Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Project/Cytochromes
From 2013.igem.org
m |
|||
| (97 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
<html> | <html> | ||
<style> | <style> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
#leftcol ul {padding-left:40px; padding-right:40px;} | #leftcol ul {padding-left:40px; padding-right:40px;} | ||
| Line 40: | Line 38: | ||
padding:0px 20px; | padding:0px 20px; | ||
| - | |||
</style> | </style> | ||
| Line 69: | Line 66: | ||
| - | [[Image:Bielefeld-germany-project-overview-cytochromes.png|left|thumb|250px|'''Figure 1:''' Extracellular electron transfer via cytochromes in E. coli with a minimal set of | + | [[Image:Bielefeld-germany-project-overview-cytochromes.png|left|thumb|250px|'''Figure 1:''' Extracellular electron transfer via cytochromes in ''E. coli'' with a minimal set of proteins from ''Shewanella oneidensins'' MR-1.]] |
<p align="justify"> | <p align="justify"> | ||
| - | To enable transfer of electrons from the general metabolism to the outside of the cell the ''mtrCAB'' operon from [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genome/1082?project_id=57949 ''Shewanella oneidensis'' MR-1] was heterologously expressed in ''E. coli''. This operon encodes for a minimal set of genes required to build an electron shuttle pathway via different c-type cytochromes. | + | To enable transfer of electrons from the general metabolism to the outside of the cell, the ''mtrCAB'' operon from [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genome/1082?project_id=57949 ''Shewanella oneidensis'' MR-1] was heterologously expressed in ''E. coli''. This operon encodes for a minimal set of genes required to build an electron shuttle pathway via different c-type cytochromes. Electrons from the native ''E. coli'' protein [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/EGT66377.1 NapC] are passed to the periplasmic [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717386.1 MtrA], which transports them to the outer membrane protein [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717385.1 MtrB]. Via the membrane-bound [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717387.1 MtrC] the corresponding electrons can be transferred to extracellular electron acceptors like the anode of a microbial fuel cell. |
| + | <br> | ||
| + | The ''mtrCAB'' cluster contains two illegal restriction sites, which were removed by generating a silent mutation via site-directed mutagenesis. The resulting three fragments were combined and ligated with [http://parts.igem.org/Part:pSB1C3 pSB1C3] by [https://2013.igem.org/Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Labjournal/ProtocolsPrograms#Gibson_assembly Gibson assembly]. Subsequently, this gene cluster was combined with three different promoters and ribosome binding sites of varying strength. It has not yet been possible to experimentally verify the functional expression of the cytochromes. Furthermore, it was ineffectual attempted to clone the ''ccmAH'' cluster as well. The Ccm proteins are required for the maturation of the decaheme cytochromes [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717386.1 MtrA] and [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717387.1 MtrC] and are natively not expressed under aerobic conditions. This is, however, a minor issue, since the Microbial Fuel Cell will work under anareobic conditions. | ||
| + | |||
| + | For a correct heme insertion into the decaheme cytochromes [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717386.1 MtrA] and [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717387.1 MtrC], the cytochrome c maturation machinery is required. The corresponding genes are naturally expressed in ''E. coli'' under anaerobic conditions, for aerobic expression they have to be expressed via plasmid. | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
==Theory== | ==Theory== | ||
<p align="justify"> | <p align="justify"> | ||
| - | Cell membranes work as a natural insulator and prevent the flow from electrons out of the cell. To enable transfer of electrons from the general metabolism to the outside of the cell we had to alter the membrane of our organism E. coli without | + | Cell membranes work as a natural insulator and prevent the flow from electrons out of the cell. To enable transfer of electrons from the general metabolism to the outside of the cell we had to alter the membrane of our organism ''E. coli'' without affecting cell growth, membrane stability or cell metabolism. |
| - | + | <br> | |
| - | + | Some species from the genera ''Shewanella'' and ''Geobacter'' have developed different mechanisms to allow extracellular electron transfer. Members of the ''Shewanella'' species are the Gram-negative γ-proteobacteria which are known for their respiratory versatility. They are reported to be using over 20 terminal electron acceptors for respiration (Nealson et al. 2003).'' Shewanella oneidensis'' MR-1 expresses many c-type cytochromes, membrane-bound redox-active proteins or soluble periplasmatic proteins, which play an important in the electron transport in the bacterial respiration and photosynthesis. | |
| - | + | <br> | |
| - | + | There have been already numerous approaches, where the Mtr proteins were introduced into ''E.coli'' strains and could be successfully expressed under anaerobic conditions (Goldbeck et al. 2012) | |
| - | There have been already numerous approaches, where the | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
| - | + | <br><br><br> | |
==Genetic Approach== | ==Genetic Approach== | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | [[Image:Bielefeld-Germany2013_genomic_region_mtrCAB.png|left|thumb|600px|'''Figure2:''' The genomic region of the ''mtrCAB'' is shown | + | ===Isolation of the ''mtrCAB'' gene cluster=== |
| - | + | [[Image:Bielefeld-Germany2013_genomic_region_mtrCAB.png|left|thumb|600px|'''Figure2:''' The genomic region of the ''mtrCAB'' operon is shown.[http://ncbi.nlm.nih.gov (NCBI)]. ]] | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
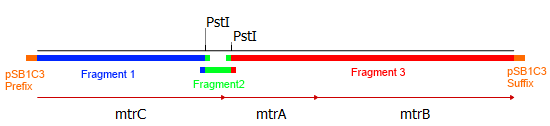
| - | + | [[Image:Bielefeld-Germany2013-MtrCAB_Fragments.png|left|thumb|600px|'''Figure3:''' Graphic representation of the illegal restriction sites within the ''mtrCAB'' operon and the resulting fragments from the site-directed mutagenesis approach. The colored overlaps indicate homologous sequences,that facilitate the religation via [https://2013.igem.org/Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Labjournal/ProtocolsPrograms#Gibson_assembly Gibson assembly]. The parts labeled 'pSB1C3 prefix' and 'pSB1C3 suffix' are overlaps homologous to the vectors prefix and suffix, respectivly.]] | |
| - | + | ||
| - | [[Image:Bielefeld- | + | |
<p align="justify" style="clear:both;"> | <p align="justify" style="clear:both;"> | ||
| - | The resulting fragments are listed in the table below. | + | <br> |
| + | As shown in Figure2, the three ''mtr'' genes are organized in an operon in the donor organism ''Shewanella oneidensis'' MR-1 and could therefore amplified altogether. Since two illegal PstI restriction sites exist in this cluster it had to be subdivided into three fragments. The illegal restriction sites were subsequently deleted by incorporating a silent mutation via site-directed mutagenesis. Eventually the fragments should be joined back together and ligated with the shipping backbone <bbpart>pSB1C3</bbpart> via [https://2013.igem.org/Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Labjournal/ProtocolsPrograms#Gibson_assembly Gibson assembly]. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | This approach required specifically designed primers that can bind the targeted genetic sequence and hold an overlap to facilitate ligation with the other fragments and the backbone. Hence, eight primers were designed, two for each fragment of the ''mtrCAB'' operon and two for the <bbpart>pSB1C3</bbpart> vector to generate proper backbone-overlaps as well. The resulting fragments are depicted in Figure 3. The colored overlaps indicate homologous sequences that facilitate the re-ligation via [https://2013.igem.org/Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Labjournal/ProtocolsPrograms#Gibson_assembly Gibson assembly]. The parts labeled 'pSB1C3 prefix' and 'pSB1C3 suffix' are overlaps homologous to the vectors prefix and suffix, respectively. The genes and resulting fragments are listed in the table below. The fragment sizes incorporate the aforementioned primer overlaps of 20 bp each. | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
| - | {| class="wikitable" | + | {| class="wikitable" style="margin-left:20px;" |
| - | ! | + | !Device |
| - | ! | + | !Regulatory Part |
| + | !Promoter | ||
| + | !RBS | ||
| + | !Activity | ||
|- | |- | ||
| - | | | + | |<bbpart>BBa_K1172403</bbpart> |
| - | | | + | |<bbpart>BBa_K608006</bbpart> |
| + | |Anderson 0.33 | ||
| + | |[http://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_B0032 medium] | ||
| + | |medium | ||
|- | |- | ||
| - | | | + | |<bbpart>BBa_K1172404</bbpart> |
| - | | | + | |<bbpart>BBa_K608002</bbpart> |
| + | |Anderson 0.77 | ||
| + | |[http://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_B0034 strong] | ||
| + | |strong | ||
|- | |- | ||
| - | | | + | |<bbpart>BBa_K1172405</bbpart> |
| - | | | + | |<bbpart>BBa_K525998</bbpart> |
| + | |T7 induced | ||
| + | |[http://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_B0034 strong] | ||
| + | |very strong | ||
|} | |} | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | + | ===Promoter strength=== | |
| - | + | <p align="justify"> | |
| - | + | Due to the complex interaction of the Mtr proteins with both, themselves and the Ccm system the transcriptional balance is crucial for the complex formation. Previous works proved that only a small range for optimal MtrCAB expression exists. Most important, the synthesis of the mature holocytochromes [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717387.1 MtrC] and [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717386.1 MtrA] actually decreases at a high corresponding promoter activity. A possible explanation for this is the low reaction speed of the Ccm machinery which cannot cope with a high level of apocytochromes. This results in an accumulation of inmature apocytochromes which are then degraded by periplasmatic proteases. Furthermore, a too low level of Ccm proteins inhibits the maturation of the apocytochromes, whereas expression above a certain treshold decreases the overall efficiency of the Ccm system. | |
| + | <br> | ||
| + | Since the genes are heterologously expressed on a high copy plasmid, the promoter strength plays a key role in a controlled and therefore successfull expression. To cover a wide range of expression levels three different promoters, with varying strength and ribosome binding sites were combined with the genes. An overview is given in the table below. | ||
| + | </p> | ||
| - | + | {| class="wikitable" style="margin-left:20px;" | |
| - | + | !Part | |
| - | + | !Promoter | |
| + | !RBS | ||
| + | !Activity | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |<bbpart>BBa_K525998</bbpart> | ||
| + | |T7 uninduced | ||
| + | |[http://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_B0034 strong] | ||
| + | |weak (basal) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |<bbpart>BBa_K608006</bbpart> | ||
| + | |Anderson 0.33 | ||
| + | |[http://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_B0032 medium] | ||
| + | |medium | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |<bbpart>BBa_K608002</bbpart> | ||
| + | |Anderson 0.77 | ||
| + | |[http://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_B0034 strong] | ||
| + | |strong | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |<bbpart>BBa_K525998</bbpart> | ||
| + | |T7 induced | ||
| + | |[http://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_B0034 strong] | ||
| + | |very strong | ||
| + | |} | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
===Protein Overview=== | ===Protein Overview=== | ||
| + | [[Image:Bielefeld-germany-project-overview-cytochromes.png|left|thumb|250px|'''Figure 4:''' Extracellular electron transfer via cytochromes in ''E. coli'' with a minimal set of genes from ''Shewanella oneidensins'' MR-1.]] | ||
| + | <p align="justify"> | ||
| + | ''Shewanella oneidensis'' MR-1 expresses many c-type cytochromes, membrane-bound redox-active proteins or soluble periplasmatic proteins, which play an important in the electron transport in the bacterial respiration and photosynthesis. One of the electron-transfer models is based on c-type cytochromes encoded by the ''mtrCAB'' gene cluster (Myers and Myers, 1997). Although additional proteins like OmcA and NapC are involved in the electron transport chain, a minimal set of the three proteins [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717387.1 MtrC], [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717386.1 MtrA] and [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717385.1 MtrB] is necessary to heterologously express this pathway in ''E. coli'' (Jensen et al. 2010). | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | The process of the electron transport is illustrated in Figure 4. NapC ist natively expressed in ''E.coli'' and interacts very well with the proteins from ''S. oneidensis''. The inner membrane cytochrome c NapC accepts electrons generated by the reduction of menaquinone to menaquinol. The electrons are then passed from NapC to the periplasmic decaheme cytochrome c [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717386.1 MtrA] in the periplasm. MtrA transports them to [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717385.1 MtrB], a 72-kD β-barrel outer membrane protein which is physically connected with [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717387.1 MtrC], a 69-kDa membrane-bound decaheme cytochrome c. From [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717387.1 MtrC] the corresponding electrons can be transferred to extracellular electron acceptors such as iron oxide or, as in our case, an anode in a Microbial Fuel Cell. (Meyers and Meyers 2004) | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | The CcmAH complex composed of the eight membrane proteins CcmABCDEFGH is essential for the biosynthesis of the decaheme cytochromes [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717386.1 MtrA] and [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717387.1 MtrC]. The system first transports the heme into the periplasm and catalyzes the formation of thioester bonds that link the heme to two cysteine residues in the apocytochrome. Afterwards, the axial ligands are located towards the heme and the holocytochrome is folded (Sanders et al. 2010). Naturally the Ccm proteins are expressed by ''E. coli'' solely under anaerobic conditions, which corresponds to our anaerobically operating Microbial Fuel Cell. | ||
| + | </p> | ||
| - | + | <br> | |
| - | + | {|class="wikitable" style="margin-left:20px; width:600px;" | |
| - | + | !style="width:25%;"|[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717387.1 MtrC] | |
| - | + | !style="width:25%;"|[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717386.1 MtrA] | |
| - | + | !style="width:25%;"|[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717385.1 MtrB] | |
| - | + | !style="width:25%;"|CcmAH | |
| - | + | |- | |
| - | + | |outer membrane decaheme type c cytochrome | |
| - | + | |periplamatic decaheme type c cytochrome | |
| - | + | |28 strand β-barrel membrane protein | |
| - | + | |cytochrome c maturation machinery | |
| - | + | |- | |
| - | + | |671 aa | |
| - | + | |333 aa | |
| - | + | |697 aa | |
| - | + | |''various'' | |
| - | + | |- | |
| - | + | |69 kDa | |
| - | + | |32 kDa | |
| - | + | |72 kDa | |
| - | + | |''various'' | |
| - | + | |- | |
| - | + | |-needs Ccm-machinery for heme insertion <br> -needs [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717385.1 MtrB] for correct localisation | |
| - | + | |-needs Ccm-machinery for heme insertion | |
| - | + | |-needs [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717386.1 MtrA] for stability | |
| - | + | |-expressed only under anaerobic conditions | |
| - | + | |} | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
===Difficulties=== | ===Difficulties=== | ||
| - | *MtrA seems to be necessary for the stability of MtrB (Schicklberger et al. 2011) | + | *[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717386.1 MtrA] seems to be necessary for the stability of [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717385.1 MtrB] (Schicklberger et al. 2011) |
| - | *MtrB itself is required for the correct location and incorporation of MtrC ( | + | *[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717385.1 MtrB] itself is required for the correct location and incorporation of [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717387.1 MtrC] (Meyers and Meyers 2002) and is involved in the interaction between [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717387.1 MtrC] and [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717386.1 MtrA] (Beliaev AS et al. 1998). |
| - | *Furthermore extensive postranslational processing is required for correct incorporation of all hemes, folding and localisation of the cytochromes. Considering these difficulties the expression of even a single cytochrome is a major challenge (Jensen et al. 2010). | + | *Furthermore extensive postranslational processing is required for correct incorporation of all hemes, folding, and localisation of the cytochromes. Considering these difficulties the expression of even a single cytochrome is a major challenge (Jensen et al. 2010). |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | <br><br><br> | ||
==Results== | ==Results== | ||
===Genetics=== | ===Genetics=== | ||
| - | *The | + | *The amplification of the ''mtrCAB'' cluster from the genome of ''S. oneidensis'' and the deletion of illegal restriction sites was accomplished. |
| - | *The gene cluster was succesfully ligated into the shipping vector pSB1C3 forming the | + | *The gene cluster was succesfully ligated into the shipping vector <bbpart>pSB1C3</bbpart> forming the BioBrick <bbpart>BBa_K1172401</bbpart> |
| - | *The gene cluster was ligated into three | + | *The gene cluster was ligated into three expression vectors with varying promoter strength forming the following devices |
| - | **<bbpart>BBa_K1172403</bbpart> | + | **<bbpart>BBa_K1172403</bbpart>, <bbpart>BBa_K1172404</bbpart>, <bbpart>BBa_K1172405</bbpart> |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
===Characterisation=== | ===Characterisation=== | ||
| - | * | + | *To prove the expression of the Mtr proteins, ''E. coli'' cultures were transformed transformed with <bbpart>BBa_K1172403</bbpart>, <bbpart>BBa_K1172405</bbpart> (uninduced) and <bbpart>BBa_K1172401</bbpart> as a control and then cultivated anaerobically. Membrane and periplasmatic fractions of the cells were isolated by [https://2013.igem.org/Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Labjournal/ProtocolsPrograms#Cold_osmotic_shock Cold osmotic shock fractioning.] and analyzed by [https://2013.igem.org/Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Labjournal/ProtocolsPrograms#Sodium_dodecyl_sulfate_polyacrylamide_gel_electrophoresis_.28SDS-PAGE.29 SDS-PAGE]; the results are shown in Figure 5. |
| - | *The | + | **The membrane fraction should contain [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717385.1 MtrB] and [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717387.1 MtrC] of the Mtr complex, with sizes of 72 kDa and 69 kDa, respectively. |
| + | **The periplasmatic fraction should only contain the [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717386.1 MtrA] protein of the Mtr complex (32 kDa). | ||
| + | [[Image:Bielefeld-Germany2013_SDS-PAGE_mtrCAB_ladder.png|center|400px|thumb|'''Figure 5:''' Image of a SDS-PAGE with periplasmatic and membrane fractions of colonies transformed with <bbpart>K1172401</bbpart> as a control, besides <bbpart>K1172403</bbpart> and <bbpart>K1172405</bbpart> (undinduced) for analysis. Ladder: PageRuler unstained Protein Ladder (Fermentas)]] | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| + | *It was not possible to confirm the expression of the Mtr proteins by [https://2013.igem.org/Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Labjournal/ProtocolsPrograms#Sodium_dodecyl_sulfate_polyacrylamide_gel_electrophoresis_.28SDS-PAGE.29 SDS-PAGE] analysis, as no significant differences between control and experimental condition were visible at the relevant heights of the SDS-PAGE. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *The redox activity of [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717386.1 MtrA] and [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717387.1 MtrC] was probed via absorption spectroscopy and did not show significant indications for a positive result as the expected shift of the Soret peak from 410 nm to 420 nm could not be observed. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Conclusion=== | ||
| + | *The electron transfer system from ''Shewanella oneidensis'' MR-1 seems to be suitable for the usage in our Microbial Fuel Cell in principle. However, expression regulation, heme-loading, and correct folding as well as localization of the cytochromes are very complex and therefore our team was not able to produce the functional system in the available time. | ||
| + | <br><br><br> | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| Line 245: | Line 269: | ||
| - | <div id=" | + | <div id="asdf"> |
| + | <html> | ||
| + | <div id="nav2" style="width:210px; padding-bottom:5px; padding-left:15px;"> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div class="navbutton" id="home" style="float:left; padding-left:55px; margin-left:10px; padding-top:0px;"> | ||
| + | <a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Bielefeld-Germany" title="Jump to Frontpage"> | ||
| + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/f/f6/Bielefeld-Germany2013-ButtonHome.png" height="15px"> | ||
| + | </a> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <div class="navbutton" id="top" style="float:left; padding-left:10px; margin-left:10px; padding-top:0px;"> | ||
| + | <a href="#" title="Jump to top"> | ||
| + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/a/ab/Bielefeld-Germany2013-Up_orange_new.png" height="15px"> | ||
| + | </a> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </html> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <div id="rightcol" style="width:210px; height:100%; overflow-y:auto; box-shadow:0px 0px 2px 0px grey;" padding:0px 20px;> | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
| - | + | </div> | |
| + | |||
| + | |||
</div> | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
Latest revision as of 03:06, 29 October 2013
Cytochromes
Overview
To enable transfer of electrons from the general metabolism to the outside of the cell, the mtrCAB operon from [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genome/1082?project_id=57949 Shewanella oneidensis MR-1] was heterologously expressed in E. coli. This operon encodes for a minimal set of genes required to build an electron shuttle pathway via different c-type cytochromes. Electrons from the native E. coli protein [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/EGT66377.1 NapC] are passed to the periplasmic [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717386.1 MtrA], which transports them to the outer membrane protein [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717385.1 MtrB]. Via the membrane-bound [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717387.1 MtrC] the corresponding electrons can be transferred to extracellular electron acceptors like the anode of a microbial fuel cell.
The mtrCAB cluster contains two illegal restriction sites, which were removed by generating a silent mutation via site-directed mutagenesis. The resulting three fragments were combined and ligated with [http://parts.igem.org/Part:pSB1C3 pSB1C3] by Gibson assembly. Subsequently, this gene cluster was combined with three different promoters and ribosome binding sites of varying strength. It has not yet been possible to experimentally verify the functional expression of the cytochromes. Furthermore, it was ineffectual attempted to clone the ccmAH cluster as well. The Ccm proteins are required for the maturation of the decaheme cytochromes [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717386.1 MtrA] and [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717387.1 MtrC] and are natively not expressed under aerobic conditions. This is, however, a minor issue, since the Microbial Fuel Cell will work under anareobic conditions.
For a correct heme insertion into the decaheme cytochromes [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717386.1 MtrA] and [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717387.1 MtrC], the cytochrome c maturation machinery is required. The corresponding genes are naturally expressed in E. coli under anaerobic conditions, for aerobic expression they have to be expressed via plasmid.
Theory
Cell membranes work as a natural insulator and prevent the flow from electrons out of the cell. To enable transfer of electrons from the general metabolism to the outside of the cell we had to alter the membrane of our organism E. coli without affecting cell growth, membrane stability or cell metabolism.
Some species from the genera Shewanella and Geobacter have developed different mechanisms to allow extracellular electron transfer. Members of the Shewanella species are the Gram-negative γ-proteobacteria which are known for their respiratory versatility. They are reported to be using over 20 terminal electron acceptors for respiration (Nealson et al. 2003). Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 expresses many c-type cytochromes, membrane-bound redox-active proteins or soluble periplasmatic proteins, which play an important in the electron transport in the bacterial respiration and photosynthesis.
There have been already numerous approaches, where the Mtr proteins were introduced into E.coli strains and could be successfully expressed under anaerobic conditions (Goldbeck et al. 2012)
Genetic Approach
Isolation of the mtrCAB gene cluster
As shown in Figure2, the three mtr genes are organized in an operon in the donor organism Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 and could therefore amplified altogether. Since two illegal PstI restriction sites exist in this cluster it had to be subdivided into three fragments. The illegal restriction sites were subsequently deleted by incorporating a silent mutation via site-directed mutagenesis. Eventually the fragments should be joined back together and ligated with the shipping backbone <bbpart>pSB1C3</bbpart> via Gibson assembly.
This approach required specifically designed primers that can bind the targeted genetic sequence and hold an overlap to facilitate ligation with the other fragments and the backbone. Hence, eight primers were designed, two for each fragment of the mtrCAB operon and two for the <bbpart>pSB1C3</bbpart> vector to generate proper backbone-overlaps as well. The resulting fragments are depicted in Figure 3. The colored overlaps indicate homologous sequences that facilitate the re-ligation via Gibson assembly. The parts labeled 'pSB1C3 prefix' and 'pSB1C3 suffix' are overlaps homologous to the vectors prefix and suffix, respectively. The genes and resulting fragments are listed in the table below. The fragment sizes incorporate the aforementioned primer overlaps of 20 bp each.
| Device | Regulatory Part | Promoter | RBS | Activity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| <bbpart>BBa_K1172403</bbpart> | <bbpart>BBa_K608006</bbpart> | Anderson 0.33 | [http://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_B0032 medium] | medium |
| <bbpart>BBa_K1172404</bbpart> | <bbpart>BBa_K608002</bbpart> | Anderson 0.77 | [http://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_B0034 strong] | strong |
| <bbpart>BBa_K1172405</bbpart> | <bbpart>BBa_K525998</bbpart> | T7 induced | [http://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_B0034 strong] | very strong |
Promoter strength
Due to the complex interaction of the Mtr proteins with both, themselves and the Ccm system the transcriptional balance is crucial for the complex formation. Previous works proved that only a small range for optimal MtrCAB expression exists. Most important, the synthesis of the mature holocytochromes [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717387.1 MtrC] and [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717386.1 MtrA] actually decreases at a high corresponding promoter activity. A possible explanation for this is the low reaction speed of the Ccm machinery which cannot cope with a high level of apocytochromes. This results in an accumulation of inmature apocytochromes which are then degraded by periplasmatic proteases. Furthermore, a too low level of Ccm proteins inhibits the maturation of the apocytochromes, whereas expression above a certain treshold decreases the overall efficiency of the Ccm system.
Since the genes are heterologously expressed on a high copy plasmid, the promoter strength plays a key role in a controlled and therefore successfull expression. To cover a wide range of expression levels three different promoters, with varying strength and ribosome binding sites were combined with the genes. An overview is given in the table below.
| Part | Promoter | RBS | Activity |
|---|---|---|---|
| <bbpart>BBa_K525998</bbpart> | T7 uninduced | [http://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_B0034 strong] | weak (basal) |
| <bbpart>BBa_K608006</bbpart> | Anderson 0.33 | [http://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_B0032 medium] | medium |
| <bbpart>BBa_K608002</bbpart> | Anderson 0.77 | [http://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_B0034 strong] | strong |
| <bbpart>BBa_K525998</bbpart> | T7 induced | [http://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_B0034 strong] | very strong |
Protein Overview
Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 expresses many c-type cytochromes, membrane-bound redox-active proteins or soluble periplasmatic proteins, which play an important in the electron transport in the bacterial respiration and photosynthesis. One of the electron-transfer models is based on c-type cytochromes encoded by the mtrCAB gene cluster (Myers and Myers, 1997). Although additional proteins like OmcA and NapC are involved in the electron transport chain, a minimal set of the three proteins [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717387.1 MtrC], [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717386.1 MtrA] and [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717385.1 MtrB] is necessary to heterologously express this pathway in E. coli (Jensen et al. 2010).
The process of the electron transport is illustrated in Figure 4. NapC ist natively expressed in E.coli and interacts very well with the proteins from S. oneidensis. The inner membrane cytochrome c NapC accepts electrons generated by the reduction of menaquinone to menaquinol. The electrons are then passed from NapC to the periplasmic decaheme cytochrome c [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717386.1 MtrA] in the periplasm. MtrA transports them to [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717385.1 MtrB], a 72-kD β-barrel outer membrane protein which is physically connected with [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717387.1 MtrC], a 69-kDa membrane-bound decaheme cytochrome c. From [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717387.1 MtrC] the corresponding electrons can be transferred to extracellular electron acceptors such as iron oxide or, as in our case, an anode in a Microbial Fuel Cell. (Meyers and Meyers 2004)
The CcmAH complex composed of the eight membrane proteins CcmABCDEFGH is essential for the biosynthesis of the decaheme cytochromes [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717386.1 MtrA] and [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717387.1 MtrC]. The system first transports the heme into the periplasm and catalyzes the formation of thioester bonds that link the heme to two cysteine residues in the apocytochrome. Afterwards, the axial ligands are located towards the heme and the holocytochrome is folded (Sanders et al. 2010). Naturally the Ccm proteins are expressed by E. coli solely under anaerobic conditions, which corresponds to our anaerobically operating Microbial Fuel Cell.
| [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717387.1 MtrC] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717386.1 MtrA] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717385.1 MtrB] | CcmAH |
|---|---|---|---|
| outer membrane decaheme type c cytochrome | periplamatic decaheme type c cytochrome | 28 strand β-barrel membrane protein | cytochrome c maturation machinery |
| 671 aa | 333 aa | 697 aa | various |
| 69 kDa | 32 kDa | 72 kDa | various |
Difficulties
- [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717386.1 MtrA] seems to be necessary for the stability of [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717385.1 MtrB] (Schicklberger et al. 2011)
- [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717385.1 MtrB] itself is required for the correct location and incorporation of [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717387.1 MtrC] (Meyers and Meyers 2002) and is involved in the interaction between [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717387.1 MtrC] and [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717386.1 MtrA] (Beliaev AS et al. 1998).
- Furthermore extensive postranslational processing is required for correct incorporation of all hemes, folding, and localisation of the cytochromes. Considering these difficulties the expression of even a single cytochrome is a major challenge (Jensen et al. 2010).
Results
Genetics
- The amplification of the mtrCAB cluster from the genome of S. oneidensis and the deletion of illegal restriction sites was accomplished.
- The gene cluster was succesfully ligated into the shipping vector <bbpart>pSB1C3</bbpart> forming the BioBrick <bbpart>BBa_K1172401</bbpart>
- The gene cluster was ligated into three expression vectors with varying promoter strength forming the following devices
- <bbpart>BBa_K1172403</bbpart>, <bbpart>BBa_K1172404</bbpart>, <bbpart>BBa_K1172405</bbpart>
Characterisation
- To prove the expression of the Mtr proteins, E. coli cultures were transformed transformed with <bbpart>BBa_K1172403</bbpart>, <bbpart>BBa_K1172405</bbpart> (uninduced) and <bbpart>BBa_K1172401</bbpart> as a control and then cultivated anaerobically. Membrane and periplasmatic fractions of the cells were isolated by Cold osmotic shock fractioning. and analyzed by SDS-PAGE; the results are shown in Figure 5.
- The membrane fraction should contain [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717385.1 MtrB] and [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717387.1 MtrC] of the Mtr complex, with sizes of 72 kDa and 69 kDa, respectively.
- The periplasmatic fraction should only contain the [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717386.1 MtrA] protein of the Mtr complex (32 kDa).
- It was not possible to confirm the expression of the Mtr proteins by SDS-PAGE analysis, as no significant differences between control and experimental condition were visible at the relevant heights of the SDS-PAGE.
- The redox activity of [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717386.1 MtrA] and [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_717387.1 MtrC] was probed via absorption spectroscopy and did not show significant indications for a positive result as the expected shift of the Soret peak from 410 nm to 420 nm could not be observed.
Conclusion
- The electron transfer system from Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 seems to be suitable for the usage in our Microbial Fuel Cell in principle. However, expression regulation, heme-loading, and correct folding as well as localization of the cytochromes are very complex and therefore our team was not able to produce the functional system in the available time.
References
- Beliaev AS, Saffarini DA (1998)Shewanella putrefaciens mtrB encodes an outer membrane protein required for Fe(III) and Mn(IV) reduction. [http://jb.asm.org/content/180/23/6292.short J Bacteriol 180:6292–6297]
- Beliaev, A. S., D. A. Saffarini, J. L. McLaughlin, and D. Hunnicutt. 2001. MtrC, an outer membrane decahaem c cytochrome required for metal reduction in Shewanella putrefaciens MR-1. [http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1046/j.1365-2958.2001.02257.x/full Mol. Microbiol. 39:722-730]
- Grove, J., Tanapongpipat, S., Thomas, G., Griffiths, L., Crooke, H., and Cole, J. (1996)Escherichia coliK-12 genes essential for the synthesis of c-type cytochromes and a third nitrate reductase located in the periplasm. [http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1046/j.1365-2958.1996.383914.x/abstract Mol. Microbiol. 19, 467−481]
- Jensen HM, Albers AE, Malley KR, Londer YY, Cohen BE, et al. (2010) Engineering of a synthetic electron conduit in living cells. [http://www.pnas.org/content/107/45/19213.short Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 10.1073/pnas.1009645107 Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 107, 19213–19218 (2010).]
- Myers CR, Myers JM (2002) MtrB is required for proper incorporation of the cytochromes OmcA and OmcB into the outer membrane of Shewanella putrefaciens MR-1. [http://aem.asm.org/content/68/11/5585.short Appl Environ Microbiol68:5585–5594]
- Sanders, C., Turkarslan, S., Lee, D.-W., and Daldal, F. (2010) Cytochromecbiogenesis: the Ccm system. [http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0966842X10000442 Trends Microbiol. 18, 266−274]
- Schicklberger, M., Bucking, C., Schuetz, B., Heide, H., and Gescher, J. (2011) Involvement of the Shewanella oneidensis decaheme cytochrome MtrA in the periplasmic stability of the beta-barrel protein MtrB. [http://aem.asm.org/content/77/4/1520.short Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 77, 1520−1523]
- Thony-Meyer L, Fischer F, Kunzler P, Ritz D, Hennecke H (1995)Escherichia coligenes required for cytochrome c maturation. [http://jb.asm.org/content/177/15/4321.short J Bacteriol 177:4321–4326]
 "
"





