Team:TU-Eindhoven/StochasticModel
From 2013.igem.org



Contents |
Decoy Sites
To tune the level of protein expression, we used decoy sites. Decoy sites are tandem repeats of DNA where transcriptional factor can bind to. Therefore it competes with promoter sites and lowers the binding ratio of promoter sites. LeeDecoyTek-Hyung Lee and Narendra Maheshri, A regulatory role for repeated decoy transcription factor binding sites in target gene expression. Molecular Systems Biology 8, 576 (2012) The T is a transcriptional activator, which in our model, is the active FNR. The N is the decoy site and the P is the promoter site. The protein expression rate is then assumed to be proportional to TF/ T0. The subscript 0 refers to the total amount.
Stochastic Model
The stochastic model is used to simulate the interactions of molecules in a small scale. In the ODE models, the assumptions are made that the molecule pool is very large and molecules are always evenly distributed, i.e., no transportation limit. However in the scope of promoter this is not applicable as promoter sites only exist in small numbers.

Simulation Result
The input is the concentration of FNR protein. This result is taken from the part of FNR protein and converted from micro molar concentrations to number of molecules.

The simulated result of decoy site binding ratio
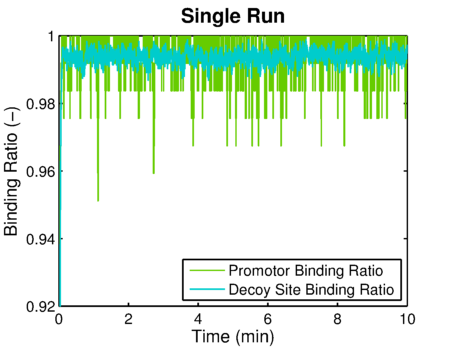 The simulated result of promoter binding ratio
The simulated result of promoter binding ratio
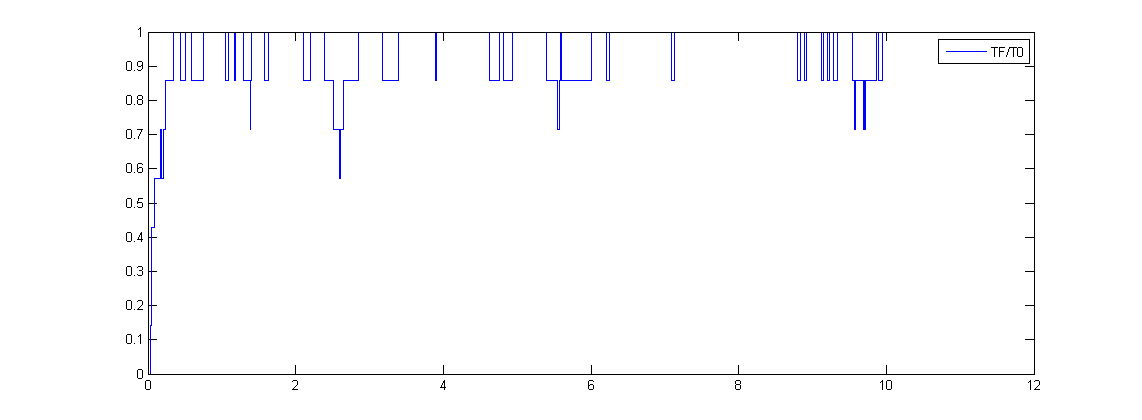 This would be the input for the modeling of protein generation. We assume the protein production rate is linear to the promoter binding ratio.LeeDecoy
This would be the input for the modeling of protein generation. We assume the protein production rate is linear to the promoter binding ratio.LeeDecoy
References
 "
"



