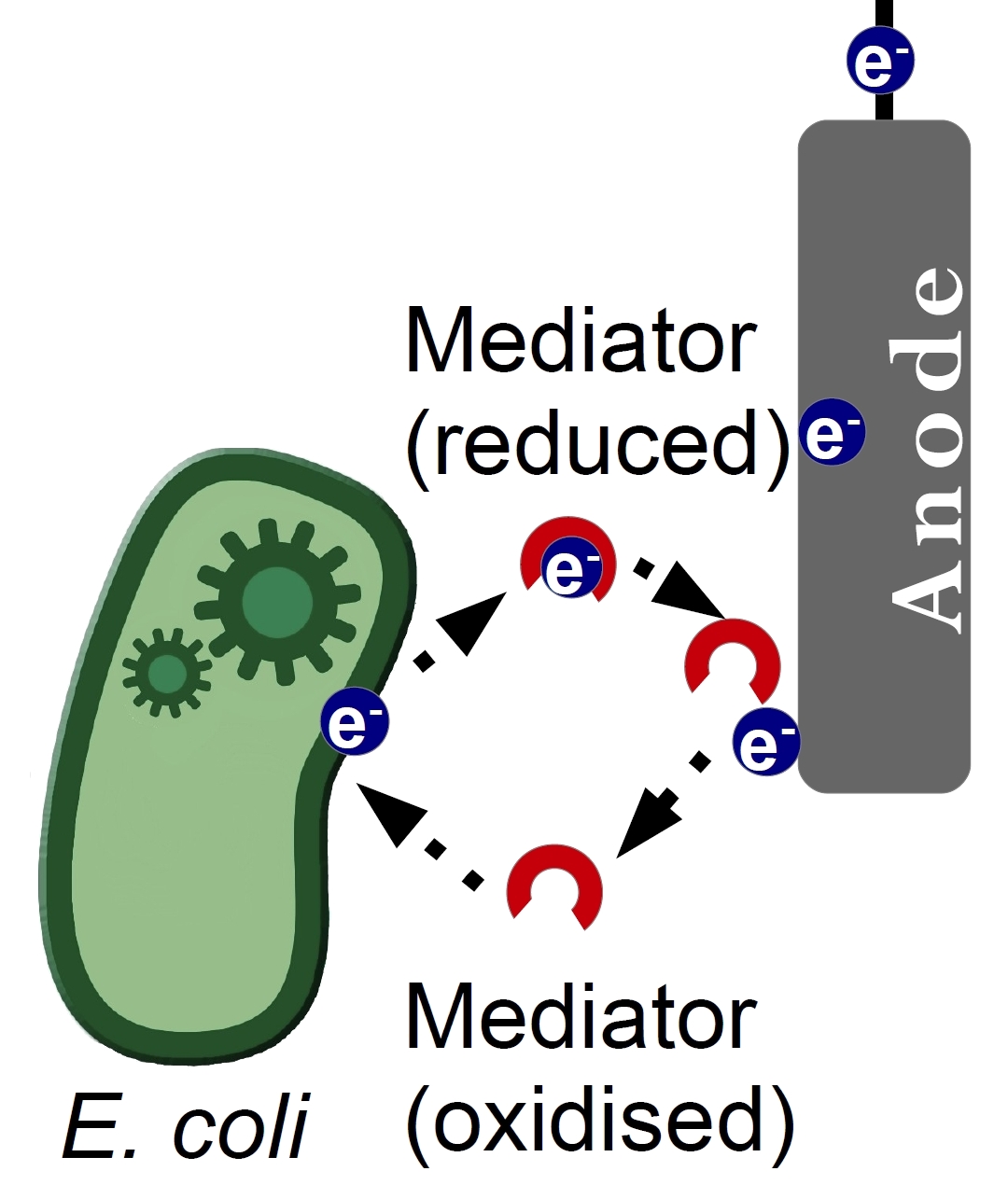
Of great interest is the production of endogenous mediators. The overexpression of glyceroldehydrogenase in E. coli is a promising approach. Because many derivates of glyceroldehydrogenase are small, water-soluble redoxmolecules, they have the properties of a mediator. Futhermore, it will be tested, if there is a possibility of expressing the mediator phenazin. Phenazin is an endogenous mediator of Pseudomonas species.
 "
"