Team:ETH Zurich/Processing 2
From 2013.igem.org
| (8 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
<h1> Creation of a promoter library </h1> | <h1> Creation of a promoter library </h1> | ||
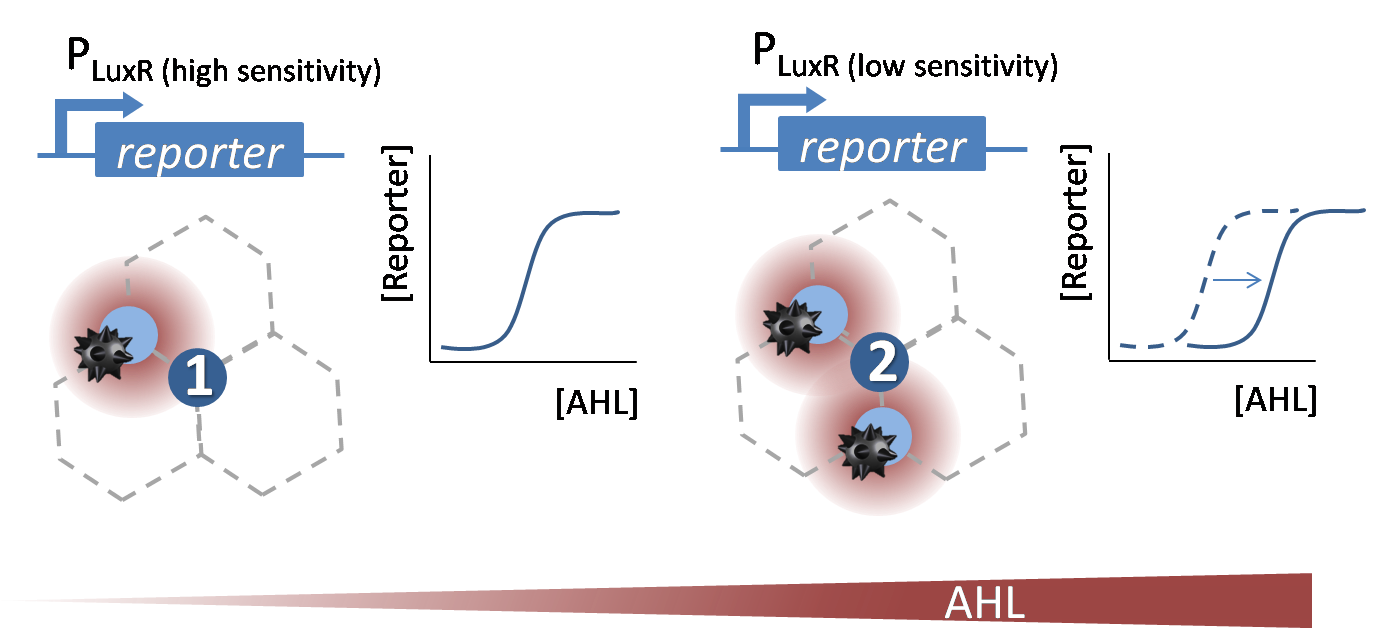
| - | [[File:Why_infoproc.png|600px|left|thumb|<b>Figure 1. Theoretical | + | [[File:Why_infoproc.png|600px|left|thumb|<b>Figure 1. Theoretical sensitivity shift of the P<sub>LuxR</sub> promoter to sense and distinguish different AHL concentrations.</b>]] |
| - | The wild-type P<sub>LuxR</sub> promoter ([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_R0062 BBa_R0062]) gets activated in presence of AHL. In our project we need different sensitive promoters to distinguish between different levels of the AHL concentrations according to the different number of surrounding mines. | + | The wild-type P<sub>LuxR</sub> promoter ([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_R0062 BBa_R0062]) in the Plac-LuxR-pLuxR [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_J09855 BBa_J09855] construct gets activated in presence of AHL. In our project we need <b>different sensitive promoters</b> to distinguish between different levels of the AHL concentrations according to the different number of surrounding mines. Therefore we need to <b>shift the dose-response curve</b> of the initial [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_R0062 BBa_R0062] promoter. We decided to do <b>site directed saturation mutagenesis</b> (see below) to achieve a sensitivity shift and create a <b>promoter library</b>. For more details please see the experimental results page of [https://2013.igem.org/Team:ETH_Zurich/Experiments_5 processing]. |
<br clear="all"/> | <br clear="all"/> | ||
<html><a id="high-pass-filter_mutagenesis" class="frog"></a></html> | <html><a id="high-pass-filter_mutagenesis" class="frog"></a></html> | ||
| - | <h1>Site directed saturation mutagenesis PCR of the BBa_R0062 | + | <h1>Site directed saturation mutagenesis PCR of the BBa_R0062 P<sub>LuxR</sub></h1> |
| - | [[File:promotermutations1.png|left|750px|thumb|<b>Figure 2: Promoter mutation sites</b> The wild type promoter from the biobrick | + | [[File:promotermutations1.png|left|750px|thumb|<b>Figure 2: Promoter mutation sites</b> The wild type promoter from the biobrick [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_R0062 BBa_R0062] was mutated using site directed saturation mutagenesis. The library shows the targeted sites for site directed saturation mutagenesis. The sequences for the library, the [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_R0062 BBa_R0062], the [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1216007 BBa_K1216007] and the wild type luxR promoter from literature [https://2013.igem.org/Team:ETH_Zurich/References#Antunes2007 Antunes ''et. al.'', 2007.] are given.]] |
| - | <p align="justify">The [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_R0062 BBa_R0062] promoter contains a binding site for a LuxR-AHL complex as well as | + | <p align="justify">The [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_R0062 BBa_R0062] promoter contains a binding site for a LuxR-AHL complex as well as an RNA polymerase binding site. Our system needs different sensitive promoters to detect different concentrations of AHL according to the number of surrounding mines. Therefor we need to engineer this promoter in order to shift the dose response curve (which we first had to characterize). Finally after some research we decided to do site directed saturation mutagenesis in the <b>palindromic LuxR binding sites</b> of the <i>luxbox</i> according to the results taken from literature [https://2013.igem.org/Team:ETH_Zurich/References#Antunes2007 Antunes ''et. al.'', 2007.] (see Figure 2).<br><br>About the <b>promoter library</b>:<br> |
| - | First of all we isolated the mutated P<sub> | + | First of all we isolated the mutated P<sub>LuxR</sub> [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1216007 BBa_K1216007] which shows an important shift. We than back-mutated this mutant using oligomers and finally isolated 7 new additional promoters. (We did not have time to submit them to the registry). Please see the [https://2013.igem.org/Team:ETH_Zurich/Experiments_5 results page] to see our library</p> |
<br clear="all"/> | <br clear="all"/> | ||
{{:Team:ETH_Zurich/templates/footer}} | {{:Team:ETH_Zurich/templates/footer}} | ||
Latest revision as of 02:04, 29 October 2013
Creation of a promoter library
The wild-type PLuxR promoter ([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_R0062 BBa_R0062]) in the Plac-LuxR-pLuxR [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_J09855 BBa_J09855] construct gets activated in presence of AHL. In our project we need different sensitive promoters to distinguish between different levels of the AHL concentrations according to the different number of surrounding mines. Therefore we need to shift the dose-response curve of the initial [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_R0062 BBa_R0062] promoter. We decided to do site directed saturation mutagenesis (see below) to achieve a sensitivity shift and create a promoter library. For more details please see the experimental results page of processing.
Site directed saturation mutagenesis PCR of the BBa_R0062 PLuxR

The [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_R0062 BBa_R0062] promoter contains a binding site for a LuxR-AHL complex as well as an RNA polymerase binding site. Our system needs different sensitive promoters to detect different concentrations of AHL according to the number of surrounding mines. Therefor we need to engineer this promoter in order to shift the dose response curve (which we first had to characterize). Finally after some research we decided to do site directed saturation mutagenesis in the palindromic LuxR binding sites of the luxbox according to the results taken from literature Antunes et. al., 2007. (see Figure 2).
About the promoter library:
First of all we isolated the mutated PLuxR [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1216007 BBa_K1216007] which shows an important shift. We than back-mutated this mutant using oligomers and finally isolated 7 new additional promoters. (We did not have time to submit them to the registry). Please see the results page to see our library
 "
"