Team:ETH Zurich/Experiments 3
From 2013.igem.org
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
<h1>Enzyme-substrate reactions</h1> | <h1>Enzyme-substrate reactions</h1> | ||
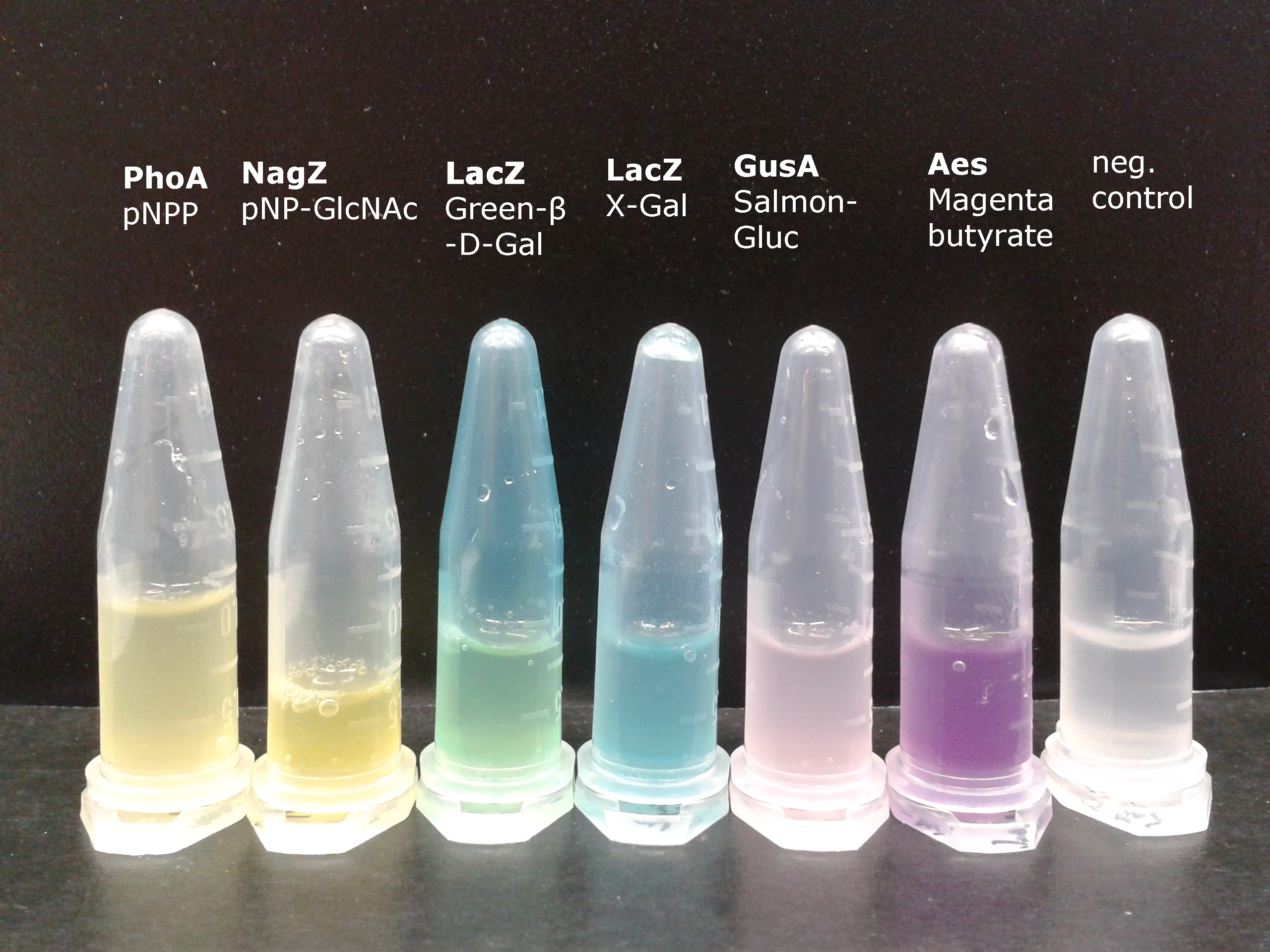
| - | [[File:2013-09-16 09.30 (1).png|450px|right|thumb|<b>Figure 1: Colorimetric output</b> This image shows liquid cultures of our mutant ''Escherichia coli'' strain expressing the enzymes PhoA, NagZ, LacZ, GusA or Aes to convert specific chromogenic substrates into the color outputs needed for our project. There is a possibility to create more colors, since our hydrolases have a large spectrum of substrates to convert to give different colorimetric outputs. As an example of multi-substrate conversion, there is the LacZ which can convert X-Gal into a blue output and Green-β-D-Gal into a green output.]] | + | [[File:2013-09-16 09.30 (1).png|450px|right|thumb|<b>Figure 1: Colorimetric output.</b> This image shows liquid cultures of our mutant ''Escherichia coli'' strain expressing the enzymes PhoA, NagZ, LacZ, GusA or Aes to convert specific chromogenic substrates into the color outputs needed for our project. There is a possibility to create more colors, since our hydrolases have a large spectrum of substrates to convert to give different colorimetric outputs. As an example of multi-substrate conversion, there is the LacZ which can convert X-Gal into a blue output and Green-β-D-Gal into a green output.]] |
<p align="justify">To generate visible output by adding substrates to colonies in Colisweeper, we made use of orthogonal enzyme-substrate reactions. A set of chromogenic substrates was chosen to produce different colors depending on the abundant hydrolases and thereby to uncover the identity of each colony to the player.<br> | <p align="justify">To generate visible output by adding substrates to colonies in Colisweeper, we made use of orthogonal enzyme-substrate reactions. A set of chromogenic substrates was chosen to produce different colors depending on the abundant hydrolases and thereby to uncover the identity of each colony to the player.<br> | ||
Chromogenic substrates incorporate a chromophore whose absorbance properties change after the enzyme reaction, and the color signal produced then is directly related to the enzyme-catalyzed reaction.<br> | Chromogenic substrates incorporate a chromophore whose absorbance properties change after the enzyme reaction, and the color signal produced then is directly related to the enzyme-catalyzed reaction.<br> | ||
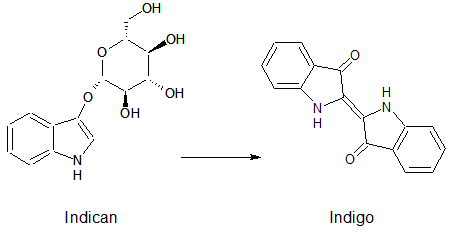
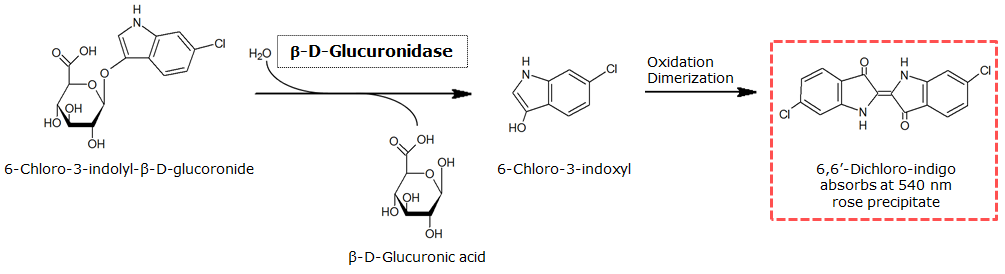
Indican is a chromogenic glycoside hydrolase substrate which belongs to a family of natural glycosides found in plants. Cleavage of the glycosidic bond forms an unstable hydroxyindole intermediate, which dimerizes by oxidation to form indigo as a blue precipitate:</p> | Indican is a chromogenic glycoside hydrolase substrate which belongs to a family of natural glycosides found in plants. Cleavage of the glycosidic bond forms an unstable hydroxyindole intermediate, which dimerizes by oxidation to form indigo as a blue precipitate:</p> | ||
| - | [[File:IndicanIndigo.png|250px|center|]] | + | [[File:IndicanIndigo.png|250px|center|]]<br> |
<p align="justify">Numerous enzyme substrates have been designed following this natural product example, giving rise to many colored phenols that are used to detect enzyme activities.<br><br> | <p align="justify">Numerous enzyme substrates have been designed following this natural product example, giving rise to many colored phenols that are used to detect enzyme activities.<br><br> | ||
As shown in Figure 1, some of the hydrolases used in the Colisweeper reporter system can catalyze hydrolysis of various substrates, with different chromophores that give rise to a wide range of colors. This variety of substrates and color outputs enables change of positions and function of these enzymes. Other possible substrates that can be used for the enzymes of this system can be seen in the [https://2013.igem.org/Team:ETH_Zurich/Experiments_7 Hydrolases] section. | As shown in Figure 1, some of the hydrolases used in the Colisweeper reporter system can catalyze hydrolysis of various substrates, with different chromophores that give rise to a wide range of colors. This variety of substrates and color outputs enables change of positions and function of these enzymes. Other possible substrates that can be used for the enzymes of this system can be seen in the [https://2013.igem.org/Team:ETH_Zurich/Experiments_7 Hydrolases] section. | ||
Revision as of 19:53, 4 October 2013
Contents |
Enzyme-substrate reactions

To generate visible output by adding substrates to colonies in Colisweeper, we made use of orthogonal enzyme-substrate reactions. A set of chromogenic substrates was chosen to produce different colors depending on the abundant hydrolases and thereby to uncover the identity of each colony to the player.
Chromogenic substrates incorporate a chromophore whose absorbance properties change after the enzyme reaction, and the color signal produced then is directly related to the enzyme-catalyzed reaction.
Indican is a chromogenic glycoside hydrolase substrate which belongs to a family of natural glycosides found in plants. Cleavage of the glycosidic bond forms an unstable hydroxyindole intermediate, which dimerizes by oxidation to form indigo as a blue precipitate:
Numerous enzyme substrates have been designed following this natural product example, giving rise to many colored phenols that are used to detect enzyme activities.
As shown in Figure 1, some of the hydrolases used in the Colisweeper reporter system can catalyze hydrolysis of various substrates, with different chromophores that give rise to a wide range of colors. This variety of substrates and color outputs enables change of positions and function of these enzymes. Other possible substrates that can be used for the enzymes of this system can be seen in the Hydrolases section.
In Colisweeper, the set of enzyme-substrate pairs are chosen as illustrated in the following table:
| Hydrolase | Complementary substrate / IUPAC name | Visible color | Concentration[M] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LacZ | Beta-Galactosidase | X-Gal | 5-Bromo-4chloro-3-indolyl-beta-galactopyranoside | Blue | |
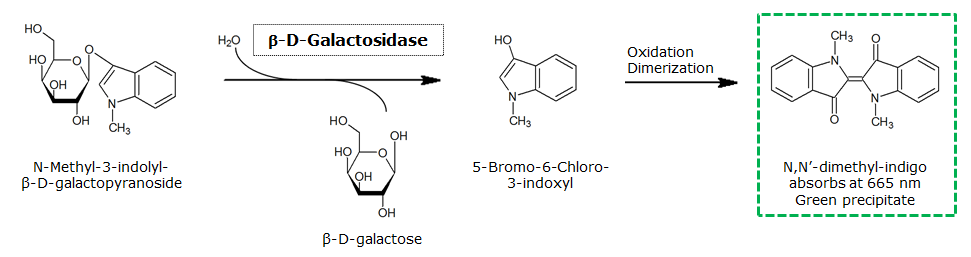
| LacZ | Beta-Galactosidase | Green-beta-D-Gal | N-Methyl-3-indolyl-beta-D_galactopyranoside | Green | |
| GusA | Beta-glucuronidase | Magenta glucuronide | 6-chloro-3-indolyl-beta-D-glucuronide-cycloheylammonium salt | Salmon | |
| PhoA | Alkaline phosphatase | pNPP | 4-Nitrophenylphosphatedi(tris) salt | Yellow | |
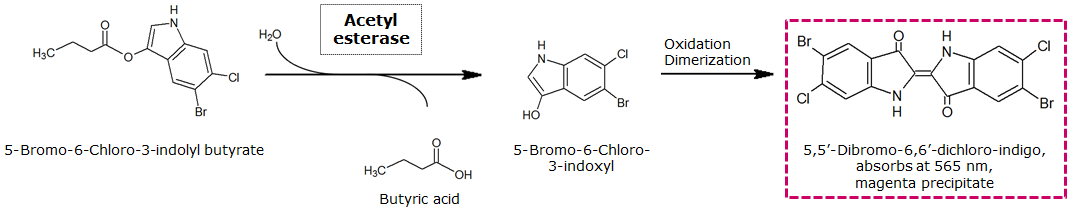
| Aes | Acetyl esterase | Magenta butyrate | 5-bromo-6-chloro-3-indoxyl butyrate | Magenta | |
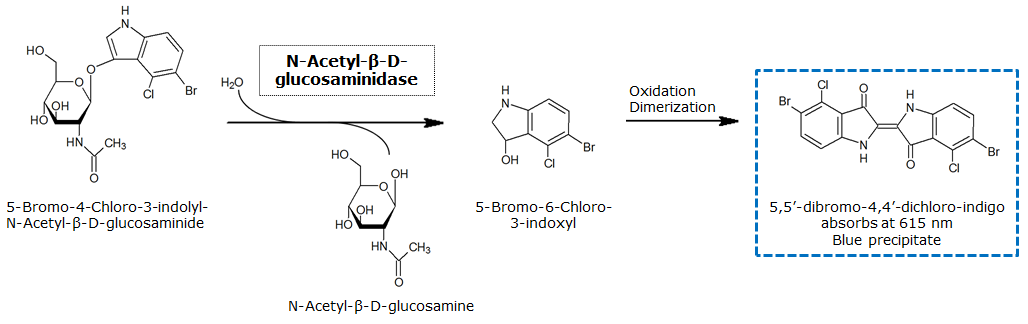
| NagZ | Glycoside hydrolase | X-glucosaminide X-Glucnac | 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl-N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminide | Blue | |
Acetyl esterase(Aes)
Chemical conversion
Colorimetric response in liquid culture
Colorimetric response on LB-Agar
Alkaline phosphatase(PhoA)
Chemical conversion
Colorimetric response in liquid culture
Colorimetric response on LB-Agar
Beta-galactosidase(LacZ)
Chemical conversion
Colorimetric response in liquid culture
Colorimetric response on LB-Agar
Beta-glucuronidase(GusA)
Chemical conversion
Colorimetric response in liquid culture
Colorimetric response on LB-Agar
β-N-Acetylglucosaminidase(NagZ)
Chemical conversion
Colorimetric response in liquid culture
Colorimetric response on LB-Agar
 "
"