Team:Evry/ChemicalTools
From 2013.igem.org
Chemical reasoning
There are 6 enzyms involved in the natural process of the enterobactin production:
- EntA :
- EntB :
- EntC :
- EntD :
- EntE :
- EntF :

For now, we consider each one of these steps as a simple chemical reaction:

We are using the enzymatic kinetic model of Michaelis-Menten, which divides each reaction into two consecutives steps:

The speed of the reaction is calculated as below:
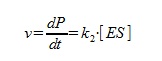
The steady state approximation gives us:

And thus,

where  and
and  are classic kinetic parameters.
are classic kinetic parameters.
Important result:
For simple enzymatic reactions (one reagent, one product and one enzyme) with the steady state approximation, we can directly determine the speed:
Enterobactin production kinetiks
The enterobactin's pathway is divided into 4 steps:

The first two steps fulfill the conditions previously established. We can thus say:

In Escherichia-coli, NAD+, NADH and H+ are considered abundant: their concentration will not be affected much by the reaction.
From a kinetic point of view, we can write this new reaction: (this is just a notation)

And so:

As the ATP, L-Serin, AMP, diphosphate and H+ are all considered abundant in Escherichia-coli, we applied the same principle for the fourth reaction:

Now, the difference is that four enzymes are requested. In order to study it, we divided the reaction into 4 theorical consecutive reactions:

Note that the order in which the reactions and the enzymes are displayed is arbitrary. The RI1, RI2 and RI3 are theoretical reaction intermediate that represent the influence of the enzymes on the reaction.
The steady state approximation gives us:

Yet, since the first theorical reaction fulfills our hypothesis,

So:

The w2, w3 and w4 speeds cannot be expressed in concrete terms, because they are supposed to measure theoretical reaction intermediates.
Conclusion:

 "
"













