Team:ETH Zurich/Processing 2
From 2013.igem.org
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
<h1> Creation of a promoter library </h1> | <h1> Creation of a promoter library </h1> | ||
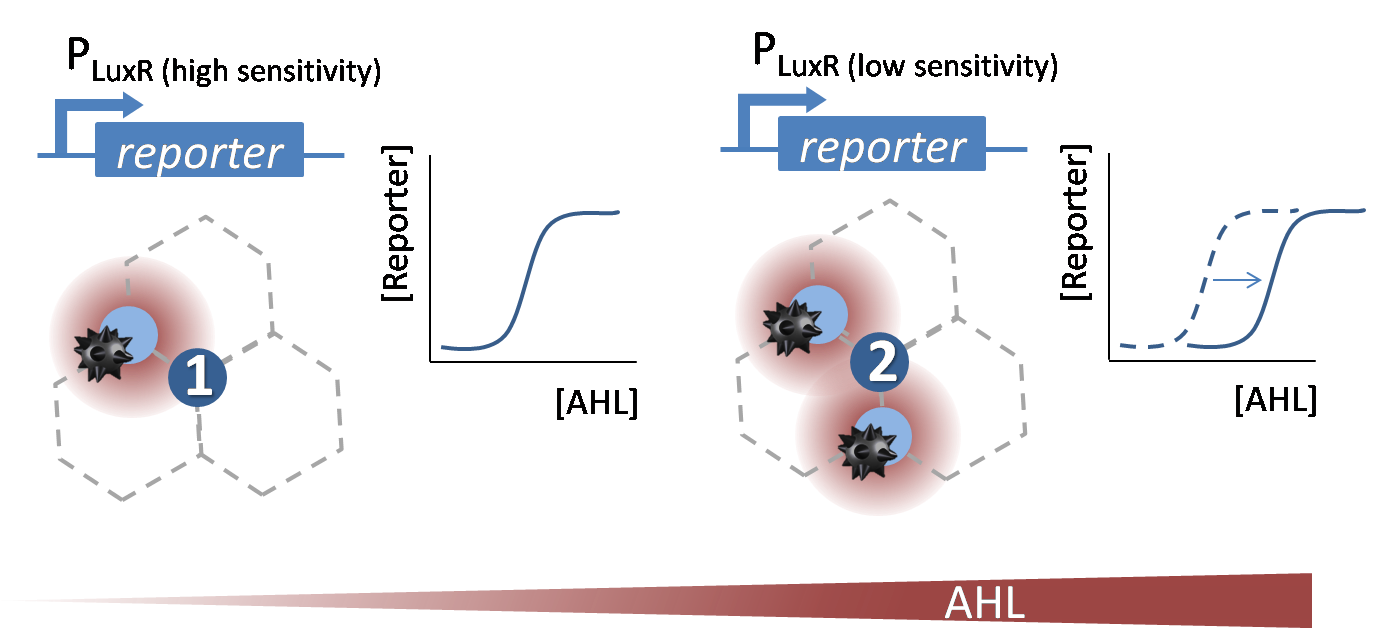
[[File:Why_infoproc.png|600px|left|thumb|<b>Figure 1. Theoretical sensivity shift of the P<sub>LuxR</sub> promoter to sense and distinguish different AHL concentrations.</b>]] | [[File:Why_infoproc.png|600px|left|thumb|<b>Figure 1. Theoretical sensivity shift of the P<sub>LuxR</sub> promoter to sense and distinguish different AHL concentrations.</b>]] | ||
| - | The wild-type P<sub>LuxR</sub> promoter ([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_R0062 BBa_R0062]) gets activated in presence of AHL. In our project we need different sensitive promoters to distinguish between different levels of the AHL concentrations according to the different number of surrounding mines. Therefor we need to shift the dose-response curve of the initial BBa_R0062 promoter. We decided to do site directed saturation mutagenesis (see below) to achieve a sensitivity shift.For more details please see the experimental results page for [https://2013.igem.org/Team:ETH_Zurich/Experiments_5 processing]. | + | The wild-type P<sub>LuxR</sub> promoter ([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_R0062 BBa_R0062]) gets activated in presence of AHL. In our project we need different sensitive promoters to distinguish between different levels of the AHL concentrations according to the different number of surrounding mines. Therefor we need to shift the dose-response curve of the initial [ http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_R0062 BBa_R0062] promoter. We decided to do site directed saturation mutagenesis (see below) to achieve a sensitivity shift. For more details please see the experimental results page for [https://2013.igem.org/Team:ETH_Zurich/Experiments_5 processing]. |
<br clear="all"/> | <br clear="all"/> | ||
<html><a id="high-pass-filter_mutagenesis" class="frog"></a></html> | <html><a id="high-pass-filter_mutagenesis" class="frog"></a></html> | ||
<h1>Site directed saturation mutagenesis PCR of the BBa_R0062 PluxR</h1> | <h1>Site directed saturation mutagenesis PCR of the BBa_R0062 PluxR</h1> | ||
| - | [[File:promotermutations1.png|left|750px|thumb|<b>Figure 2: Promoter mutation sites</b> The wild type promoter from the biobrick BBa_R0062 was mutated using site directed saturation mutagenesis. The library shows the targeted sites for site directed saturation mutagenesis. The sequences for the library, the BBa_R0062, the BBa_K1216007 and the wild type luxR promoter from literature [https://2013.igem.org/Team:ETH_Zurich/References#Antunes2007 Antunes ''et. al.'', 2007.] are given. All assays were carried out in duplicates, results are presented as mean ± standard deviation.]] | + | [[File:promotermutations1.png|left|750px|thumb|<b>Figure 2: Promoter mutation sites</b> The wild type promoter from the biobrick [the BBa_R0062] was mutated using site directed saturation mutagenesis. The library shows the targeted sites for site directed saturation mutagenesis. The sequences for the library, the [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_R0062 BBa_R0062], the [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1216007 BBa_K1216007] and the wild type luxR promoter from literature [https://2013.igem.org/Team:ETH_Zurich/References#Antunes2007 Antunes ''et. al.'', 2007.] are given. All assays were carried out in duplicates, results are presented as mean ± standard deviation.]] |
<p align="justify">We did site directed saturation mutagenesis of specific sites of the ''lux'' box according to the results taken from literature [https://2013.igem.org/Team:ETH_Zurich/References#Antunes2007 Antunes ''et. al.'', 2007.] (see Figure 2).<br> | <p align="justify">We did site directed saturation mutagenesis of specific sites of the ''lux'' box according to the results taken from literature [https://2013.igem.org/Team:ETH_Zurich/References#Antunes2007 Antunes ''et. al.'', 2007.] (see Figure 2).<br> | ||
We mutated the promoter directly in the BBa_J09855 construct and cloned it in front an eGFP gene as a reporter to be able to screen for differences in the dose response curves. At first we incubated the transformed cells on an AHL containing plate to rule out all AHL-insensitive mutations. All colonies expressing GFP were then restreaked on a plate which contained no AHL, thus allowing us to rule out constitutive promoters. The remaining clones were then grown in luquid cultures on 96-well plates and tested for sensitivity over a broad range of AHL concentrations. Promising candidates were then measured in a flow cytometer to check for bistable promoters. The results of all these processes can be seen [https://2013.igem.org/Team:ETH_Zurich/Experiments_5 here.]</p> | We mutated the promoter directly in the BBa_J09855 construct and cloned it in front an eGFP gene as a reporter to be able to screen for differences in the dose response curves. At first we incubated the transformed cells on an AHL containing plate to rule out all AHL-insensitive mutations. All colonies expressing GFP were then restreaked on a plate which contained no AHL, thus allowing us to rule out constitutive promoters. The remaining clones were then grown in luquid cultures on 96-well plates and tested for sensitivity over a broad range of AHL concentrations. Promising candidates were then measured in a flow cytometer to check for bistable promoters. The results of all these processes can be seen [https://2013.igem.org/Team:ETH_Zurich/Experiments_5 here.]</p> | ||
Revision as of 11:38, 25 October 2013
Creation of a promoter library
The wild-type PLuxR promoter ([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_R0062 BBa_R0062]) gets activated in presence of AHL. In our project we need different sensitive promoters to distinguish between different levels of the AHL concentrations according to the different number of surrounding mines. Therefor we need to shift the dose-response curve of the initial [ http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_R0062 BBa_R0062] promoter. We decided to do site directed saturation mutagenesis (see below) to achieve a sensitivity shift. For more details please see the experimental results page for processing.
Site directed saturation mutagenesis PCR of the BBa_R0062 PluxR

We did site directed saturation mutagenesis of specific sites of the lux box according to the results taken from literature Antunes et. al., 2007. (see Figure 2).
We mutated the promoter directly in the BBa_J09855 construct and cloned it in front an eGFP gene as a reporter to be able to screen for differences in the dose response curves. At first we incubated the transformed cells on an AHL containing plate to rule out all AHL-insensitive mutations. All colonies expressing GFP were then restreaked on a plate which contained no AHL, thus allowing us to rule out constitutive promoters. The remaining clones were then grown in luquid cultures on 96-well plates and tested for sensitivity over a broad range of AHL concentrations. Promising candidates were then measured in a flow cytometer to check for bistable promoters. The results of all these processes can be seen here.
 "
"