Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Labjournal/August
From 2013.igem.org
| Line 278: | Line 278: | ||
*Riboflavin | *Riboflavin | ||
| - | **We were able to profit from the experiences we had already gained while working on other cloning subprojects. | + | **We were able to profit from the experiences we had already gained while working on other cloning subprojects. So we started right away with designing specific pSB1C3-Gibson-primers. Every one of our four desired parts got an unique pSB1C3 with overlaps that were homologues to the ends of the insert. This way, we were able to shut down the “religation problem” (see Failbook). |
| - | + | **Gradient PCR´s with above Primers and pSB1C3 a template gave good results. Actually, they were that good, that we just cleaned up and pooled all nanotubes for further experiments. | |
| + | **Meanwhile we started to isolate the genes responsible for riboflavin expression from the genome of shewanella oneidensis (link to genome isolation) | ||
| + | |||
Revision as of 00:29, 30 September 2013
August
Milestones
Week 14
Organization
- We had a second radio interview in the Bielefeld university campus radio (radio 87.9 hertz) to introduce our project and the iGEM competition.
- Having an expert interview with Dr. Falk Harnisch from the Helmholtz Institute in Leipzig, who has got a great knowledge in the field of MFC.
MFC
Mediators
- Glycerol dehydrogenase
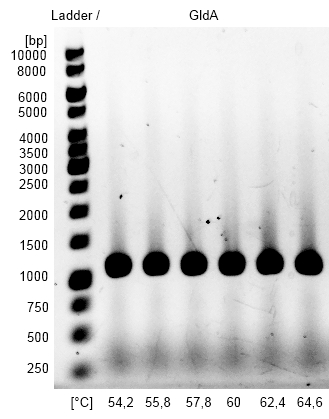
- Gradient PCR on the <bbpart>BBa_J04450</bbpart> Biobrick with Forward and Reverse Primer pSB1C3 GldA to amplify pSB1C3 backbone with GldA specific overlaps for Gibson assembly. The optimal Primer Binding temperature was 60 °C.
- Optimization of PCR on the GldA gene of Escherichia coli with temperature gradient PCR using Forward and Reverse GldA Primer. The optimal Primer binding temperature was 60 °C.
- GldA PCR product and the corresponding pSB1C3 Gibson backbone were isolated by Agarose gel electrophorese and purificated.
- Gibson Assembly with optimized GldA PCR product and pSB1C3 PCR product with GldA specific overlaps using Gibson Assembly with 3:1 molar ratio of insert to vector with 100 ng insert.
- GldA BioBrick was successfully cloned into pSB1C3 shipping vector.
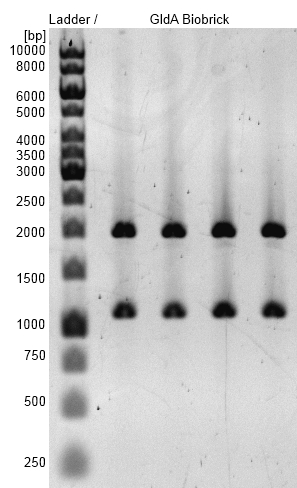
Figure 3: Agarosegel with GeneRuler™ 1 kb DNA Ladder from Thermo Scientific as marker. Bands are showing restriction analysis from cloning of GldA into pSB1C3 shipping vector with Gibson Assembly. Bands are at the expected size of 1100 bp (GldA) and 2000 bp (pSB1C3). GldA BioBrick (<bbpart>BBa_K1172201</bbpart>) was examined.
- GldA BioBrick plasmid (<bbpart>BBa_K1172201</bbpart>) was examined by restriction analysis with restriction enzymes EcoRI und XbaI. Bands are at the expected size of 1100 bp (GldA) and 2000 bp (pSB1C3).
Cytochromes
- Restriction of ccmAH and psB1C3 and Suffix-Insertion
- The backbone and shipping vector psB1C3 was cut with EcoRI, SpeI, the insert ccmAH with EcoRI and XbaI to perfom a standard suffix insertion.
- We used approx. 200ng insert and 42ng vector, which repressnts a 2-fold molar excess of insert.
- The Ligation was incubated for 15 min at 37°C, followed by a heat-inactivation at 80°C for 20 min.
- The subsequent gel electrophoresis did not yield any positiv results, probably due to the use of buffer and enzymes from two different manufactures.
- Validation of all intermediate products via gel electrophoresis
- A gel electrophoresis was performed to ensure that all former products have the correct size and this could be ruled out as an error source.
- It showed that all products were indeed correct.
- Amplification of psB1C3 with insert-specific primers
- The backbone and shipping plasmid psB1C3 was amplified with the new designed insert-specific primers for mtrCAB. These primers have a specific overlap complementary to 20nt at the beginning and end of the insert. This was necessary, because we had to deal with constant religation of the vector. We investigated this issue and found out, that prefix and suffix of the psB1C3 vector have a very similarity, which facilates religation. The correct band was extracted from the gel and cleaned up.
- NanoDrop:
- 4-0108-301: 1.1 ng/ul
- 4-0108-302: 1.0 ng/ul
- Gibson-Assembly of psB1C3 and fragment 1,2 and 3 of the mtrCAB cluster
- We use a custom 15 ul reaction mixture, prepared in our lab. After thawing on ice, a total amount of 5 ul DNA is added and the whole mixture is incubated at 50°C for approx. 60min.
- Mixture:
- psB1C3 (4-0108-301): 2.2 ng
- Fragment1 (4-2607-304): 13.1 ng
- Fragment2 (4-2707-004): 16.9 ng
- Fragment3 (4-2607-301): 14.4 ng
- Notes:The inserts were not equimolar and not added in a 3-fold excess to the vector
- Transformation to self-made electrocompetent E.coli cells. A total volume of 1ul could be used.
Biosafety
- We did Gibson-Assembly according to the typical Gibson-Assembly protocol with the different purified plasmids. :
- Fragment: "pSB1C3_plac_alr+ pSB1C3_alr_rev"+"pSB1C3_plac_pre+ pSB1C3_alr_suf",
- "pSB1C3_alr_fwd+ pSB1C3_alr_rev"+"pSB1C3_alr_pre+ pSB1C3_alr_suf",
- "araC_d1+ araC_d2"+"araC_d3+ araC_d4", with pKO4
- After the Gibson Assembly we transformated the Gibson fragments into self produced competent E.coli KRX cells and plated the cells on LB+CM20-plates
Porines
- Gradient PCR on the <bbpart>BBa_J04450</bbpart> Biobrick with Forward and Reverse Primer pSB1C3 OprF to amplify pSB1C3 backbone with OprF specific overlaps for Gibson assembly. The optimal Primer Binding temperature was 60 °C.
Week 15
Organization
- The TV station WDR made a video with us about our project. This can be seen in the OWL local time, a television program of the WDR.
MFC
Mediators
- Glycerol dehydrogenase
- The following parts were isolated from 2013 Distribution Kit and transformed into Escherichia coli KRX strain:
- <bbpart>BBa_K608002</bbpart> (<bbpart>J23104</bbpart> + <bbpart>B0034</bbpart>)
- <bbpart>BBa_K608003</bbpart> (<bbpart>J23104</bbpart> + <bbpart>B0032</bbpart>)
- <bbpart>BBa_K608004</bbpart> (<bbpart>J23104</bbpart> + <bbpart>B0031</bbpart>)
- <bbpart>BBa_K608006</bbpart> (<bbpart>J23110</bbpart> + <bbpart>B0032</bbpart>)
- <bbpart>BBa_K608007</bbpart> (<bbpart>J23110</bbpart> + <bbpart>B0031</bbpart>)
- <bbpart>BBa_K525998</bbpart> (T7 Promotor + <bbpart>B0034</bbpart>)
- <bbpart>BBa_K081005</bbpart> (<bbpart>J23100</bbpart> + <bbpart>B0030</bbpart>)
- Plasmids were isolated for later Suffix Insertion.
- GldA BioBrick plasmid (<bbpart>BBa_K1172201</bbpart>) was examined by sequencing.
- The following parts were isolated from 2013 Distribution Kit and transformed into Escherichia coli KRX strain:
Cytochromes
Biosafety
- We did plasmid isolation with different samples. The first six samples were put out of the distribution plates and transformed into KRX electro competent cells to concentrate the DNA. The other samples were taken after the transformation before. The reason for the red and white colonie samples is that we wanted to use the Biobrick of Bettencourt 2012 but they wasn't physically in the parts registry although it was written that this was the fact. We asked Bettencourt to send us the Biobricks. After a week we get the Biobrick but as we plated the sample out there were red and white colonies. We decided to check both of them.:
- BBa_I13541 A: 95,1 ng/µL (9-88-451)
- BBa_I13541 B: 165,1 ng/µL (9-88-452)
- BBa_K914004 A white: 198,8 ng/µL (9-88-453)
- BBa_K914004 B white: 204,9 ng/µL (9-88-454)
- BBa_K914004 A red: 476,5 ng/µL (9-88-455)
- BBa_K914004 B red: 400,9 ng/µL (9-88-456)
- AraC_del A: 82,4 ng/µL (9-88-457)
- AraC_del B: 64,5 ng/µL (9-88-458)
- pSB1C3_alr A: 120,4 ng/µL (9-88-459)
- pSB1C3_alr B: 168,4 ng/µL (9-88-460)
- pSB1C3_alr C: 137,2 ng/µL (9-88-461)
- ptac_alr A: 24,7ng/µL (9-108-451)
- ptac_alr B: 39,6 ng/µL (9-108-452)
Porines
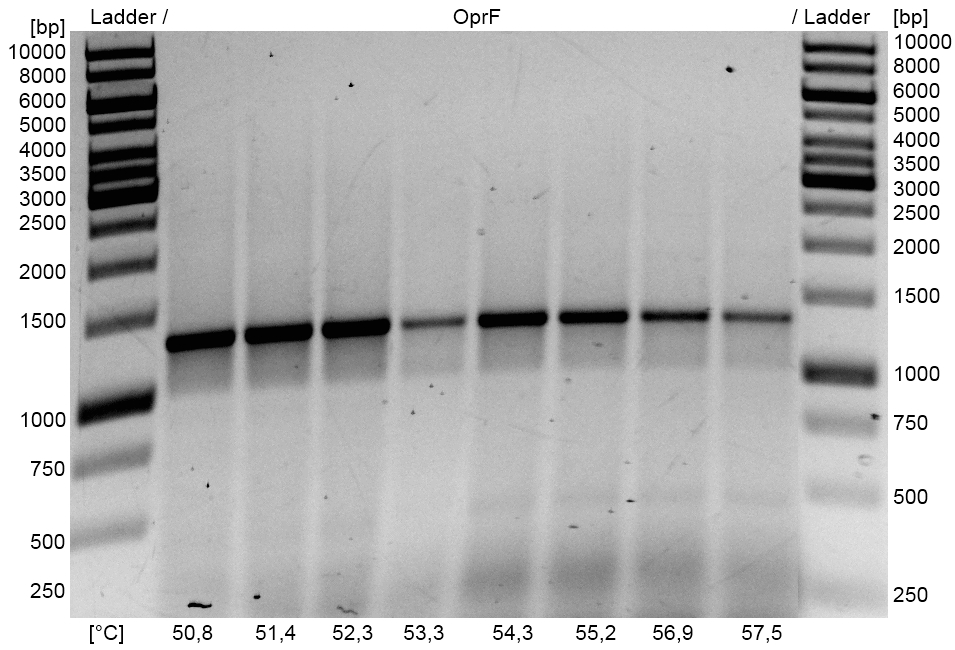
- Optimization of PCR on the OprF gene of Pseudomonas fluorescens with temperature gradient PCR using Forward and Reverse OprF Primer. The optimal Primer binding temperature was 51 °C.
- OprF PCR product and the corresponding pSB1C3 Gibson backbone were isolated by Agarose gel electrophorese and purificated.
- Gibson Assembly with optimized OprF PCR product and pSB1C3 PCR product with OprF specific overlaps using Gibson Assembly with 3:1 molar ratio of insert to vector with 100 ng insert.
- OprF BioBrick was successfully cloned into pSB1C3 shipping vector.

- OprF BioBrick plasmid <bbpart>BBa_K1172501</bbpart> was examined by restriction analysis with restriction enzymes EcoRI und XbaI. Bands are at the expected size of 1300 bp (OprF) and 2000 bp (pSB1C3).
- OprF BioBrick plasmid <bbpart>BBa_K1172501</bbpart> was examined by sequencing.
Week 16
Organization
- Final preparations for CeBiTec pupil academy in the next week.
MFC
Mediators
- Glycerol dehydrogenase
- Adding the following parts with promoter and RBS to the GldA Biobrick <bbpart>BBa_K1172201</bbpart> by Standard Biobrick assembly Suffix Insertion modified from Silver lab: <bbpart>BBa_K525998</bbpart>, <bbpart>BBa_J04500</bbpart> and <bbpart>BBa_K608006</bbpart>
- Promotor insertion was examined by restriction analysis and the following GldA Biobrick Devices with promotor and RBS could be added:
- <bbpart>BBa_K1172203</bbpart>: <bbpart>BBa_K1172201</bbpart> + <bbpart>BBa_K525998</bbpart>
- <bbpart>BBa_K1172204</bbpart>: <bbpart>BBa_K1172201</bbpart> + <bbpart>BBa_J04500</bbpart>
- <bbpart>BBa_K1172205</bbpart>: <bbpart>BBa_K1172201</bbpart> + <bbpart>BBa_K608006</bbpart>

Figure 7: Agarosegel with GeneRuler™ 1 kb DNA Ladder from Thermo Scientific as marker. Bands are showing restriction analysis from suffix insertion of GldA (<bbpart>BBa_K1172201</bbpart>) into <bbpart>BBa_K525998</bbpart>, <bbpart>BBa_J04500</bbpart> and <bbpart>BBa_K608006</bbpart> with Standard Biobrick assembly Suffix Insertion modified from Silver lab. Bands are at the expected size. GldA BioBrick devices (<bbpart>BBa_K1172203</bbpart>, <bbpart>BBa_K1172204</bbpart>, <bbpart>BBa_K1172205</bbpart>) were examined.
- GldA BioBrick plasmid (<bbpart>BBa_K1172201</bbpart>) with different promotors and RBS were examined by restriction analysis with restriction enzymes EcoRI und XbaI for part <bbpart>BBa_K1172205</bbpart> and with restriction enzyme EcoRI for parts <bbpart>BBa_K1172203</bbpart> and <bbpart>BBa_K1172204</bbpart>. All bands are at the expected size.
Cytochromes
Biosafety
- We wanted to use Barnase (RNase Ba) from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens as a degradation part of our safety system. Because of this we first had to isolate the whole genome of it and get the Barnase out of it with special designed primer. We used different species because we didn't exactly know which species had the barnase in its genome. We isolated the genomes and measured the DNA concentration of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens
- DMS-1061: 20ng/µL (9-138-451)
- Wildtype H 10A1: 766,6 ng/µL (9-138-452)
- Wildtype R+M+ 10A3: 825,2 ng/µL (9-138-453)
- Wildtype DSMZ7: 25,8 ng/µL (9-138-454)
- We did restriktion analysis of the plasmids from 8.8.2013 to check if there is the correct insert is in the vectors. We used the restriction enzymes EcoR1 and Pst1 to cut the vector. The analysis did not show the right bands on the right higth apart from BBa_I13541.
- BBa_I13541, BBa_K914004 white colony, BBa_K914004 red colony, araC, alr
- Result: failed
- Further we did colony-PCR to check the insert. The gel also didn't show the right bands apart from BBa_I13541. We used 1 µL of a in 50µl resuspended colony suspension and the normal PCR protocol.:
- BBa_I15341, BBa_K194004 white, BBa_K194004 red, pSB1C3_alr, ptac_alr+insertprimern
- Result: failed
- BBa_I15341, BBa_K194004 white, BBa_K194004 red, pSB1C3_alr, ptac_alr+insertprimern
- We also did a restriction analysis our samples we guesed that there was the alanine racemase in it. We cut the vector also with EcoR1 and Pst1 but the gel didn't show the right bands by the right higth.:
- Alr 1,2,3,4
- Result: no bands as expected
Porines
- Adding the following parts with promoter and RBS to the OprF Biobrick <bbpart>BBa_K1172501</bbpart> by Standard Biobrick assembly Suffix Insertion modified from Silver lab: <bbpart>BBa_K525998</bbpart>, <bbpart>BBa_J04500</bbpart>, <bbpart>BBa_K608002</bbpart>, <bbpart>BBa_K608006</bbpart>, <bbpart>BBa_K608007</bbpart>.
- Promotor insertion was examined by restriction analysis and the following OprF Biobrick Devices with promotor and RBS could be added:
- <bbpart>BBa_K1172502</bbpart>: <bbpart>BBa_K1172501</bbpart> + <bbpart>BBa_K525998</bbpart>
- <bbpart>BBa_K1172503</bbpart>: <bbpart>BBa_K1172501</bbpart> + <bbpart>BBa_J04500</bbpart>
- <bbpart>BBa_K1172504</bbpart>: <bbpart>BBa_K1172501</bbpart> + <bbpart>BBa_K608007</bbpart>
- <bbpart>BBa_K1172505</bbpart>: <bbpart>BBa_K1172501</bbpart> + <bbpart>BBa_K608006</bbpart>
- <bbpart>BBa_K1172507</bbpart>: <bbpart>BBa_K1172501</bbpart> + <bbpart>BBa_K608002</bbpart>
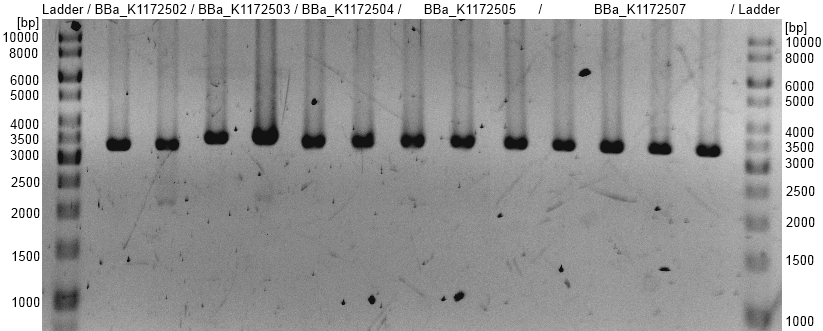
- OprF BioBrick plasmid (<bbpart>BBa_K1172501</bbpart>) with different promotors and RBS was examined by restriction analysis with restriction enzymes EcoRI. All bands are at the expected size and show a successful suffix insertion.
Week 17
Organization
- Our Team will participate at the conference ‘60 Years of DNA’ in Berlin at 14. September.
MFC
Mediators
- Glycerol dehydrogenase
- Escherichia coli KRX strain and modified E. coli KRX with pSB1C3 and <bbpart>BBa_K1172203</bbpart>, <bbpart>BBa_K1172204</bbpart> and <bbpart>BBa_K1172205</bbpart> was cultivated over night, with induction of gene expression for <bbpart>BBa_K1172203</bbpart> by 0,5 % Rhamnose and for <bbpart>BBa_K1172204</bbpart> by 0,7 mM IPTG. Ribolysation of over night culture for total cell disruption. After centrifugation 15 min at maximal speed supernatant was prepared for SDS-PAGE.
- SDS-PAGE shows protein Glycerol dehydrogenase at expected size of 40 kDa. In contrast to Escherichia coli KRX Wildtyp, weak Anderson promoter (<bbpart>BBa_K1172205</bbpart>) shows only a slightly stronger band, whereas T7 (<bbpart>BBa_K1172203</bbpart>) and Lac (<bbpart>BBa_K1172204</bbpart>) promotor show a strong band, which is equated with a strong expression and overproduction of GldA.

Figure 9: SDS-PAGE with Prestained Protein Ladder from Thermo Scientific as marker. Comparison of protein expression between Escherichia coli KRX wild type and Escherichia coli KRX with <bbpart>BBa_K1172205</bbpart>, <bbpart>BBa_K1172204</bbpart> and <bbpart>BBa_K1172203</bbpart> after total cell disruption. The right-hand gel was loaded with a higher protein concentration. SDS-PAGE shows protein Glycerol dehydrogenase at expected size of 40 kDa. Enhanced overproduction with increasing promotor strength.
- For showing an endogenous mediator production, the plan is to establish a fast NADH assay by direct using supernatant after cell disruption and testing specific NADH fluorescens with excitation at 340 nm and emission at 460 nm.
- First NADH assay test shows the need of a cell washing step, because of high background signals with LB-medium.
- Riboflavin
- We were able to profit from the experiences we had already gained while working on other cloning subprojects. So we started right away with designing specific pSB1C3-Gibson-primers. Every one of our four desired parts got an unique pSB1C3 with overlaps that were homologues to the ends of the insert. This way, we were able to shut down the “religation problem” (see Failbook).
- Gradient PCR´s with above Primers and pSB1C3 a template gave good results. Actually, they were that good, that we just cleaned up and pooled all nanotubes for further experiments.
- Meanwhile we started to isolate the genes responsible for riboflavin expression from the genome of shewanella oneidensis (link to genome isolation)
Cytochromes
Biosafety
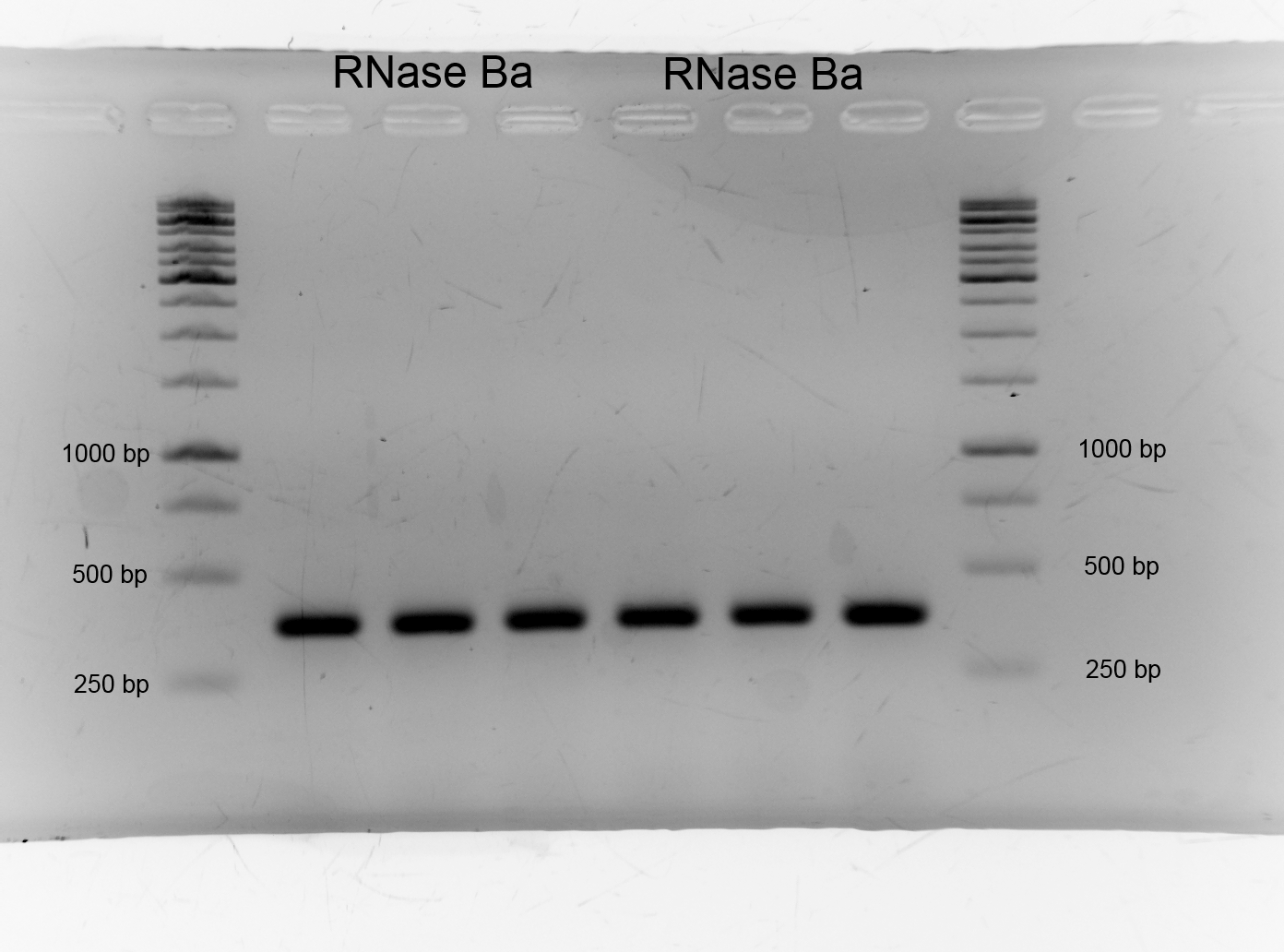
- After we isolated the genome of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens we had to get the Barnase. We picked the genome of DSMZ7. We amplificated DNase Ba via PCR and designed primer. We had success as the gel shows. The band lies on the higth of 350 bp as expected.:
- Size: 350bp
- After we successfully got the Barnase we had to do gel purification of the fragments. We did this as described in the protocols. After purification we measured the concentration of DNA via nanodrop.:
- RNase Ba fwdrevinsert 27,5ng/µL (9-238-451)
- RNase Ba presufVektor 67,3ng/µL (9-238-452)
- We have produced a knockout. This AraC-Deletion in K12 Δalr Δdadx causes that this K12 E.coli can't produce araC of itself and that it is dependent of the supplementation of D-alanine or the supplementation of a vector where araC is expressed. The reason for this knockout is that we want to raise plasmid stability of the strain. When the strain isn't able to produce araC then it dies.
- After checking if the AraC deletion was successfull we plated the colonies 1,5,7,8,14,15 out.
- We cultivated K12-WT and K12 Δalr Δdadx ΔaraC and produced electro competent cells as it is written in the standard protocol.
- We did Gibson-Assembly with alr, ptac und RNase Ba to clone it into the pSB1C3 shipping vector.
- After the Assembly we transformated the vectors in E.coli KRX electro competent cells via eletroporation for a plasmid isolation.
- We isolateed the plasmids of DNase Ba in pSB1C3. We did restriction analysis with EcoR1 and Pst1 to check if the correct insert is in the pSB1C3. But there were no expected bands.
- Restriction analysis:
- Result: no expected bands!
Porines
- Starting with characterization of Escherichia coli KRX with porin OprF (<bbpart>BBa_K1172501</bbpart> up to <bbpart>BBa_K1172507</bbpart>).
- Testing Hexadecan-Assay for characterization of hydrophobicity of the outer membrane. Using Escherichia coli KRX Wildtyp and comparing it with:
- <bbpart>BBa_K1172504</bbpart>: <bbpart>BBa_K1172501</bbpart> + <bbpart>BBa_K608007</bbpart>
- <bbpart>BBa_K1172505</bbpart>: <bbpart>BBa_K1172501</bbpart> + <bbpart>BBa_K608006</bbpart>
- <bbpart>BBa_K1172507</bbpart>: <bbpart>BBa_K1172501</bbpart> + <bbpart>BBa_K608002</bbpart>
- E. coli KRX with OprF plasmids and Anderson promoters show higher membrane hydrophobicity than Wildtyp. Hydrophobicity is about 37 up to 77 % higher in comparison to the KRX Wildtyp. Assay must be improved because of too high standard deviation.
- Membrane permeability was further tested with two uptake assays. ONPG and NPN uptake assay were performed. The values indicate a successful expression of OprF porin in the outer membrane. The permeability increases by introducing the plasmids with OprF.
- Protein isolation of outer membrane porin oprF by Release of periplasmic protein fraction from E. coli by cold osmotic shock for later SDS-PAGE. OprF could not been detected on the PAGE. It seems to be that only periplasmic proteins were isolated whereas outer membrane proteins werere not soluble in the supernatant.

Contents |
 "
"