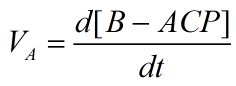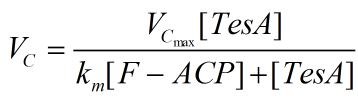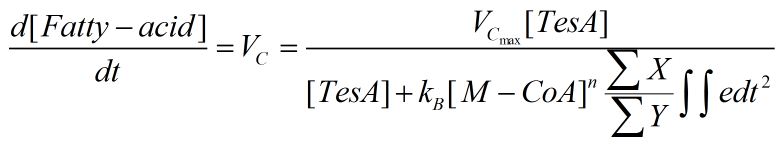|
|
Metabolismt Optimization
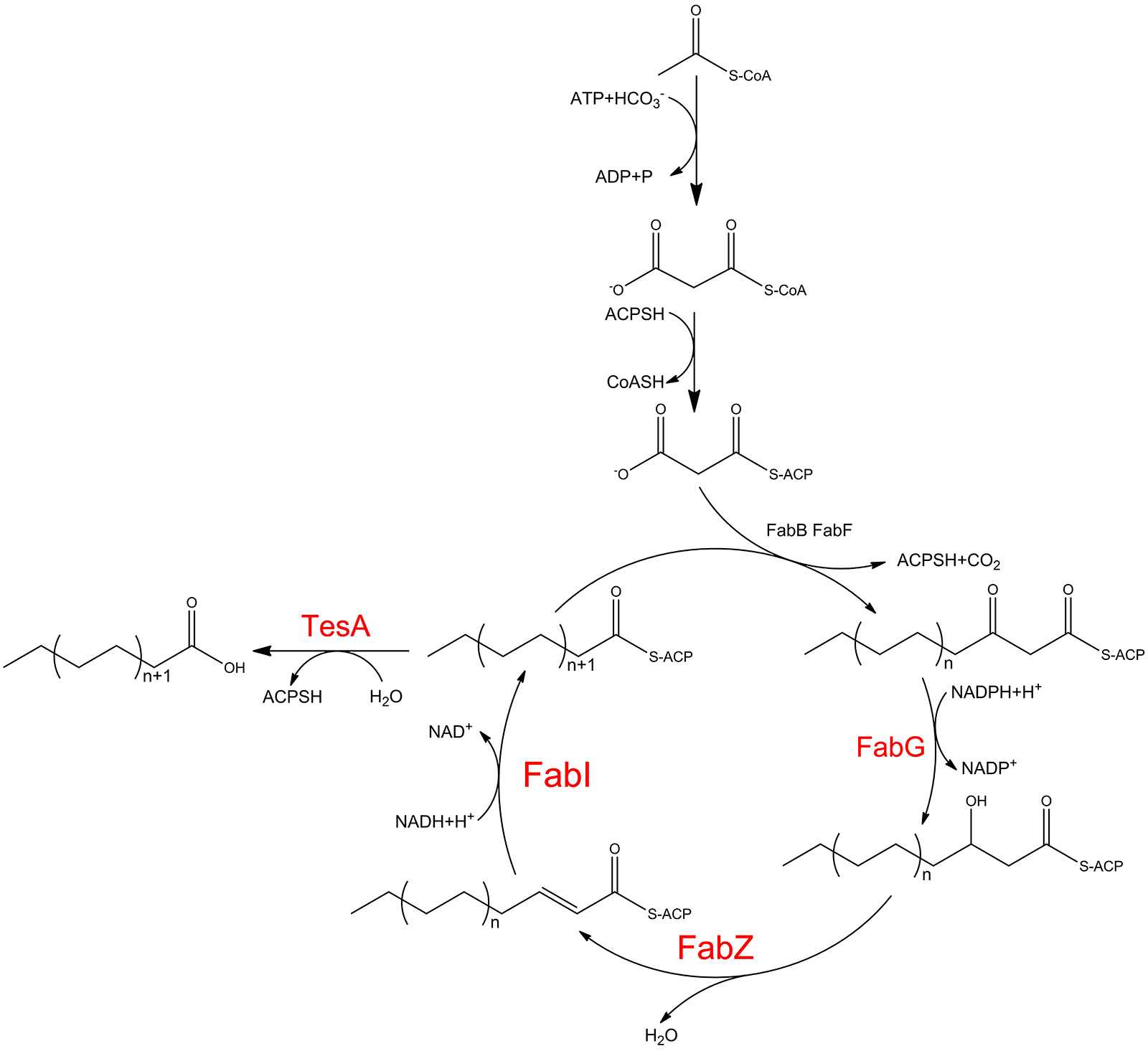
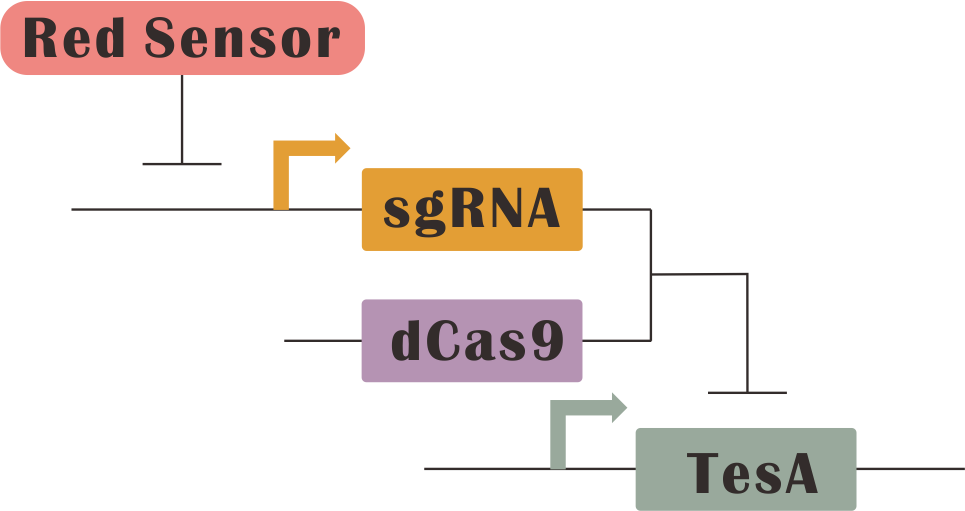
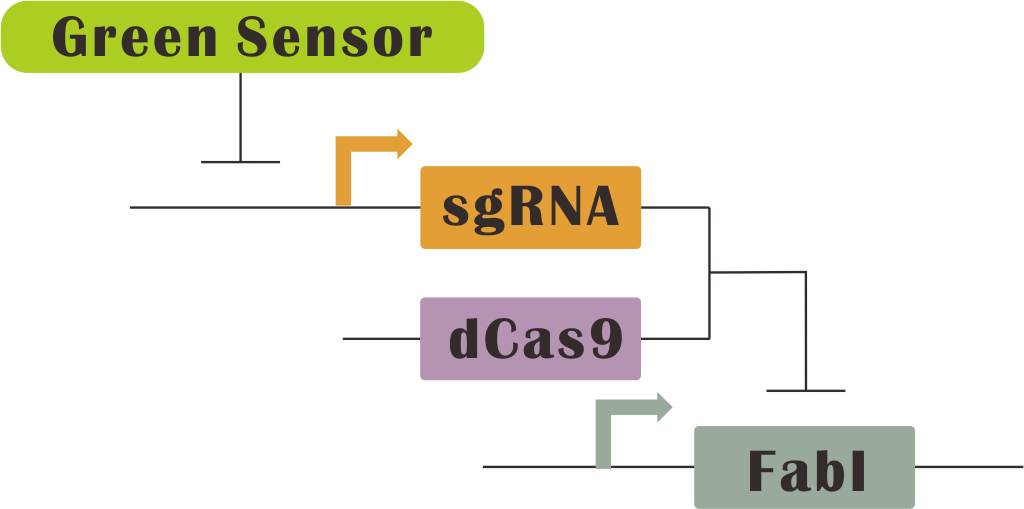
We plan to choose the Fatty acid metabolic pathway for our system's application. We combine three key enzymes in Fatty acid metabolic pathway with our light controlled system. They are TesA, FabI and FabZ which affect three very pivotal reaction process. We expect that we can regulate the proportion of three enzymes by three different light-dCas9 systems to control the productive rate of fatty acid. We use the modeling tools to simulate the regulate process to verification our plan.
Circuit
Three main circuit are as follows:
Main Reaction
We call three main reactions which we controlled reaction A, B and C.

Models and Explains
In order to make the explaination of our model short and sweet, we simplify three main reactions as follows:
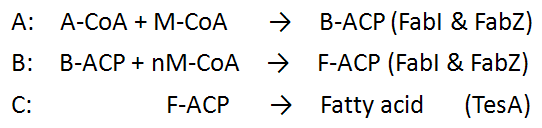
Reaction A
For reaction A, it is a double substrates enzymatic reaction, consideration of substrate self-inhibition, we set this reaction model:
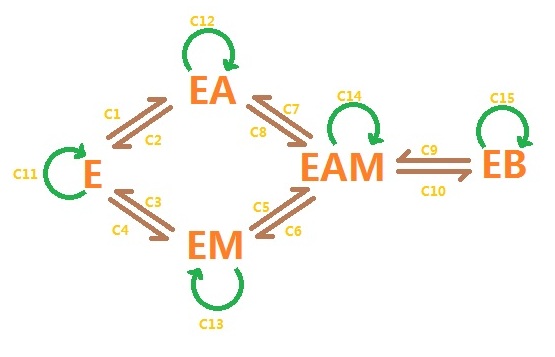
In the picture, EA means the complex of enzyme and A-CoA, EM means the complex of enzyme and M-CoA, EAM means the complex of enzyme and two substrates, EB means the complex of enzyme and B-ACP.
c1-c15 means different reaction rate of combination.
Due to the King-Altman algorithm, we can handle the reaction as follows:

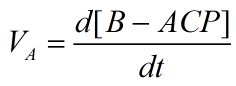
a means the concentration of A-CoA, b means the concentration if M-CoA, e means the concentration of enzyme (FabI & FabZ), z means the concentration of B-ACP.
Reaction B
For reaction B we set two equations to describe it:

Reaction C
This is a typical single substrate single enzymatic reaction, we handle it with a Michaelis-Mentenequation.
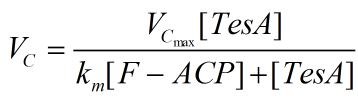
Simultaneous
By simultaneous differential equations we can get a short and sweet conclusion:
for convenience, we sign

We can find the algebra relationship between the concentration of TesA and e (including FabI & FabZ) in the regulation process of fatty acid metabolism in such a single equation.
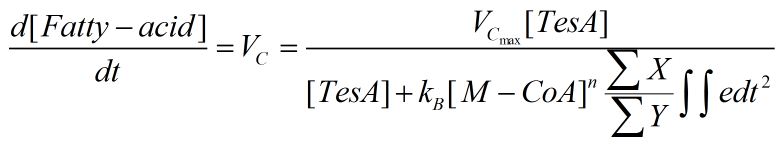
Thus we can know the best proportion of three enzymes for the fatty acid metabolism optimization if we can get the mentioned reaction constant.
|
 "
"