciferase. Efter that we just take the Luciferase band visible on the gel, cut it out, and smash the gel to prepare it for futher purification steps.
July 24
Today we were interviewed on the Swedish radio channel ”Sveriges Radio P4 Östergötland” Anna and David got to explain what we are trying to do in our project and inform people about synthetic biology and the iGEM competition. They did a great job! If you want to listen to the interview (in Swedish) just click on the link below!
http://sverigesradio.se/sida/artikel.aspx?programid=2949&artikel=5600104
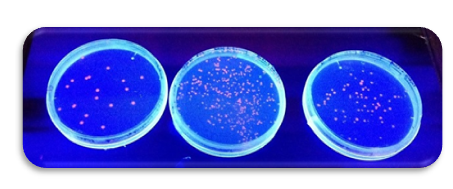
July 23
After some attempts we finally got a good transformation! The red dots glowing in the UV-light are E.Coli that during the electroporation successfully managed to take up the DNA for RFP (Red Fluorescent Protein) and started to produce this.
June 3
To start with, we needed to find some E.Coli. With the help from Cecilia at LiU, we got a compatible stem of E.Coli, ready for electroporation. To assure that all concentrations were right, the agar was correctly prepared, and that the bacteria would manage the electroporation and grow as desired, we decided to do some transformation attempts using only RFP and Luciferase. In this way, we increase our chanses of getting the best possible result with the Antibody-Complex DNA later on.






 "
"