Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Project/Riboflavine
From 2013.igem.org
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
<html> | <html> | ||
| - | <h1> | + | <h1>Riboflavin</h1> |
<div id="buttonrow" style="padding-top:30px; padding-bottom:70px; padding-left:45px; clear:both;"> | <div id="buttonrow" style="padding-top:30px; padding-bottom:70px; padding-left:45px; clear:both;"> | ||
Revision as of 09:45, 30 September 2013
Riboflavin
Overview
Of great interest is the production of endogenous mediators. The overexpression of glyceroldehydrogenase in E. coli is a promising approach. Because many derivates of glyceroldehydrogenase are small, water-soluble redoxmolecules, they have the properties of a mediator. Futhermore, it will be tested, if there is a possibility of expressing the mediator phenazin. Phenazin is an endogenous mediator of Pseudomonas species.
Theory
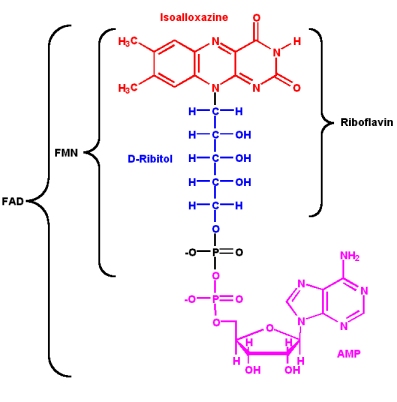
Since its discovery in 1879 and its first structural characterisation in 1930th (in the 1930’s/in 1930), a lot of properties of riboflavin were elucidated. This substance is a precursor of FMN (flavin mononucleotide) and FAD (flavin adenine dinucleotide), which play an essential role as cofactors in many oxidative processes.
The modern name Riboflavin, also named Lactoflavin, is composed of two parts: «ribo» indicating the presence of the sugar alcohol ribitol, and «flavin» meaning «yellow»; to accentuate the yellow coloring of the oxidized molecule. Chemically this substance consists of two functional subunits, an already mentioned short-chain ribitol and a tricyclic heterosubstituted isoalloxazine ring.
The latter, also known as a riboflavin ring, exists in three redox states and is responsible for the diverse chemical activity of riboflavin. A fully oxidized quinone, a one-electron semiquinone and a fully reduced hydroquinone states are the three stages of riboflavin oxidation. In an aqueous solution, the quinone (fully oxidized) form of riboflavin has a typical yellow coloring. It becomes red in a semi-reduced anionic or blue in a neutral form and is colorless when fully reduced.
All these forms are present in different proportions in a living cell, making previous oxidation a necessary step if riboflavin analysis is to be conducted. Flavins have a typical yellow-green fluorescence in the UV light. The peaks of absorbance occur at 223, 266, 373 and 445 nm. The maximum fluorescence emission of the neutral solution is at 535 nm [Charles A. Abbas et al.,[http://mmbr.asm.org/content/75/2/321.full#ref-292| 2011]]. These fluorimetric properties are widely used in the analysis of riboflavin.
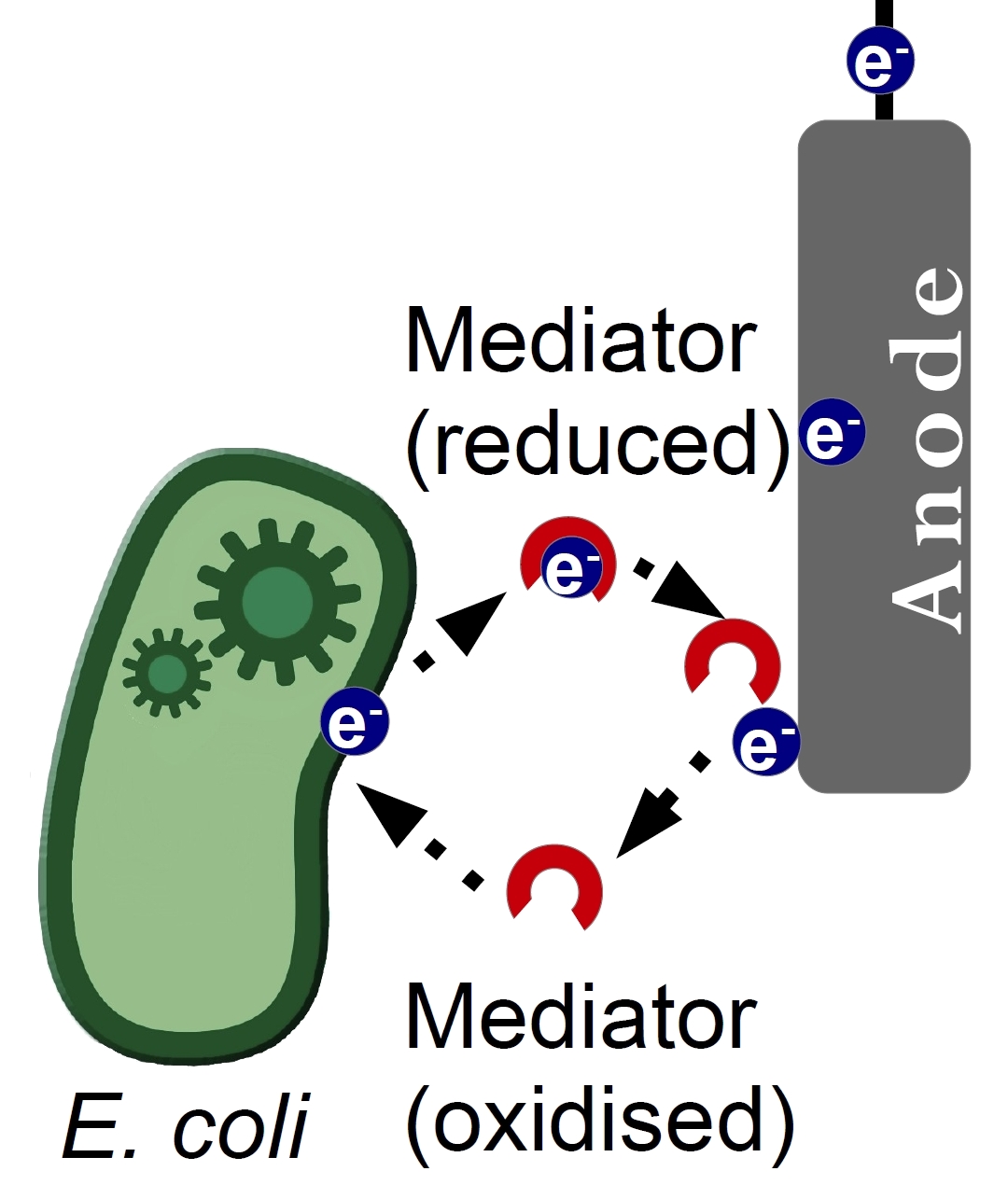
Due to its structure, which allows a transfer of two electrons from hydrogen and hydrid ions, riboflavin can be imagined as a potential electron shuttle. It was previously known, that the electron transfer from the outer membrane-associated proteins to an inorganic electron acceptor is the main limiting growth factor for Fe(III)-reducing prokaryotes, so a few mechanisms were discovered, which showed how this process can be enhanced. One of them was a secretion of water-soluble redox mediators. It was proven, that secretion of riboflavin and FMN enhances the rate of insoluble mineral oxides reduction. Indeed, Shewanella Oneidensis, a facultative Fe-III respiring bacterium uses secreted riboflavin as its electron transmitter [Harald von Canstein et al.,[http://aem.asm.org/content/74/3/615.full| 2008]]. Considering this acknowledgement, we decided to overproduce riboflavin in E.Coli to improve its efficiency in our MFC.
First of all, we have searched for a suitable microorganism, which has an active riboflavin cluster with known coding sequences. We have already used the remarkable versatility of Shewanella in order to clone the anaerobic respiratory chain (mtrCAB cluster), so now we were able to skip some initial steps, like the whole genome DNA isolation and advanced rapidly to more specific steps.
Before planning the cloning strategy, we checked [http://parts.igem.org/Main_Page| the Parts registry] for any parts we could use or enhance. A [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K769203| ribC part] was listed, but it was neither submitted nor available.
We also had a close look on the [http://www.chem.qmul.ac.uk/iubmb/enzyme/reaction/misc/riboflavin2.html|riboflavin biosynthesis pathway]. This process is well studied and a lot of appropriate literature is available. There are three types of riboflavin overproducers used in industry: yeast (Candida famate), fungi (Ashbya gossypii), and bacteria (Bacillus subtilis) [Overview, Seong Han Lim et al., [http://www.bbe.or.kr/storage/journal/BBE/6_2/6657/articlefile/article.pdf| 2001]], but a prevailing majority of microorganisms also synthesise riboflavins in low concentrations. In E.Coli, for instance, genes are scattered through the whole genome and riboflavin is produced constitutively.
The biosynthesis of riboflavin starts with ribulose-5-phosphate and GTP, converted to formate and DHBP (L-3,4-dihydroxybutan-2-one 4-phosphate). The final stage involves forming of the third isoalloxazine ring by an exchange of a 4-carbon part, catalysed by riboflavin synthetase (EC 2.5.1.9). We assumed, that the operon in Shewanella could be similar to a well-studied [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8159171| rib-operon] of Bacillus Subtilis. The operon is transcribed as a one polycistronic RNA, making a single promoter sufficient. Introduction of multiple copies of a ribA gene (coding for GTP cyclohydrolase II (EC 3.5.4.25)), comprised in the rib-operon, results in riboflavin overproduction in B.Subtilis [Hohmann H.P.,Stahmann K.P. 2010. Biotechnology of riboflavin production, p. 115–139.], so we predicted a notable riboflavin synthesis gain following a successful introduction of a multiple-copy plasmid harbouring the rib-operon under an active promoter.
Genetic Approach
Below we shortly describe each functional member of this cluster.
- Gene: RibD Sequence
- Protein: bifunctional diaminohydroxyphosphoribosylaminopyrimidine deaminase/5-amino-6-(5-phosphoribosylamino) uracil reductase RibD
- Enzyme: (EC: 3.5.4.26)
- Molecular weight: 41,257 Da
- Gene: SO_3468 Sequence
- Protein: Riboflavin synthase alpha subunit RibC-like protein
- Enzyme: EC 2.5.1.9
- Molecular weight: 23,483 Da
- Gene: RibBA → ribA & ribB Sequence
- ribA
- Protein: GTP cyclohydrolase-2
- Enzyme: EC 3.5.4.25
- Molekular weight: 22,852 Da
- ribB
- Protein: 3,4-dihydroxy-2-butanone-4-phosphate synthase
- Enzyme: EC 3.5.4.25
- Molecular weight: 22,956 Da
- Gene: ribE Sequence
- Protein: 6,7-dimethyl-8-ribityllumazine synthase
- Enzyme: EC 2.5.1.78
- Molecular Weight: 16,689 Da
Results
References
 "
"