Team:Evry/Protocols/Test
From 2013.igem.org
(Created page with "{{:Team:Evry/template_notebookbis}} <html> <div id="mainTextcontainer_notebook"> <!--*************************************** WEEK 1 *******************************************...")
Newer edit →
Revision as of 14:02, 1 October 2013
Protocols' overview

Solutions, Media and Petri Dishes
Antibiotics
Carbenicillin:
Put 150 mg of Carbenicilline in 15 mL of distilled water (10 mg per mL).
Filter with a 0,22 µm millipore,divide in 2 mL tubes and store at -4 °C.
Use 1 µL of Carbenicillin for 1 mL of solution.
Chloramphenicol:
Put 525 mg of Kanamycin in 15 mL of ethanol (35 mg per mL).
Filter with a 0,22 µm millipore,divide in 2 mL tubes and store at -4 °C.
Use 25 µL of Chloramphenicol for 1 mL of solution.
Kanamycin:
Put 750 mg of Kanamycin in 15 mL of distilled water (50 mg per mL).
Filter with a 0,22 µm millipore,divide in 2 mL tubes and store at -4 °C.
Use 1 µL of Kanamycin for 1 mL of solution.
Spectinomycin:
Put mg of Spectinomycin in 15 mL of ( mg per mL).
Filter with a 0,22 µm millipore,divide in 2 mL tubes and store at °C.
Use µL of Spectinomycin for 1 mL of solution.
Thoses antibiotics are used to select bacteria with a plasmid including an interest construction and the corresponding antibiotic resistance gene.
LB and LB Agar
Mix 20 g of LB Broth in 1L of distilled water in a bottle of 1L, then put in autoclave.
Mix 17,5 g of LB Agar in 500 mL of distilled water in a bottle of 1L, then put in autoclave.
M9 Medium
Composition for 50 mL of:
| Reagent | M9 medium (without iron) | M9 medium (with iron) |
|---|---|---|
| M9 salt (5X) | 10 mL | |
| CaCl2 (1M) | 5 µL | |
| MgSO4 (1M) | 100 µL | |
| Glycerol (50%) | 800 µL | |
| Thiamine | 5 µL | |
| NaOH (pH 7.4) | 12.5 µL | |
| H2O | 40 mL | 39 mL |
| FeSO4 (10mM) | - | 50 µL |
| Casamino acids (0.2%) | - | 1 mL |
Once the mixture is prepared, the medium must be filtered to be sterilised using 0.22 µm filter.
Petri dish
Melt the LB Agar in a microwave, and split it in 50 mL tubes.
When the tubes have cooled, put the necessary amount of antibiotics in it (50 µL for Carbenicillin and Kanamycin, 1250 µL for Chloramphenicol) and mix thoroughly.
Put 25 mL of the solution in a Petri dish.
CaCl2 and CaCl2+glycerol
Solution for 1M Cacl2:
Add 14,30g of CaCl2 into 100 ml desalted water
Solution for 0,1M Cacl2:
Add 50 mL of CaCl2 1M solution into 450 ml of desalted water
Solution for 0,1M Cacl2 + 15% glycerol:
Add 50 mL of CaCl2 1M solution and 75 mL of glycerol 100% into 450 ml of desalted water
Tris-Acetate-EDTA (TAE) Buffer solutions
NaOH solution 5M 100 mL:
Add 19,99 g of NaOH in 100 mL of distilled water.
EthyleneDiamineTetraacetic Acid (EDTA) solution 0,5M 300 mL:
Add 43,8 g of EDTA in 250 mL of distilled water.
Add NaOH 5M until EDTA is solubilized and pH~8.
Add distilled water until you reach 300 mL.
TAE Stock solution 50X 300 mL:
Add 60,5 g of TAE in 187,5 mL of distilled water.
Add 14,27 mL of acetate solution (previously put at 4°C).
Add 25 mL of EDTA solution previously prepared.
Add distilled water until you reach 250 mL.
TAE solution 1X 100 mL:
Add 5 mL of TAE Stock solution 50X in 100 mL of distilled water.
Tris HCl
Disolve 4,6g of Trisbase in 30 mL of distilled water.
Adjust pH with concentrated HCl(~4 mL) until pH=7,5.
Add distilled water until 50 mL then put in autoclave.
If the solution has a yellow coloration, do the preparation again with better Trisbase.
Tris HCl is used to store DNA.
DNA genomic extraction
Goal
The aim of the extraction step is to recover Escherichia coli genomic DNA.
The different step are use to throw other bacterial components off (proteins, cell wall, plasmids,etc).
Once we have E.coli genomic DNA
Preparation
Protocol adapted from Thermo Scientific Genomic extraction notebook1. Cell culture
Cultivate cells in LB medium overnight.
2. Cell harvesting
Set saturated E.coli LM culture into 2 mL tubes. Centrifuge at 8 000 x g for 5 minutes. Discard as much as supernatant as possible.
3. Cell lysis
Add 180 μL of Digestion Solution and 20 μL of Proteinase K Solution. Resuspend the cells thoroughly with a vortex or a pipette.
Incubate the tubes at 56°C while vortexing occassionally until the cells are completely lysed(~30 minutes).
Add 20 μL of RNase A solution, mix by vortexing and incubate the tubes for 10 minutes at room temperature.
Add 200 μL of Lysis Solution to the sample. Mix thoroughly by vortexing until a homogeneous mixture is obtained. (~15 secondes)
Add 400 μL of 50% ethanol and mix with a vortex or a pipette.
4. DNA Binding
Transfer the lysate to a GeneJET Genomic DNA Purification Column inserted in a collection tube. Centrifuge the column at 12 000 x g for 1 minute.
Discard the collection tube containing flow-through solution and place the column into a new 2 mL tube.
5. Membrane washing
Add 500 μL of Wash Buffer I (previously added with ethanol). Centrifuge at 1 600 x g. Discard the flow-through and place the purification column back into the collection tube.
Add 500 μL of Wash Buffer II (previously added with ethanol)to the purification column.
6. Dry membrane
Centrifuge at 16 000 x g for 3 minutes.
7. DNA Elution
Add 200 μL of Elution Buffer to the center of the purification column membrane to elute genomic DNA. Incubate for 2 minutes at room temperature and centrifuge at 8 000 x g for 1 minute.
Discard the purification column and store the purified DNA in TrisHCl at -20°C or use it immediatly.
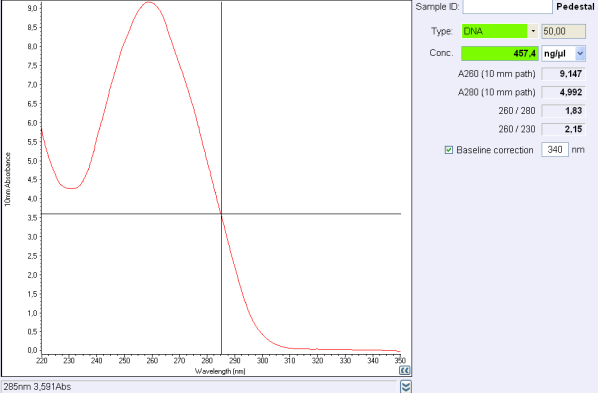
Test
260/280 ratio and 260/230 indicate the purity of DNA (or RNA).Nucleic acids absorb at 260 nm while proteins and phenols absorb at 280 nm and carbohydrates at 230 and other contaminents at 230 nm.
For DNA, a 260/280 ratio around 1,8 is concider to be pure and ange 260/230 ratio must be between 2,0 and 2,2.
Polymerase Chain Reaction
Principle
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is a molecular biology method used to amplify a small amount of genetic material (DNA or RNA), using specific primers of a target sequence.
PCR is divided into 5 steps:
- First denaturation:
- Denaturation step
- Annealing step
- Elongation step
- Final step
Denaturation step occure between 94 and 98°C.The heat breaks the hydrogen bonds and then causes the separation of the double strand of DNA into two single strands.
Annealing step occure between 50 and 65 °C. Primers anneals to DNA simple strand by complementarity of the nitrogenized bases.
Elongation step occure between 70 and 80°C, depending on the DNA polymerase used. The polymerase synthesizes a new DNA strand complementary to the DNA template
Preparation
Mixture preparation
We use two differents polymerase for our PCR: Taq Polymerase and Q5.
As Q5 is a hight fidelity polymerase, we use it to obtain sequences without mutation (for a total of 50 μL of mixture); otherwise we use Taq Polymerase instead (for a total of 25 μL of mixture).
Afterwards, we will describe the protocol for a PCR with Q5 (total amount: 50 μL).
Note: Proportion are the same with Taq Polymerase, for 25 μL or 50 μL: 1:10 of each primer, 1:5 of Buffer, 1:50 of dNTPs, 1:50 of genomic DNA and 1:100 of polymerase
Make tubes with 5 μL (1:10) of Forward primer and 5 μL (1:10) of Reverse primer for each desidered sequence.
For positive and negative controle, use primers that worked previously in the same condition of PCR.
We use primers (Primers 009 and 010) for pEntC for ou controles.
For more details about our primers, see the corresponding page.
For n tubes, prepare a master mix with the following solutions:
- (n+1) x 10 μL of Q5 Buffer
- (n+1) x 1 μL of dNTPs
- (n+1) x 27,5 μL of distilled water.
- (n+1) x 0,5 μL of Q5
Note: Take the enzyme out of -20°C just before utilisation.
Split 39 μL of the master mix in each tube.
Add 1 μL of genomic DNA in each tube, except in your negative controle tube. In this one, put 1 μL of distilled water instead.
PCR Cycles
Set the following program on your Thermo Cycler:
- First denaturation: 30 seconds at 98°C
- Denaturation step 10 seconds at 98°C
- Annealing step 20 seconds at 56°C
- Elongation step (n+1) minutes at 72°C (as n is the number of kB of your sequence)
- Final step 5 minutes at 72°C
Steps 2, 3 and 4 are repeated 29 times.
Then let the mixture cool down at 4°C.
Note: Annealing temperature depend on your primers and elongation temperature on the polymerase used.
Optimisation
Number of primer
Temperature
Golden Gate Assembly
Goal
The aim of Golden Gate assembly is to assemble in one step various fragment of DNA.Preparation
Tests
Mettre une ou deux photos de transfos réussies/foirées
 "
"