Team:NYMU-Taipei/Modeling/Linear epidemic model
From 2013.igem.org


Contents |
Epidemic model
Backgroud:
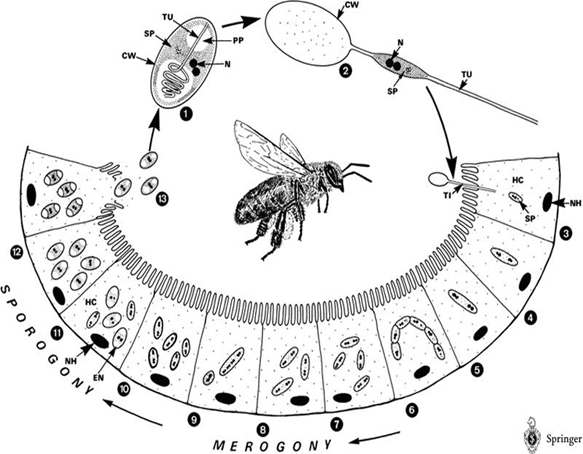
Honey bee is a social insect and can be divided into several classes – queens, drones, and workers, which can further be classified into field bee (which is responsible for getting honey from the nature) and house bee (which is responsible for cleaning hives). However, a single bee (especially field bee) may fall ill to CCD when it intakes water or food contaminated by Nosema ceranae spores. What’s worse, CCD may in turn spread to other bees through exchanging substances via mouthparts or feeding food to sacbroods.
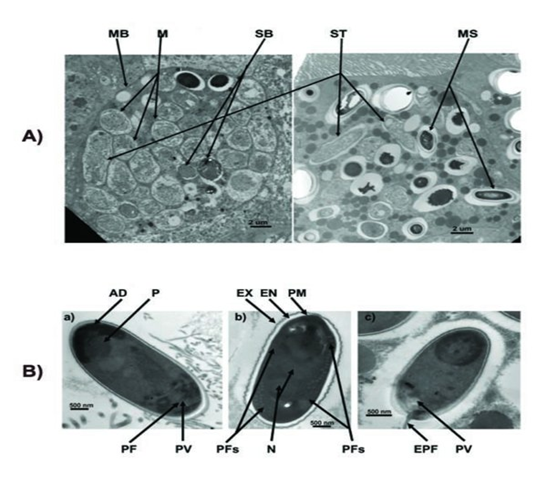
After getting into bees’ midgut, Nosema spores will germinate, elongate its polarfilament, and pierce into midgut epithelial cells to transmit its genetic material. After finishing several life cycles, the infected epithelial cells will burst, leading to the spread of Nosema spores to nearby epithelial cells.
The life cycle of Nosema Ceranae:
The spores of Nosema ceranae:
The method is let bees ingest the encapsulated Bee. coli, which is suspended in sugar solution and will proliferate in bees’ midgut to build up bees’ immunity.
The purpose of this modeling:
- How many encapsulated Bee. Coli does a bee need to get immunized and be effective to spread our Bee. Coli to other bees and let the whole hive be immunized.
- How much time does the immunization requires and to see if it can save the whole society in time.
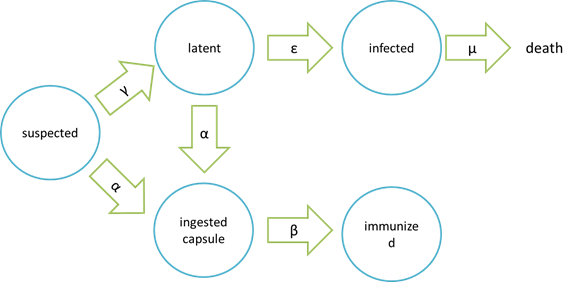
The assumption of infection and cure process:
Where “suspected” means the healthy bees, “latent” means the Nosema – infected but curable bees, “infected” means Nosema – infected bees which are incurable and doomed to death, “ingested capsule ” means bees with capsuled Bee. Coli, and “immunized” means bees immune to Nosema by Bee. coli intake.
It is assumed that the whole colony will only get into two consequences – one is dying out (once the “latent bees” turn to be the “infected bees”), and the other is survive (once the “latent” or “suspected bees” becomes “ingested capsule bees”).
Equation:
Parameters: N = total population S = suspected E = latent (eminent) I = infected C = ingested capsule R = immunized (recovery) α= suspected bees/ latent beesingested capsule bees rate constant γ= suspected bees latent bees rate constant β= ingested capsule bees immunized bees rate constant ε= latent bees infected bees rate constant μ= infected bees dead bees rate constant
Explanation: Since γSE represents the rate of suspected bees turning to latent bees by infected bees andαS the rate of suspected bees turning to ingested capsule bees after fed with sugar solution containing Bee. coli. The change rate of suspected bees(dS/dt) can therefore be expressed asγSE-αS.
Similarly, αE means the rate of latent bees turning to ingested capsule bees after fed with sugar solution containing Bee. coli andεE the rate of latent bees turning to infected bees without the treatment of Bee. coli. As a result, the change rate of latent bees(dE/dt) can therefore be expressed asγSE-εE-αE
Furthermore, μI is the rate of infected bees turning to dead bees, and thus, the change rate of infected bees (dI/dt) can therefore be expressed asεE-μI.
What’s more, βC represents the rate of ingested capsule bees turning to immunized bees after Bee. coli kicks in. The change rate of ingested capsule bees (dC/dt) and immunized bees(dR/dt)can therefore be expressed asαS +αE-βC andβC respectively.
The aim of the equation is to know the relationship of the number of all stages of bees (suspected, latent, infected, ingested capsule, immunized), namely, the survival and death rate under the influence of both Nosema infection and Bee. coli treatment over a specific period of time. For future prospect, the exponential epidemic model is considered more ideal and effective in spreading Bee. Coli throughout a bee colony. The only difference between linear and exponential epidemic model is that Bee. coli will proliferate exponentially in exponential epidemic model while in linear one , the number of Bee. coli is the same as the number of beads.
Result:
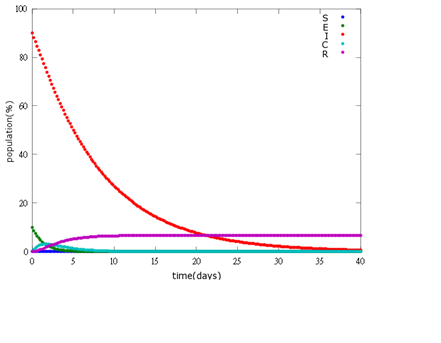
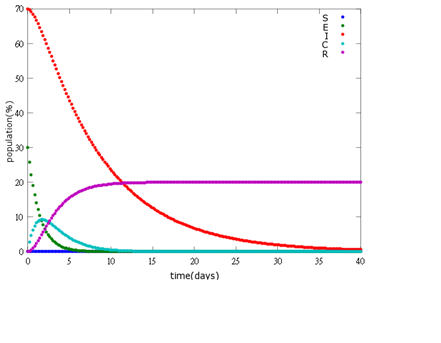
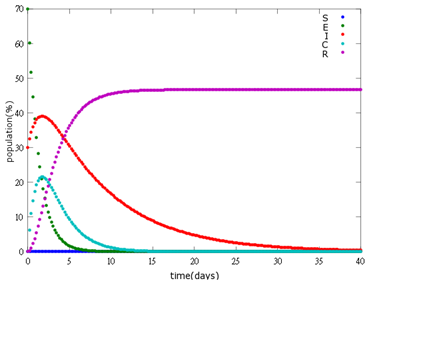
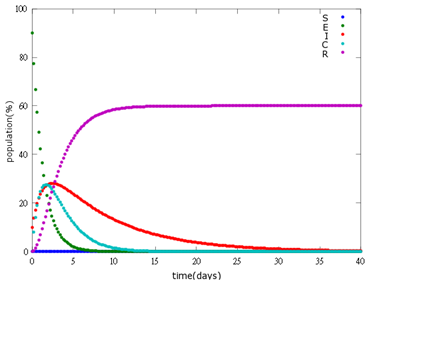
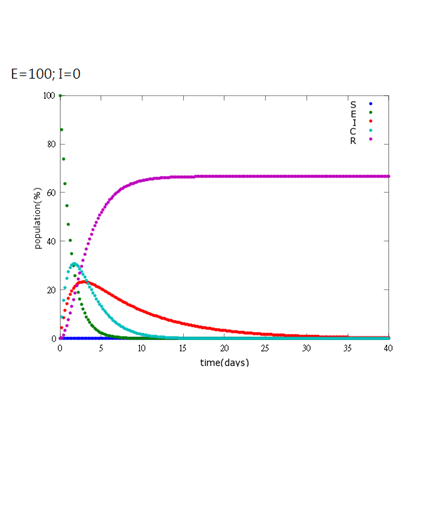
It is assumed that the whole bee colony is infected by Nosema, which is the most severe case. That is, bees are either latent or infected. According to our experiment, bees intaking sugar solution which contains capsules in a sufficient concentration have 100% of Bee. coli releasing from capsules. Here we discuss how much time it needs for the whole hive to recover from Nosema infection with different ratio of infected and latent stage.
1. E=10%, I= 90%
2. E=30%, I=70%:
3. E=70%, I=30%:
4. E=90%, 10%:
5. E=100%, I=0%:
As the pictures shows, the bigger the ratio of latent bees are, the more population of recovery bees are; the bigger the ratio of latent bees are, the lower the peak of infected bees’ population are; the bigger the ratio of latent bees are, the higher the peak of ingested capsule bees’ population are.
No matter which ratio of latent and infected bees is, it all shows that the whole bee colony will survive eventually, which fits our assumption that the whole colony will only get into two consequences – one is dying out (once the “latent bees” turn to be the “infected bees”), and the other is survive (once the “latent” or “suspected bees” becomes “ingested capsule bees”).
Parameter:
| Model | Parameter | Description | Value | Unit | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SEIR(exponential)
| b | Infection rate constant of Nosema ceranae to the suspected | 24/75 | ||
| C | D | ||||
| Model | Parameter | Description | Value | Unit | Reference |
| jkl | mno | pqr | |||
| stu | vwx | yz |
 "
"