Team:TU-Munich/Results/Recombinant
From 2013.igem.org
(→Characterization of recombinant effector proteins) |
(→Characterization of recombinant effector proteins) |
||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
|4 x 35.4 | |4 x 35.4 | ||
|?? | |?? | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |DTT Dehydrochlorinase | ||
| + | |<partinfo></partinfo> | ||
| + | |RFC[10] | ||
| + | |none | ||
| + | |4 x 35.4 | ||
| + | |none | ||
|- | |- | ||
|PP1 | |PP1 | ||
Revision as of 13:05, 3 October 2013
Characterization of recombinant effector proteins
For the development of a transgenic water filter it is important to create a collection of well described and functional effector proteins which are either able to bind (BioAccumulation) or to degrade (BioDegradation) xenobiotics present in the aquatic environment. This task was completed by the production of relevant effector proteins in E. coli and to complete their subsequent purification and characterisation. Deliberately we have chosen some well established BioBricks from the last years such as a laccae (<partinfo>BBa_K1159002</partinfo>) or the catechol dioxigenase (<partinfo>BBa_K648011</partinfo>) to improve these BioBricks. Beside these improvements we also added new BioBricks to the registry which we characterized in vitro such as the erythromycin esterase (EreB) (<partinfo>BBa_K1159000</partinfo>) or the NanoLuc luciferase (<partinfo>BBa_K1159001</partinfo>) which will be a useful tool for subsequent generations of iGEM students. For technical questions on our experiments, please see protein biochemical methods for further information.
| Protein | BioBrick | RFC | Affinity tag | Size [kDa] | Disulphid bridges | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eryhtromycin esterase (EreB) | <partinfo>BBa_K1159000</partinfo> | RFC[25] | c-term. Streptag II | 48.5 | none | |
| Laccase | <partinfo>BBa_K1159002</partinfo> | RFC[25] | c-term. Streptag II | 58.8 | yes | |
| Nano Luciferase | <partinfo>BBa_K1159001</partinfo> | RFC[25] | c-term. Streptag II | 19.4 | none | |
| XylE | <partinfo>BBa_K648011</partinfo> | RFC[25] | c-term. Streptag II | 4 x 35.4 | ?? | |
| DTT Dehydrochlorinase | <partinfo></partinfo> | RFC[10] | none | 4 x 35.4 | none | |
| PP1 | <partinfo>BBa_K1159004</partinfo> | RFC[25] | c-term. Streptag II | none | ||
| YFP_TEV_CFP | <partinfo>BBa_K1159112</partinfo> | RFC[10] | c-term. Streptag II |
Eryhtromycin Esterase (EreB) <partinfo>BBa_K1159000</partinfo>
The erythromycin esterase (EreB) is an enzyme found in some strains of E. coli and which was introduced to the Parts Registry by the TU Munich iGEM Team 2013 in RFC[25].
Protein Data Table for the erythromycin esterase (EreB) <partinfo>BBa_K1159000</partinfo>
| Protein data table for BioBrick BBa_ automatically created by the BioBrick-AutoAnnotator version 1.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nucleotide sequence in RFC 25, so ATGGCCGGC and ACCGGT were added (in italics) to the 5' and 3' ends: (underlined part encodes the protein) ATGGCCGGCAGGTTCGAA ... GTTTATGAAACCGGT ORF from nucleotide position -8 to 1260 (excluding stop-codon) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Amino acid sequence: (RFC25 scars in shown in bold, other sequence features underlined; both given below)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Sequence features: (with their position in the amino acid sequence, see the list of supported features)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Amino acid composition:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Amino acid counting
| Biochemical parameters
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Codon usage
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The BioBrick-AutoAnnotator was created by TU-Munich 2013 iGEM team. For more information please see the documentation. If you have any questions, comments or suggestions, please leave us a comment. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Production and purification of recombinant EreB
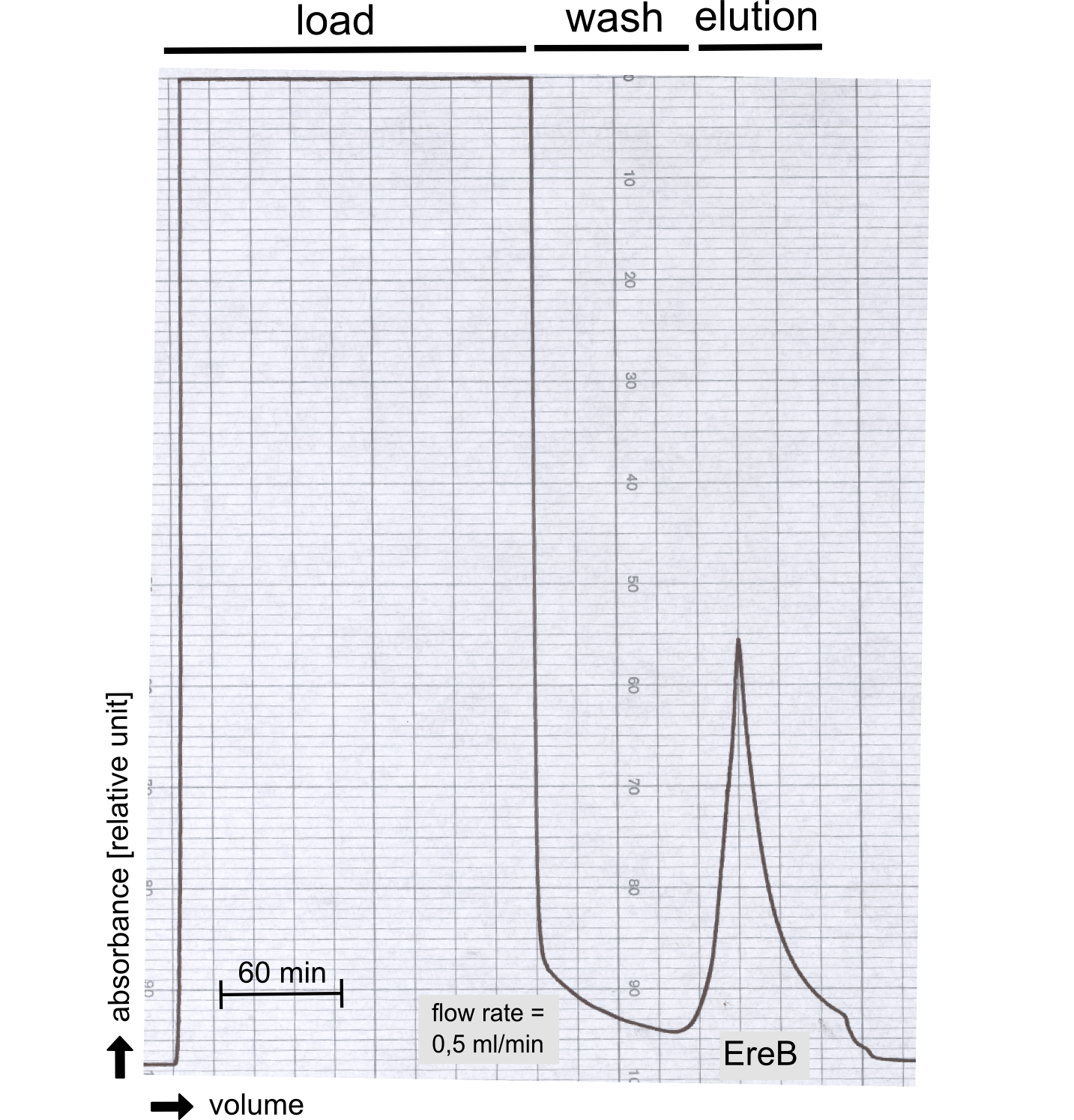
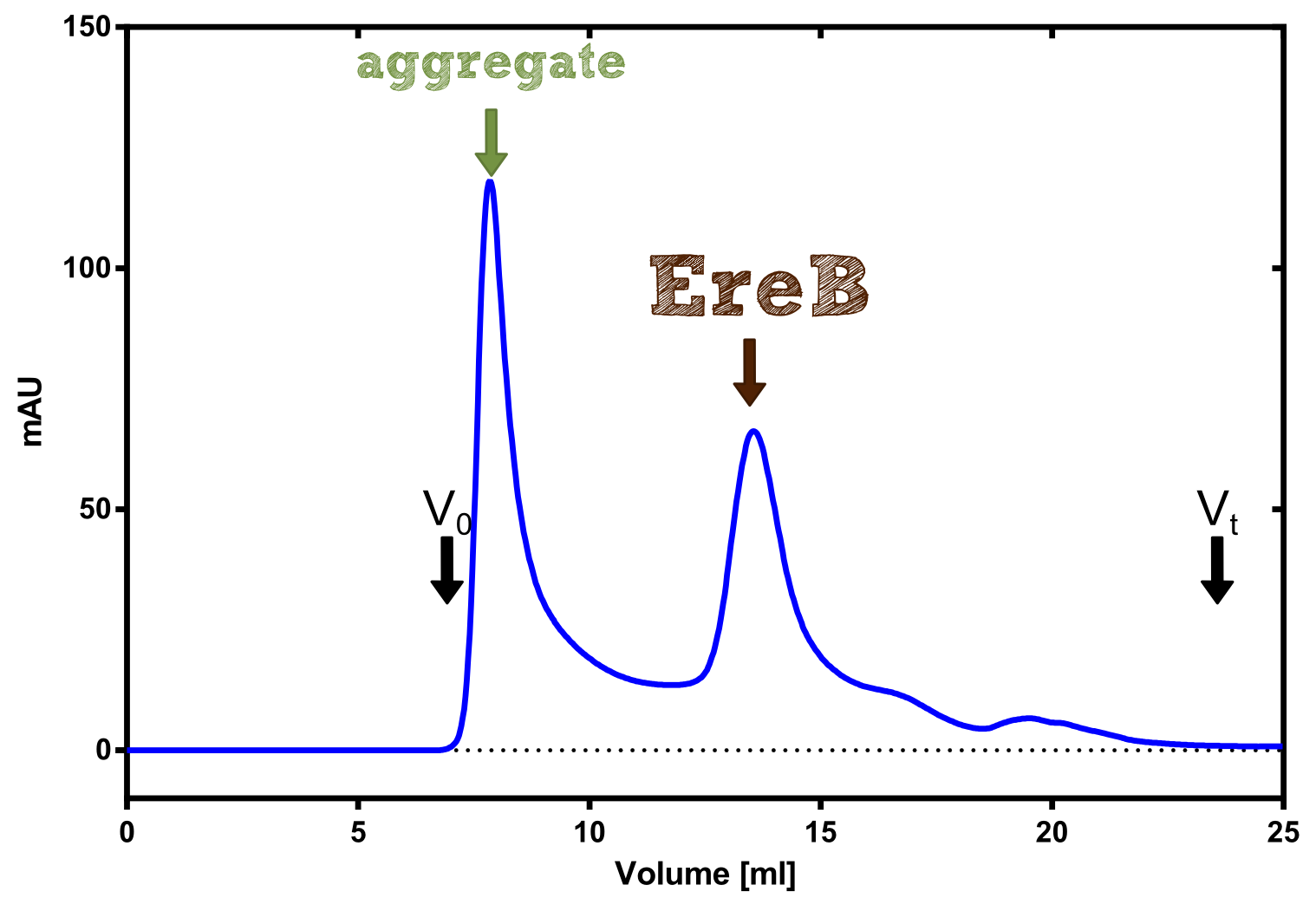
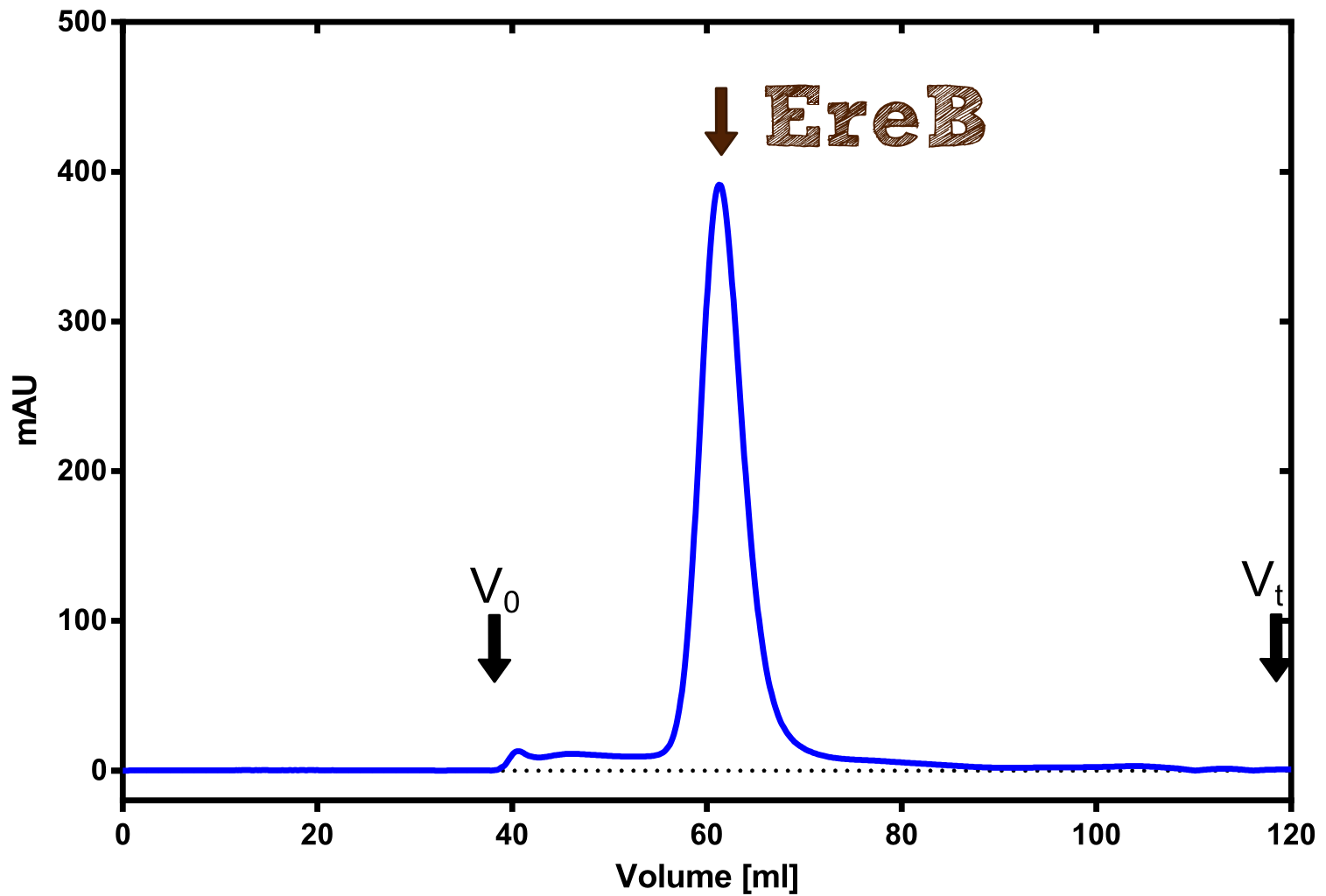
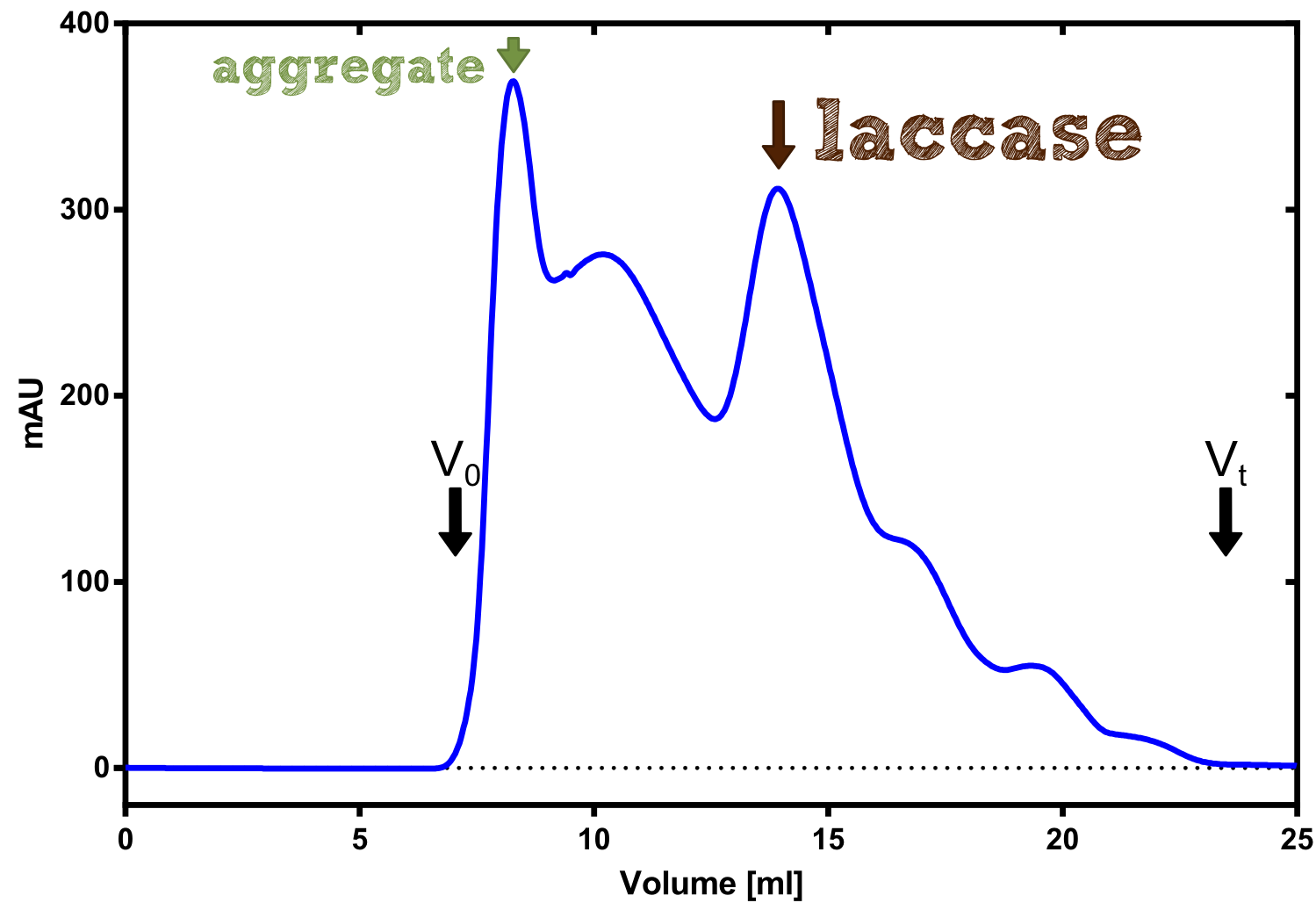
The recombinant production and purification was carried out twice, in a first attempt 2 L of LB-media were used for a analytical purpose whereas in the second attempt we produced enought pure enzyme for all subsequent experiments. This preparative preparation was carried out in 6 x 2L of LB media. Proteinproduction was in both cases induced at OD = 0.8 by adjusting the culture to 5 mM of arabinose and protein production was carried out for 4 h for the first and 5 h for the second preparation. Cell disruption was performed by ultrasonic sound in both cases. The cell lysate was then dialysed against 5 L of SA-buffer and was subsequently applied to streptavidin affinity columns. After the application of the protein the column was washed with SA-buffer until a base line was reached and subsequently the protein was eluted using 5 mM biotin. While during the first preparation 2-mercapto ethanol was just added after the chromatographic steps the preperative purification was carried out with buffers containing 5 mM of 2-mercapto ethanol in all buffers in order to avoid oxidation of cysteine residues to disulphid bridges which is not desired for the cytosolic EreB protein. When comparing the size exclusion chromatograms obtained from the analytical and the preperative purification it can be stated that in the first attempt there is still a considerable aggregation peak near the void volume (Fig. B) of the column which was nearly not the case for the preperative preparation (Fig. C), therefore we would give the advise to work under strictly reducing conditions for recombinant works with EreB. The final yiels of the preparative purification was determined by absorption measurement of the aromatic amino acids at 280 and the total yield was determined to 25 mg of pure protein which is 2.1 mg/L of LB culture.
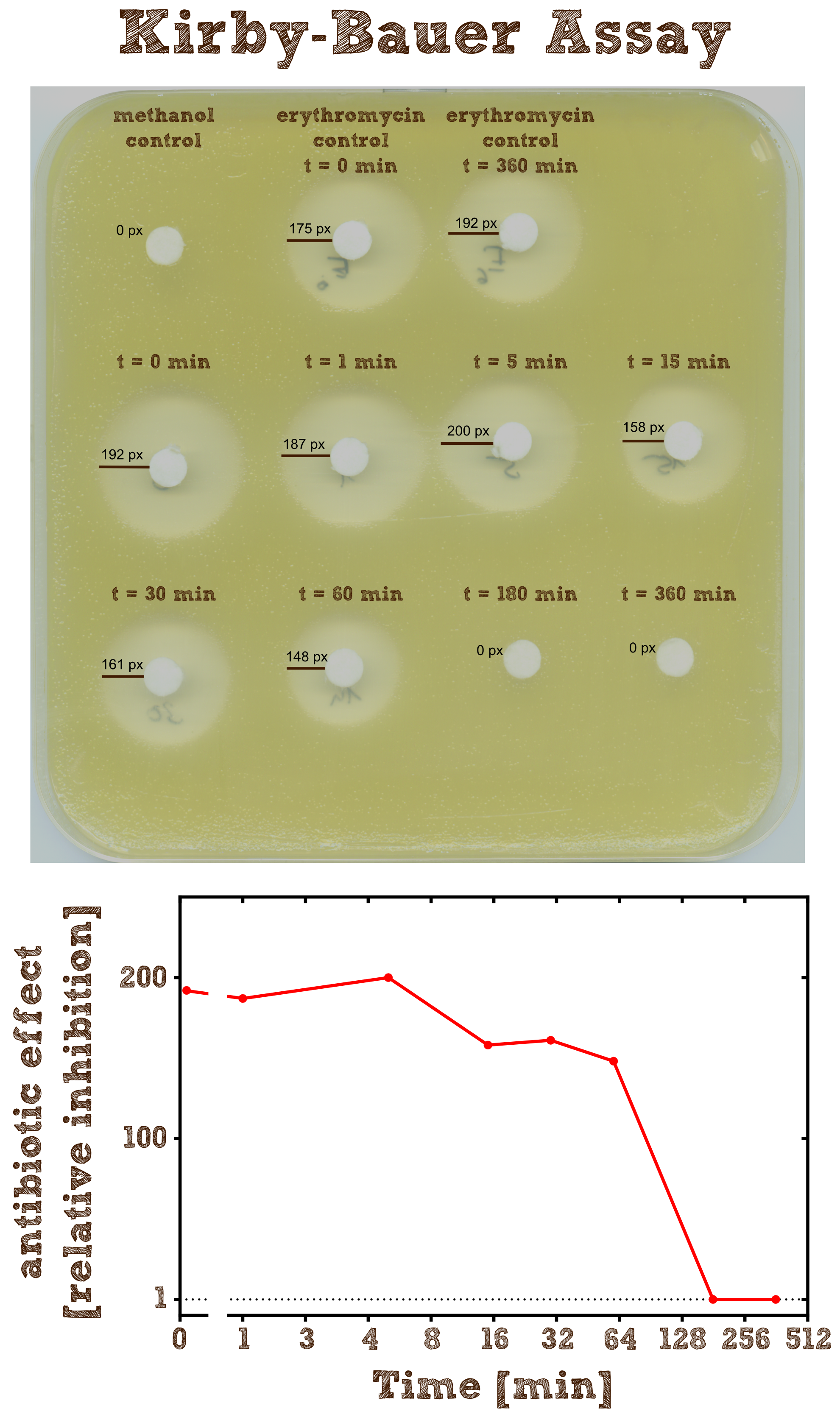
Kirby-Bauer Assay: Measuring remaining erythromycin on a pertri dish
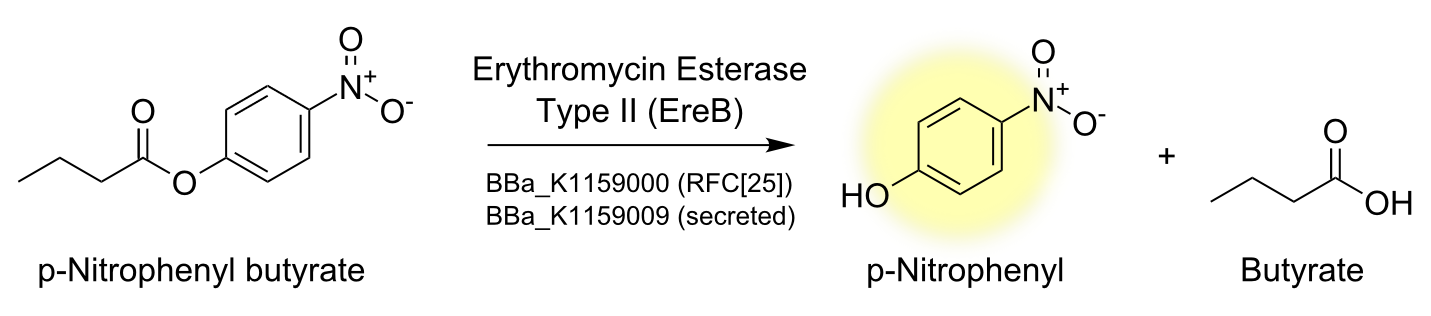
Degradation of a chromogenic esterase substrate: 4-Nitrophenyl butyrate
Degradation of Erythromycin
Reaction conditions HPLC Kirby Bauer-Assay
[...] Characterization
Laccase
[...] description [...] reaction [...] production
| Protein data table for BioBrick BBa_ automatically created by the BioBrick-AutoAnnotator version 1.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nucleotide sequence in RFC 25, so ATGGCCGGC and ACCGGT were added (in italics) to the 5' and 3' ends: (underlined part encodes the protein) ATGGCCGGCAACCTAGAA ... GATATCATCACCGGT ORF from nucleotide position -8 to 1530 (excluding stop-codon) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Amino acid sequence: (RFC25 scars in shown in bold, other sequence features underlined; both given below)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Sequence features: (with their position in the amino acid sequence, see the list of supported features)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Amino acid composition:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Amino acid counting
| Biochemical parameters
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Codon usage
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The BioBrick-AutoAnnotator was created by TU-Munich 2013 iGEM team. For more information please see the documentation. If you have any questions, comments or suggestions, please leave us a comment. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Laccase a is a secreted enzyme
Analytical präparation
[...] Characterization
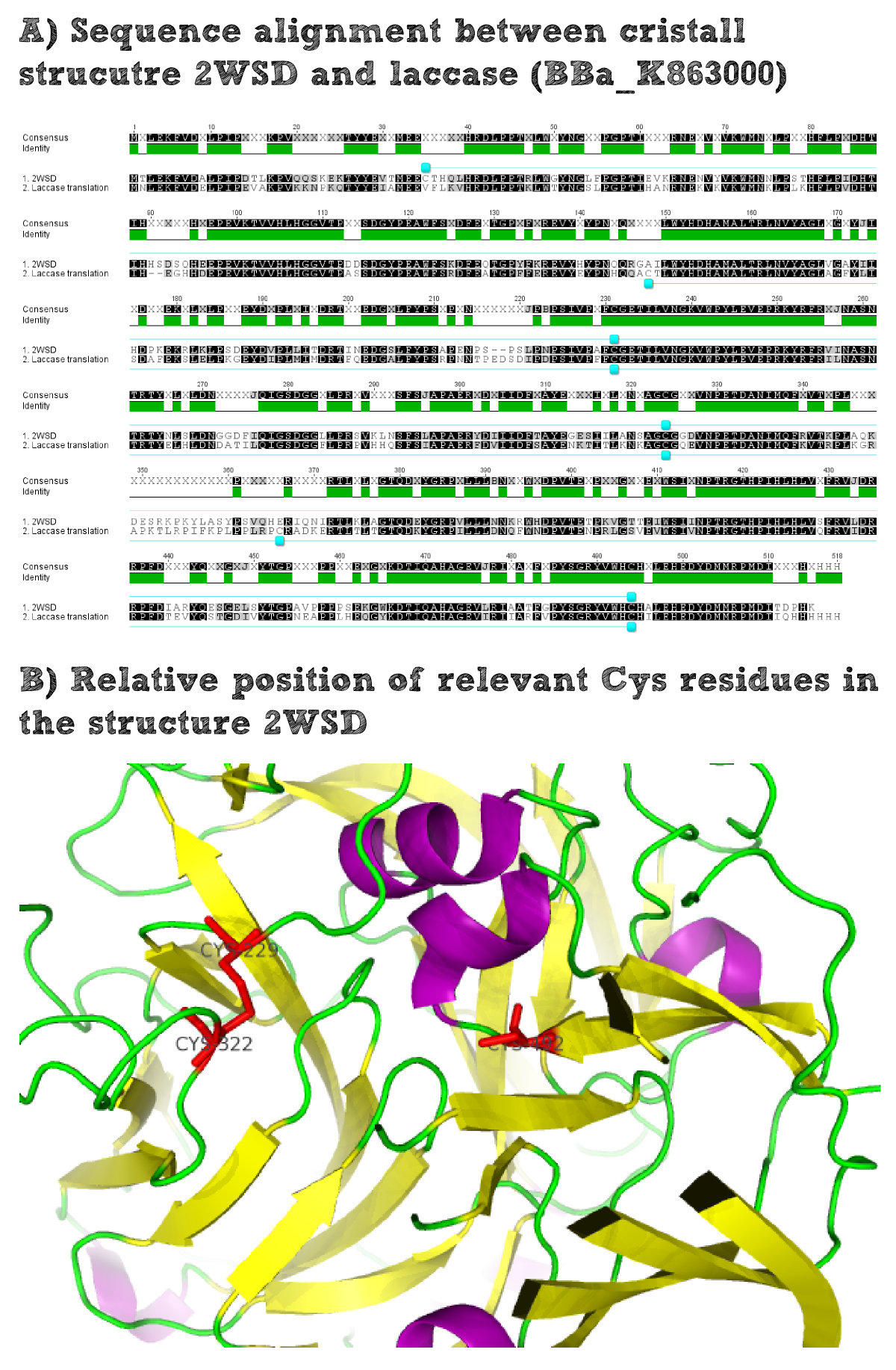
Structural consideration of Laccase from B. pumilus
Activity determination using ABTS
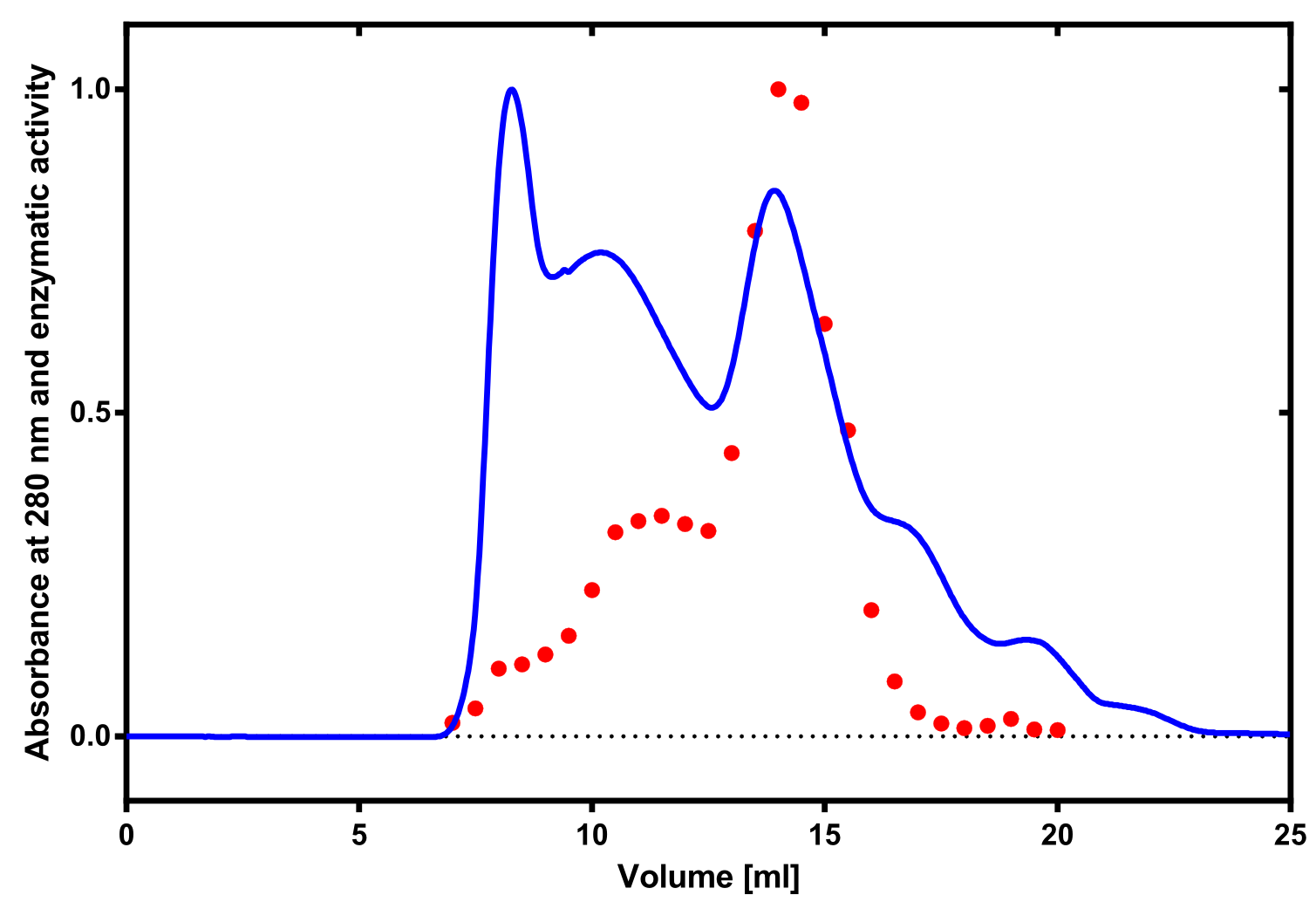
The enzymatic activity of the purified laccae was determined by the ABTS-assay. In a first pre experiment the appropriate dilution factor was determined to 100-fold. The elution fractions obtained from size exclusion chromatography were diluted 1:100 in PBS and in an ELISA plate 100 µl of the enzyme and 100 µl of ABTS substrate were mixed and a kinetic measurement at 405 nm was performed. The absorption at 280 nm in the SEC chromatogramm (blue) identifies three main protein peaks, with a first peak corresponding to aggregated protein, a shoulder which also corresponds to higher molecular protein and a single peak which was proposed to be the monomeric laccase. The relative activity obtained for the different elution fractions was plotted in the same diagramm and shows a clear peak which matches the laccase peak in the SEC. Beside this major peak a second smaller peak of active fraction was visible which appeared in earlier elution fractions and might correspond to dimerized laccase. As the laccase is a secreted enzyme which also bears disluphide bonds it was produced in the cytoplasm and subsequently it was oxidized to form the proper disulphide bond. As this process might be only partial there is a possiblity for the formation of disulphid dimers. Never the less the fractions 14 to 17 were pooled for further experiments as they showed the highest enzymatic activity. The protein concentration of the pooled fraction was determined to 0.48 mg/ml after SEC.
Oxidation of relevant xenobiotics
Diclofenac
Estradiol
Nano Luciferase
The Nano Luciferase (NanoLuc) which was introduced in 2013 by Promega is a new member of the luciferase reporter gene/protein familiy and shows some advantages compared to the other family members. The NanoLuc is very small (19 kDa) compared to the firefly luciferase (61 kDa) and the Renilla luciferase (36 kDa). On the other hand it is also said that the specific activity of the NanoLuc is about 150-fold stronger compared to conventional luciferases and the background caused by autoluminescense of the substrate shel be smaller.
| Protein data table for BioBrick BBa_K1159001 automatically created by the BioBrick-AutoAnnotator version 1.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nucleotide sequence in RFC 10: (underlined part encodes the protein) ATGGCCGGC ... GCTACCGGTTAA ORF from nucleotide position 1 to 525 (excluding stop-codon) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Amino acid sequence: (RFC 25 scars in shown in bold, other sequence features underlined; both given below)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Sequence features: (with their position in the amino acid sequence, see the list of supported features)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Amino acid composition:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Amino acid counting
| Biochemical parameters
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Plot for hydrophobicity, charge, predicted secondary structure, solvent accessability, transmembrane helices and disulfid bridges | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Codon usage
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Alignments (obtained from PredictProtein.org)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predictions (obtained from PredictProtein.org) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Subcellular Localization (reliability in brackets)
| Gene Ontology (reliability in brackets)
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Predicted features:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The BioBrick-AutoAnnotator was created by TU-Munich 2013 iGEM team. For more information please see the documentation. If you have any questions, comments or suggestions, please leave us a comment. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Production in E. coli and purification
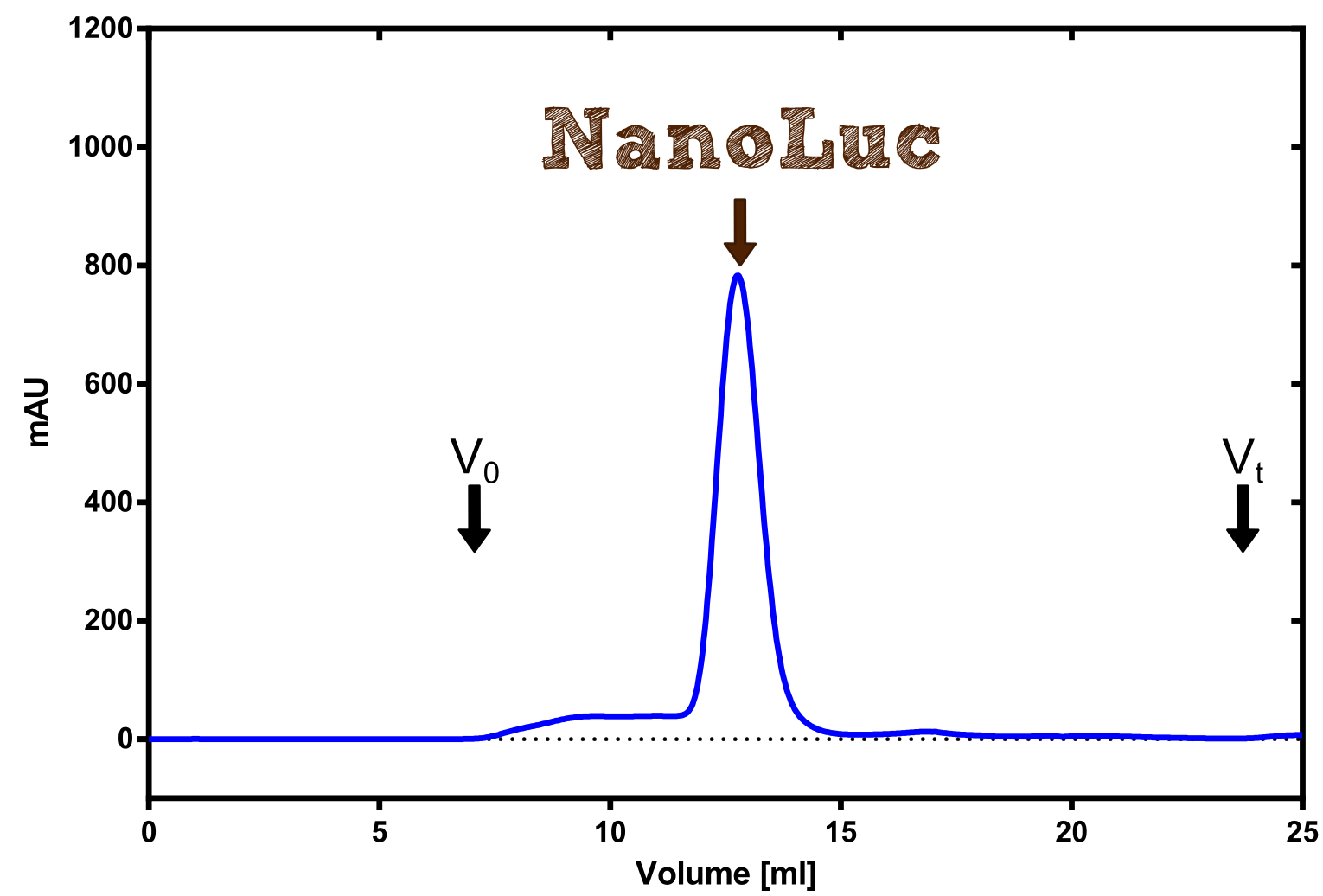
Therefore the NanoLuc was synthesized as a BioBrick in RFC[25] and was produced in E. coli using the pBad expression system with a C-terminal Strep-tag. After the production (2 l of LB-media for analytical and 12 l for preparative preparations) the cells were disrupted using sonification and the lysate was dialysed against 5 l of 1x SA-buffer. Afterwards the lysate was applied to a Streptavidin-Affinity (SA) column and was subsequently washed using SA-Buffer until a baseline was reached and the protein was then eluted using 5 mM of biotin (Attention: These are special columns which are not availible commercially. If you are using commercial colum material you have to use d-Desthiobiotin because usual biotin will elute your protein but you will not be able to regenerate the column after your chromatography). After the SA-chromatography the protein was concentrated using centrifugal concentration units (MWCO: 10 kDa). The concentrated protein was then applied on a Superdex S200/75 size exclusion chromatography.
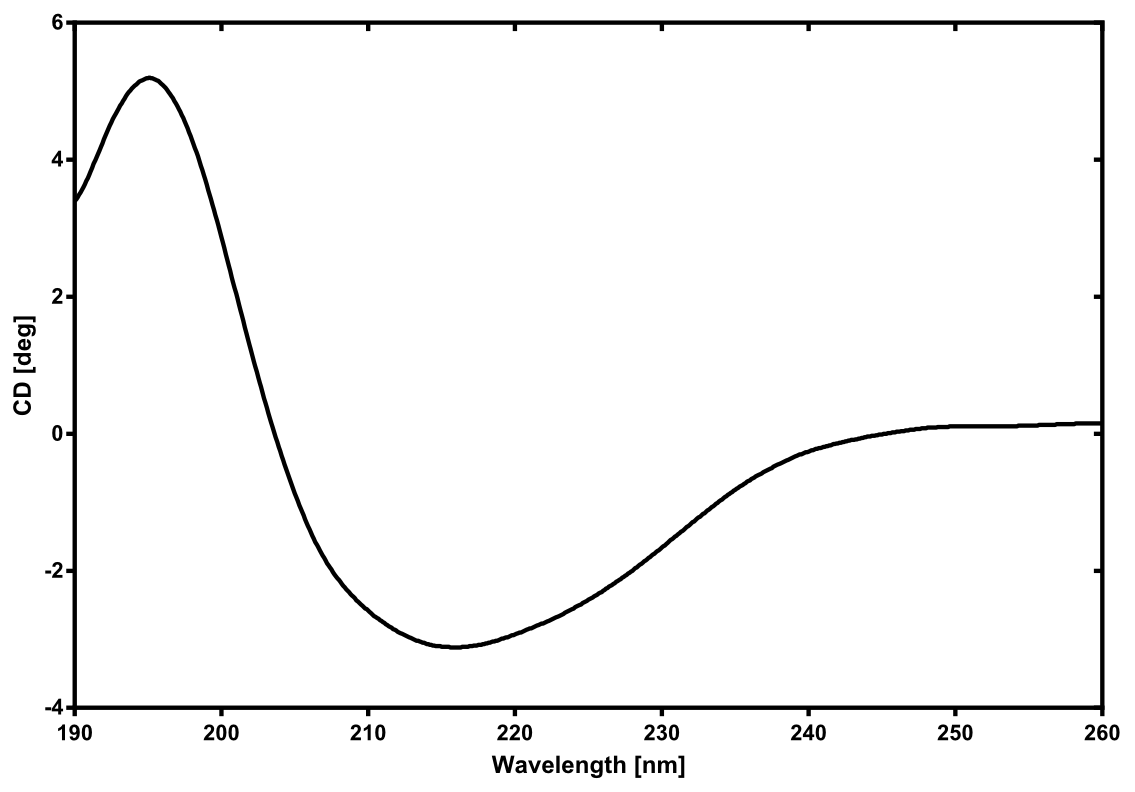
Structure of the Nano Luciferase
There is no structure availible for the NanoLuc in the [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/home/home.do Protein Data Bank]. In our protein modelling we used homolgy search and identified the structure [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore/explore.do?structureId=3PPT 3ppt_A] as the solved structure with the highest homology to the NanoLuc which has only 21% identify with a similarity of only 0.359. The result of the homology search is shown as annimated gif in Figure xx (please see our How To for an introduction). The protein was dialysed against 1x CD-buffer and subsequently a circular dichroism spectroscopy was tanken (learn about CD spectroscopy). The CD spectrum was used to predict the secondary structure content of the NanoLuc which could be determined to 35.1% helix, 27.6% b-strand, 18.5% turn and 18.8% random. As there is only a poor homology present, a detailed comparison of the determined and the predicted secondary structure is not possible. But it can be stated that both show a balanced content of different secondary structures and that the produced protein is present in an folded conformation. The mixed secondary structure content is also in consistance with the predicted secondary structure shown in the AutoAnnotator sequence window (click on show).
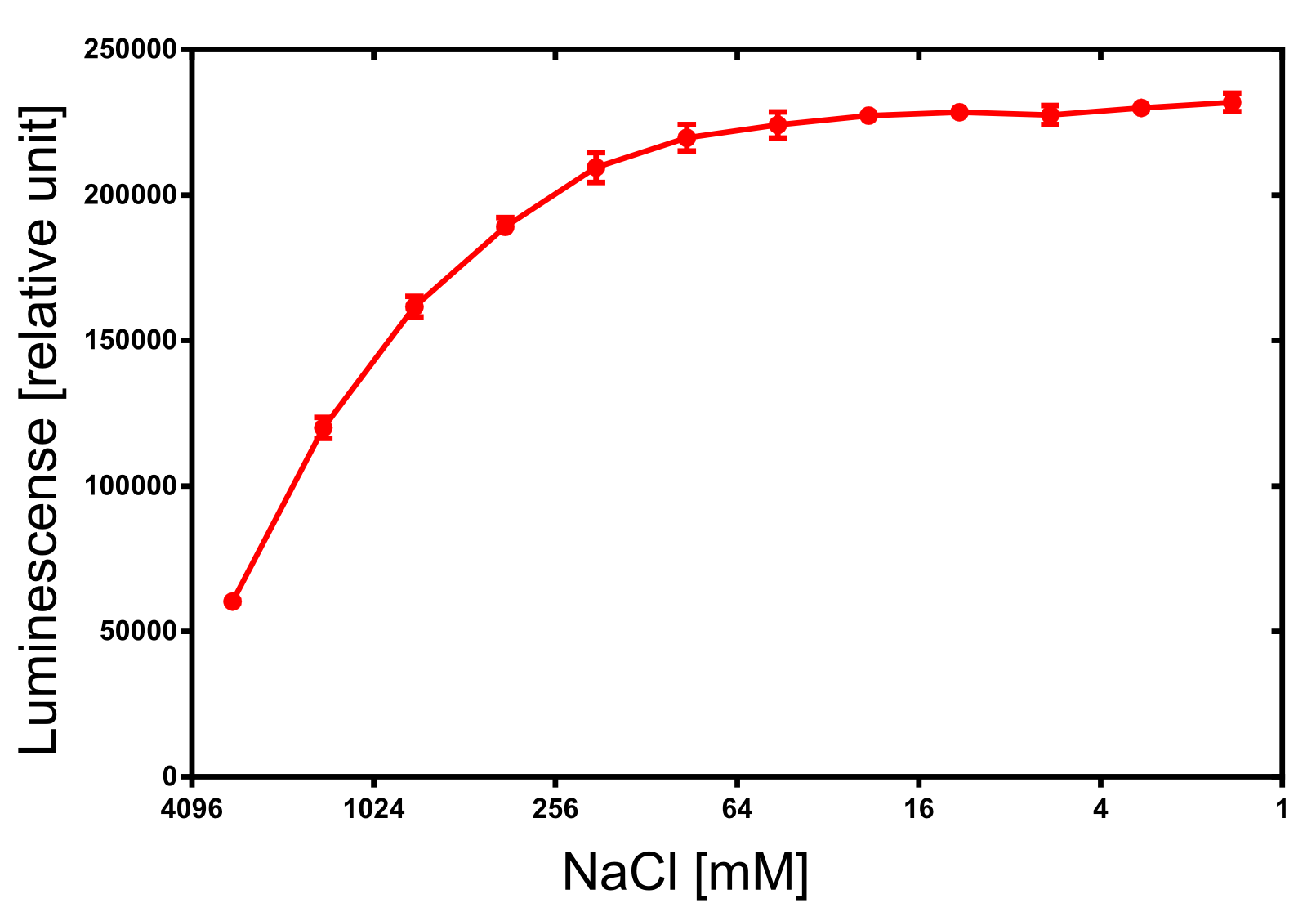
Activity determination of Luminescense
The activity of the produced NanoLuc was investigated by its luminescense. The luminescense
Catechol Dioxigenase (XylE) (<partinfo>BBa_K648011</partinfo>)
Protein Data Table for the Catechol Dioxigenase (XylE) (<partinfo>BBa_K648011</partinfo>)
| Protein data table for BioBrick BBa_ automatically created by the BioBrick-AutoAnnotator version 1.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nucleotide sequence in RFC 25, so ATGGCCGGC and ACCGGT were added (in italics) to the 5' and 3' ends: (underlined part encodes the protein) ATGGCCGGCAACAAAGGT ... GTGCTGACCACCGGT ORF from nucleotide position -8 to 924 (excluding stop-codon) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Amino acid sequence: (RFC25 scars in shown in bold, other sequence features underlined; both given below)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Sequence features: (with their position in the amino acid sequence, see the list of supported features)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Amino acid composition:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Amino acid counting
| Biochemical parameters
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Codon usage
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The BioBrick-AutoAnnotator was created by TU-Munich 2013 iGEM team. For more information please see the documentation. If you have any questions, comments or suggestions, please leave us a comment. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Analytical präparation
[...] Characterization
DDT-Dehydrochlorinase <partinfo>BBa_K648011</partinfo>
Protein Data Table for the DDT-Dehydrochlorinase <partinfo>BBa_K648011</partinfo>
| Protein data table for BioBrick BBa_ automatically created by the BioBrick-AutoAnnotator version 1.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nucleotide sequence in RFC 10: (underlined part encodes the protein) ATGGACTTT ... TTCCTGAGCTAGTAG ORF from nucleotide position 1 to 627 (excluding stop-codon) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Amino acid sequence: (RFC25 scars in shown in bold, other sequence features underlined; both given below)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Sequence features: (with their position in the amino acid sequence, see the list of supported features)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Amino acid composition:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Amino acid counting
| Biochemical parameters
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Codon usage
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The BioBrick-AutoAnnotator was created by TU-Munich 2013 iGEM team. For more information please see the documentation. If you have any questions, comments or suggestions, please leave us a comment. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Protein phosphatase 1 (from Homo sapiens) <partinfo>BBa_K1159004</partinfo>
The production of recombinant protein phosphatase 1 was part of our collaboration with Dundee iGEM team 2013. They developed this BioBrick which naturally binds [http://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Microcystine microcystine], an important environmental toxin.
Protein Data Table for the protein phosphatase 1 (PP1)
| Protein data table for BioBrick BBa_K1159004 automatically created by the BioBrick-AutoAnnotator version 1.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nucleotide sequence in RFC 25, so ATGGCCGGC and ACCGGT were added (in italics) to the 5' and 3' ends: (underlined part encodes the protein) ATGGCCGGCGGATCCGCG ... GCAAAGAAAACCGGT ORF from nucleotide position -8 to 978 (excluding stop-codon) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Amino acid sequence: (RFC 25 scars in shown in bold, other sequence features underlined; both given below)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Sequence features: (with their position in the amino acid sequence, see the list of supported features)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Amino acid composition:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Amino acid counting
| Biochemical parameters
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Plot for hydrophobicity, charge, predicted secondary structure, solvent accessability, transmembrane helices and disulfid bridges | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Codon usage
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Alignments (obtained from PredictProtein.org)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predictions (obtained from PredictProtein.org) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Subcellular Localization (reliability in brackets)
| Gene Ontology (reliability in brackets)
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Predicted features:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The BioBrick-AutoAnnotator was created by TU-Munich 2013 iGEM team. For more information please see the documentation. If you have any questions, comments or suggestions, please leave us a comment. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Production and purification of recombinant PP1 protein
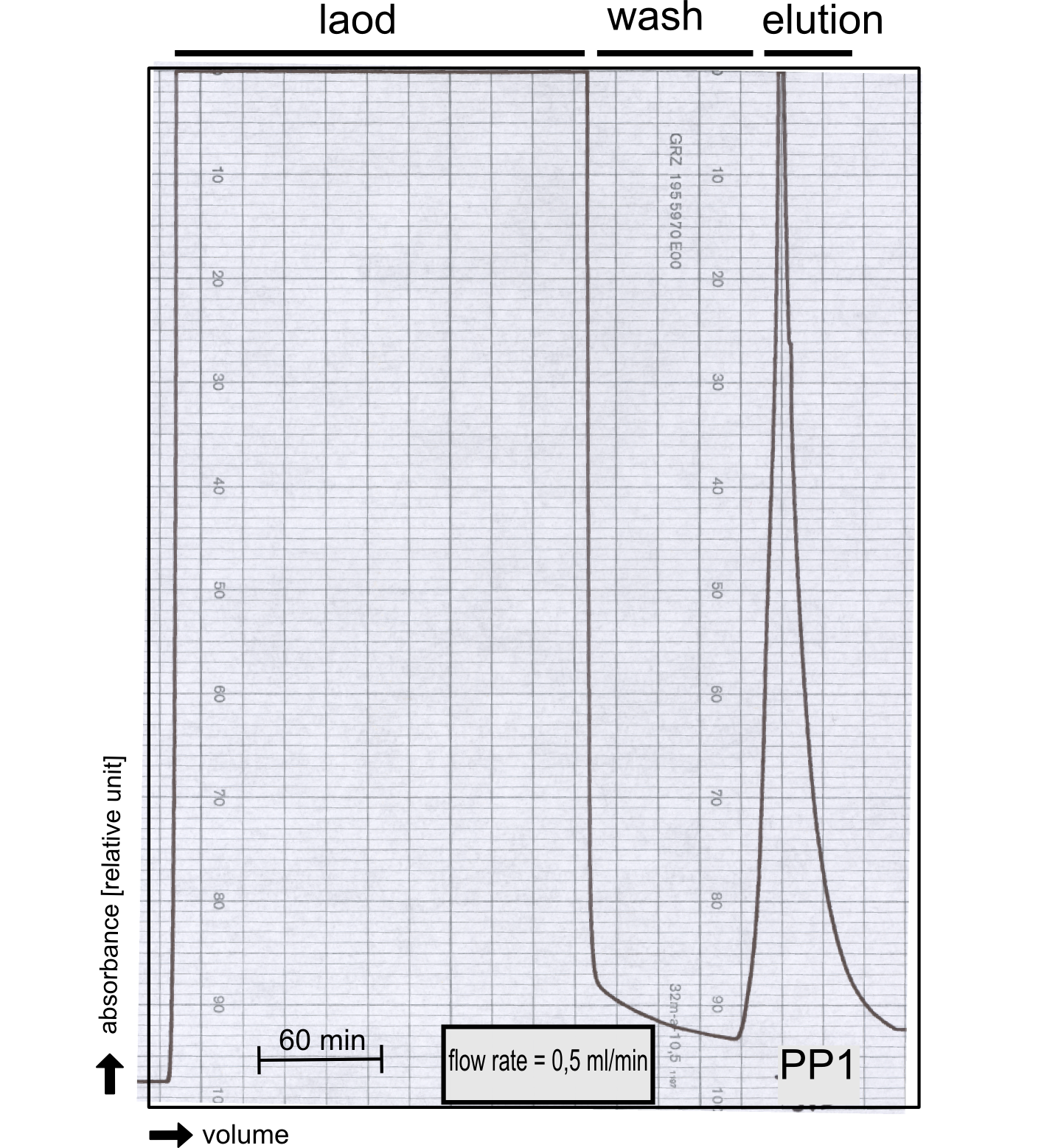
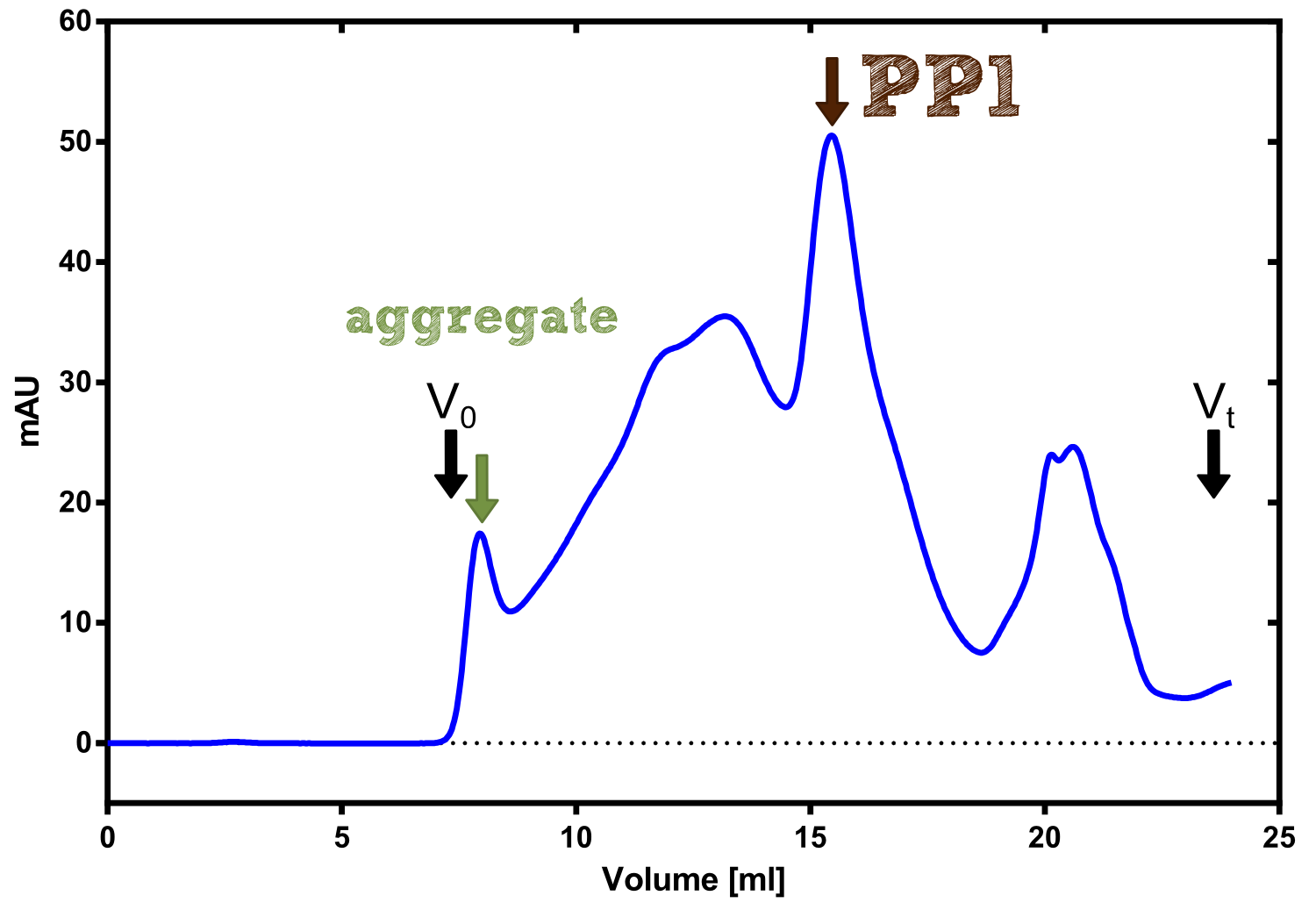
We converted this BioBrick to RFC[25] and cloned it afterward into the expression vector pBad_C-terminal_Strep. Beside the recombinant characterisation we also created a transgenic moss transformed with a receptor containing PP1 in its extracellular domain. The recombinant protein production was carried out in E. coli BL-21 which was grown in 2 L of LB-media. The protein production was induced at OD = 0.8 by addition of arabinose to a concentration of 5 mM. The cells were harvested after 4 h and subsequently resuspended in 20 mL SA-buffer with 5 mM 2-mercapto ethanol. Cell disruption was performed using ultrasonic sound. The dialysed cell extracte was applied to a streptavidin affinity column which was washed until a base line was reached and was subsequently eluted using SA-buffer containing 5 mM of biotin and 5 mM of 2-mercapto ethanol. The elution peak recorded by the continuous measurement of the absorbance at 280 nm indicated a good yield of recombinant protein (Fig. A). As a second purification step after the streptavidin affinity chromatography we concentrated the protein in centrifugal filter units in order to apply it to a size exclusion chromatography. During the concentration process there were clear signal for precipitated protein which appeared as white flakes in the concentration filter unit. This effect was by far the most drastic precipitation of recombinant that was detected during this iGEM project. Anyhow the concentrated protein was centrifuged for 5 min at 13 200 RPM to remove particles of precipitated protein and was then applied to an ÄKTA purified with a Superdex 200 10/30 column (Fig. B). There were four different peaks present in the chromatogramm which most probably correspond to (1) a peak created by aggregated protein which runs in the voit volume of the size exclusion colum, (2) a diffuse peak which might correspond to multimeric PP1, (3) a sharp peak at the elution volume where the recombinant PP1 was expected and (4) a peak which is most probably caused by low molecular buffer substances. The general signal intensity obtained in the size exclusion was very low indicating low protein concentrations. The maximal peak obtained for PP1 had an absorbance of 50 milli Absorption Units whereas this was for example for the NanoLuc in the range of 1000 for a comparable experiment. The fact that this protein does not tolerate the concentration procedure gibes an indication that it is fragile and tends to aggregation when stress is applied. Finally recombinant PP1 protein was prepared although the yield was very low compared with other effector proteins.
Possible reasons for the instability of PP1 in vitro
The high aggregation and denaturation tendency of the protein phosphatase 1 which was observed in the analytical preparation motivated this search for a possible explanation. As a first hint the amino acid composition calculated by the AutoAnnotator was examined and it can be seen that 13 cysteine residues are present in the sequence of the protein phosphatase. This corresponds to 4% of the total number of amino acid residues comapred to 2.8% cystein residues in average protein. This information taken together with the molecular function of the protein phosphatase 1 clearly shows that this BioBrick is a cytoplasmatic protein which fulfills its function in the reducing milieu of the cytoplasm and tends to aggregation when exposed to an oxidizing milieu such a the periplasm of E. coli for example.
Secondly the amino acid sequence produced by the AutoAnnotator was fed into the bioinformatic tool [http://web.expasy.org/cgi-bin/protparam/protparam ProtParam which has a stability prediction for proteins. The result was: "The instability index (II) is computed to be 42.99 - This classifies the protein as unstable."
Taken both these indications into account it still seems a good idea to express the protein phosphatase 1 cytoplasmatically to bind microcystine but it is not advisable to think about a secreted version of PP1 as the protein seems to unstable for this application.
SpyCatcher & SpyTag
[...] description [...] reaction [...] production
| Protein data table for BioBrick BBa_ automatically created by the BioBrick-AutoAnnotator version 1.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nucleotide sequence in RFC 25, so ATGGCCGGC and ACCGGT were added (in italics) to the 5' and 3' ends: (underlined part encodes the protein) ATGGCCGGCGTTGATACC ... GCTCATATTACCGGT ORF from nucleotide position -8 to 345 (excluding stop-codon) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Amino acid sequence: (RFC25 scars in shown in bold, other sequence features underlined; both given below)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Sequence features: (with their position in the amino acid sequence, see the list of supported features)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Amino acid composition:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Amino acid counting
| Biochemical parameters
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Codon usage
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The BioBrick-AutoAnnotator was created by TU-Munich 2013 iGEM team. For more information please see the documentation. If you have any questions, comments or suggestions, please leave us a comment. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Analytical präparation
[...] Characterization
References:
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6327079 Edens et al., 1984
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6327079 Edens et al., 1984 Edens, L., Bom, I., Ledeboer, A. M., Maat, J., Toonen, M. Y., Visser, C., and Verrips, C. T. (1984). Synthesis and processing of the plant protein thaumatin in yeast. Cell, 37(2):629–33.
- http://udel.edu/~gshriver/pdf/Pimenteletal1997.pdf Pmentel et al., 1997 Pimentel, D., Wilson, C., McCullum, C., Huang, R., Dwen, P., Flack, J. Tran, Q., Saltman, T., Cliff, T. (1997). Economic and environmental benefits of biodiversity. BioScience, Vol. 47, No. 11., pp. 747-757.
 "
"







AutoAnnotator:
Follow us:
Address:
iGEM Team TU-Munich
Emil-Erlenmeyer-Forum 5
85354 Freising, Germany
Email: igem@wzw.tum.de
Phone: +49 8161 71-4351