Team:Duke/Modeling/Thermo Derivation
From 2013.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
Hyunsoo kim (Talk | contribs) (→Detailed Derivation of the Thermodynamic Model (Repressor Case)) |
Hyunsoo kim (Talk | contribs) (→Navigate) |
||
| (5 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
= '''Mathematical Modeling of Bistable Toggle Switch''' = | = '''Mathematical Modeling of Bistable Toggle Switch''' = | ||
| - | |||
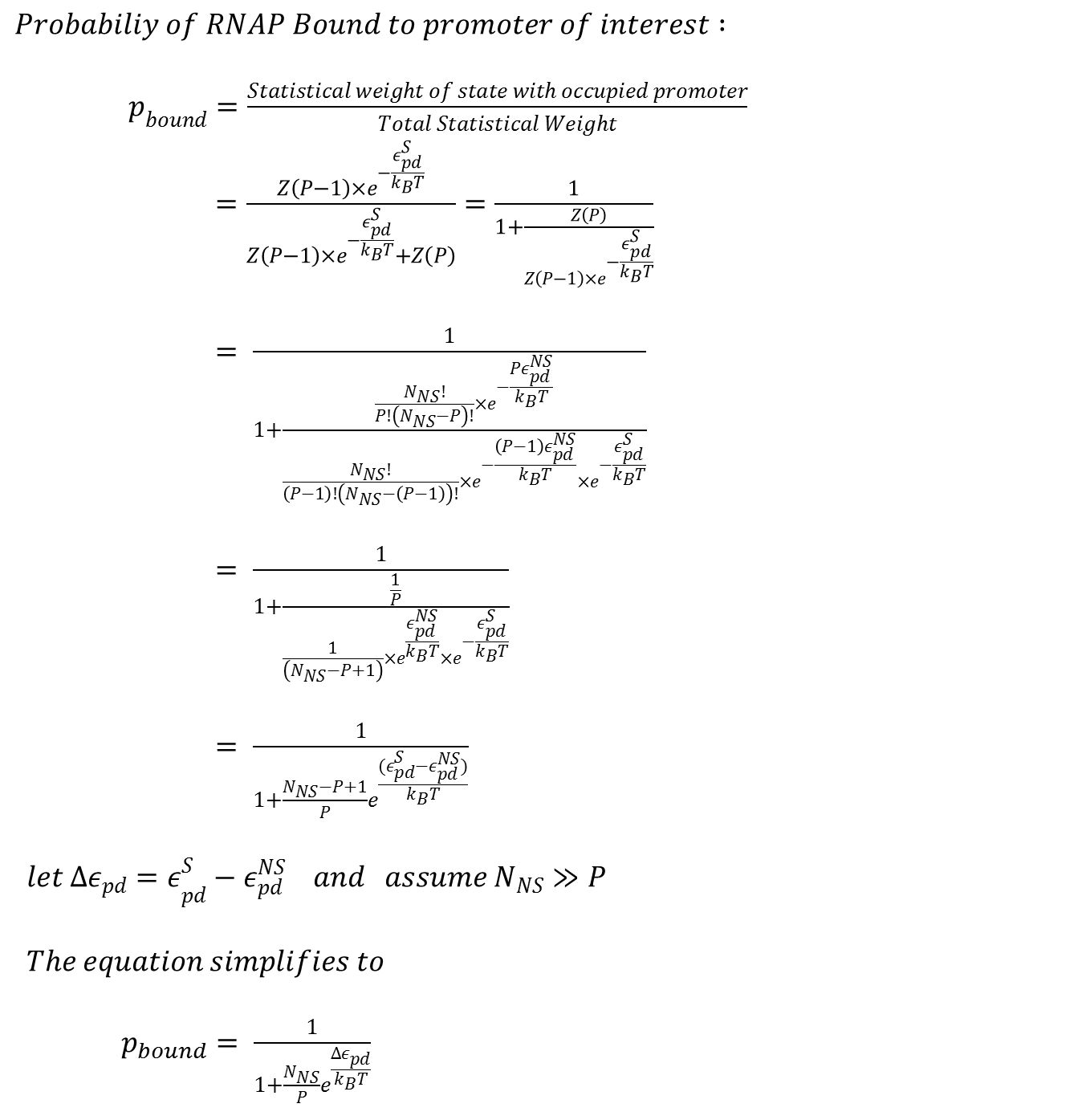
== Detailed Derivation of the Thermodynamic Model (Simple Case) == | == Detailed Derivation of the Thermodynamic Model (Simple Case) == | ||
| + | <br> | ||
[[File:Thermo_derivation.png|710px|center]] | [[File:Thermo_derivation.png|710px|center]] | ||
| - | + | <br><br><br> | |
== Detailed Derivation of the Thermodynamic Model (Repressor Case) == | == Detailed Derivation of the Thermodynamic Model (Repressor Case) == | ||
[[File:Repressor_derivation.png|800px|center]] | [[File:Repressor_derivation.png|800px|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Navigate== | ||
| + | ====Modeling Pages==== | ||
| + | #[https://2013.igem.org/Team:Duke/Modeling/Cooperativity '''Cooperativity and Hill Equation'''] | ||
| + | #[https://2013.igem.org/Team:Duke/Modeling/Thermodynamic_Model_Intro '''Thermodynamic Model: Introduction'''] | ||
| + | #[https://2013.igem.org/Team:Duke/Modeling/Thermodynamic_Model_Application '''Thermodynamic Model: Application'''] | ||
| + | #[https://2013.igem.org/Team:Duke/Modeling/Kinetic_Model '''Kinetic Model'''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Supplementary Materials==== | ||
| + | #Derivation of the Thermodynamic Model (You are here) | ||
| + | #[https://2013.igem.org/Team:Duke/Modeling/Codes '''MATLAB/Mathematica Codes Used'''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
</div> | </div> | ||
Latest revision as of 04:58, 24 September 2013
Contents |
Mathematical Modeling of Bistable Toggle Switch
Detailed Derivation of the Thermodynamic Model (Simple Case)
Detailed Derivation of the Thermodynamic Model (Repressor Case)
Modeling Pages
- Cooperativity and Hill Equation
- Thermodynamic Model: Introduction
- Thermodynamic Model: Application
- Kinetic Model
Supplementary Materials
- Derivation of the Thermodynamic Model (You are here)
- MATLAB/Mathematica Codes Used
 "
"