Team:TU-Eindhoven/PBPK
From 2013.igem.org



Contents |
Ganciclovir Distribution
Ganciclovir is the prodrug to kill the bacteria. See the principle of killing:(). The bacteria needs to be killed at a mild rate. So it is important to predict the concentration of ganciclovir in the body, especially in the tumor zone as the bacteria gather in this site. In this part we used Physiologically based pharmacokinetic model(PBPK) to describe the distribution of the drug in different tissues of body.
Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Model
The pharmacokinetic model is a useful tool to predict drug concentrations in human tissues. It models 3 processes in drug consumption:
1). Absorption describes how the drug enters to blood stream via different method of administration.
2). Distribution is how the drug distributes into different human tissues.
3). Elimination is the process that the drug is eliminated from blood stream.
And all the processes are modeled with differential equations.
The essence of pharmacokinetic model is
1). Compartmental method. Different tissues in human are modeled as compartments, like lung, kidney and fat. Within the compartment, it is assumed that drug distribution is uniform. The blood flows from one compartment to another and brings the drug throughout the body.
2). Diffusion limitation. Diffusion limitation is illustrated by the speed of blood flow and the affinity of the compartment to the drug. Some organs have a higher rate of blood flow, like lung and kidney. In these compartments, the concentration will change faster. Different compartments also have a different affinity to the drug. Affinity depends on the chemical composition of the drug and the human tissue. But generally, kidney always has the highest affinity as it is the main elimination compartment.
Model Construction
The construction of pharmacokinetic model involves of several steps. Although the principle of pharmacokinetic model looks quite simple, every design of the model should be back up with good reasons.
Tissue Grouping
In PBPK, the number of compartments depends on the data availability, aim of the study and the calculation method. There are many variations in PBPK models. But they all share the basic traits:
1).one compartment for venous blood,
2).one compartment for arterial blood,
3).at least one elimination compartment and,
4).at least one absorption compartment.
Generally, as the number of compartments increases, the accuracy of prediction is improving. But the estimation error also increases as the data availability is limited. What is usually done is to lump together tissues with similar pharmacokinetical and toxicological properties. However these data are still not there for Ganciclovir.
The rule of thumb in designing compartment is to ensure that the blood flow in each direction sums up to the cardiac output. So the two compartments, rapidly perfuse tissue and slowly perfuse tissue, are always used to compensate the blood flow.
Our model is mainly based on the study of J.Ren et al.GCVtissuedistributionJ.Ren et al, Tissue distribution of borneol-modified ganciclovir-loaded solid lipd nanoparticles in mice after intravenous administration. European Jounal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics 83, 141-148 (2013) They tested the tissue concentrations of several organs in mice. Based on their results, firstly the compartments of brain, kidney, liver, spleen and lung are decided. As the aim is to predict the drug concentration in tumor zone, the compartment of tumor is also included in the model. To ensure that the blood flow sums up to total cardiac output, the rapidly perfuse tissue and slowly perfuse tissue are added.
Finally, the structure looks like this:
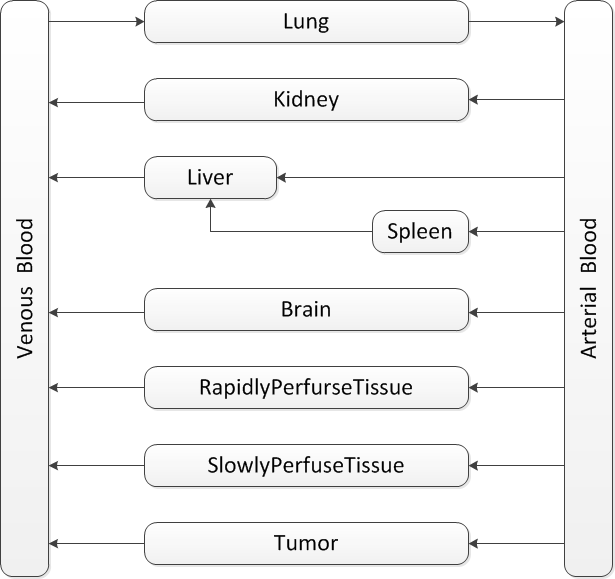
Parameter Estimation
There are two types of data in PBPK model, the drug-nonspecific and drug-specific. For each compartment, we need to estimate blood flow, tissue volume and partition coefficient. The particion coefficient is the drug specific data. It describes the relative affinity to drug. The blood flows and tissue volumes are taken from the mean values of human adult. The blood flows of brain, kidney, liver, spleen and lung are estimated from the study of Feras Khalil and Stephanie Laer.PBPKvolumeFeras Khalil and Stephanie Laer, Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling: Methodology, Applications, and Limitations with a Focus on Its Role in Pediatric Drug Development. Journal of Biomedicind and Biotechnology , (2011)
Simulation Result
References
 "
"



