Team:ZJU-China/Notebook/Protocal
From 2013.igem.org
Protocol
Contents |
Circular Polymerase Extension Cloning (CPEC)
Cloning method for assembling PCR fragments together. Primers are designed to include overlap sequence between fragments. It is important that the Tm of overlap sequence is around 60~65C, and the length of primers is of second concern.
PCR each fragment to introduce overlap sequence using high-fidelity DNA polymerase. This will prevent the addition of A to the end of the products.
1. PCR each fragment to introduce overlap sequence using high-fidelity DNA polymerase. This will prevent the addition of A to the end of the products.
2. PCR backbone with appropriate primers using high-fidelity DNA polymerase.
3. Gel purify each fragment and backbone.
4. Set up the CPEC reaction as follows:
CPEC protocol is:
5. Before running CPEC protocol, save 10 uL on ice as a control. After CPEC is done, run 10 microliters of the CPEC reaction with the control in the next lane. I find this control is always more important than DNA markers to tell the CPEC is successful or not.
6. Check that you can see your assembled reaction on the gel, or that your inserts are less visible than the control (they assembled). If so, then transform 10 microliters into regular competent cells.
Polymerase cycling assembly (PCA)
Also known as assembly PCR or fusion PCR.
1. Primers should be designed to introduce overlap sequence into each fragments. It is important to have a relatively high Tm around 60C.
2. PCR each fragment to introduce overlap sequence using high-fidelity DNA polymerase. This will prevent the addition of A to the end of the products.
3. Gel purify each fragment.
4. Add equal molar of fragments to a 20µL reaction system. The amount should typically not less than 50ng. It is recommended to use ultra-high fidelity DNA polymerase such as Phusion (NEB) or Q5 (NEB). Run the PCR with annealing temperature of 55C for 10 cycles.
5. Move 5 µL products into a new tube. Set a new 50µL PCR reaction with appropriate nested primers. It is better to use a different set of primers that are used to introduce overlap sequence.
6. Gel check and purify the fused product.
Protein biotinylation
1. Calculate millimoles of biotin reagent to add to the reaction for a 20-fold molar excess:
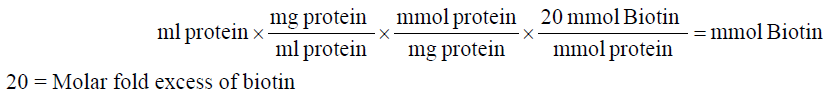
2. Calculate microliters of 10 mM biotin reagent solution to add to the reaction:
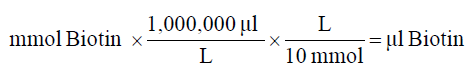
3. Prepare protein in PBS according to the calculation made in step 1.
4. Add the appropriate volume (see Calculations in step 2) of 10mM biotin reagent solution to the protein solution
5. Incubate reaction on ice for two hours or at room temperature for 30 minutes.
Cell transformation:
1 Remove competent cells on ice to thaw.
2 Add 1-10 μl of DNA to the cells.
3 Incubate on ice for 20 min.
4 Spread onto LB + antibiotic agar plate. Incubate overnight at 37℃.
Growth Curve
1 Set up cells culture in ~2mL LB + antibiotic.
2 Grow at 37℃, 250 rpm overnight.
3 Dilute in LB + antibiotic so that final OD600 is ~0.05 for each culture.
4 Take OD600 of freshly dilute cultures. Another dilution may be necessary.
5 Grow at 37℃, 250 rpm.
6 Take OD600 at 30mins.
7 Once OD600 has reached ~0.1, begin taking ODs every 20mins.
8 When OD600 =0.2, split cultures in half and induce half with 2mM IPTG.
9 Once an OD 1.0 is reached dilute the culture 1:1 with media to take an accurate OD. Then multiply the OD value by the dilution factor.
 "
"








