Team:TU-Eindhoven/CESTAgentTesting
From 2013.igem.org



Contents |
Abstract
Introduction
Initially, a total of 10 constructs with proteins were designed, all containing a high percentage of lysine and/or arginine, which have a chemical shift which can be used for CEST imaging. Four of them were naturally occurring proteins, native to either E. coli or to other organisms, in which case the protein sequence was optimized to match codon prevalence in E. coli. These were 1G70, 1ETF, 1PJN Chain-1 and Human Protamine 1 (HPM1, optimized). The other five were non-natural polypeptides consisting of a two repeating dipeptides, namely poly(arginine-glycine) (P(RG)), poly(lysine-serine) (P(KS)), poly(arginine-serine) (P(RS))and poly(threonine-lysine) (P(TK)). Like HPM1, these we E. coli optimised. Additionally, an EGFP construct would also be inserted and expressed as a positive control.
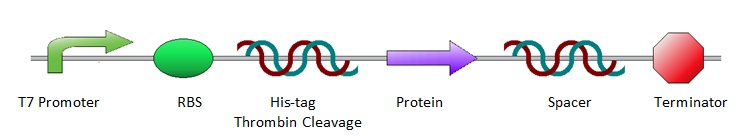
All the protein sequences were cut out of the ordered pUC57(s) vectors by NheI and XhoI restriction enzymes and ligated into pET28a vectors. As a result, all constructs shared the same lay-out, starting with prescribed iGEM restriction sites EcoRI, NotI and XbaI, followed by an T7 promotor site and ribosome binding site. Hereafter are a poly-histidine tag (for protein purification), thrombin cleavage site and NheI restriction site (to isolate the protein sequence for ligation into a pET28a vector). Subsequently comes the variable part, the protein coding sequence. Then follow an XhoI restriction site and random spacer sequence, positioning the terminator at 30 base pairs from the stop codon. After the terminator come three prescribed iGEM end restriction sites, SpeI, NotI, PstI, plus a HindIII restriction site.
Methods and Results
Cloning
Protein Expression and Sampling for CEST Measurements
MRI Measurements
Discussion and Conclusions
 "
"