Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Modelling/Optimal
From 2013.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
m |
m |
||
| Line 70: | Line 70: | ||
<p align="justify"> | <p align="justify"> | ||
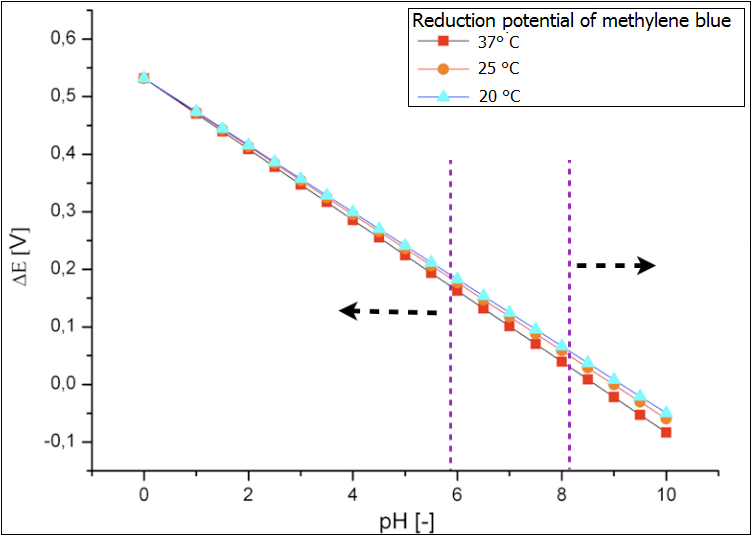
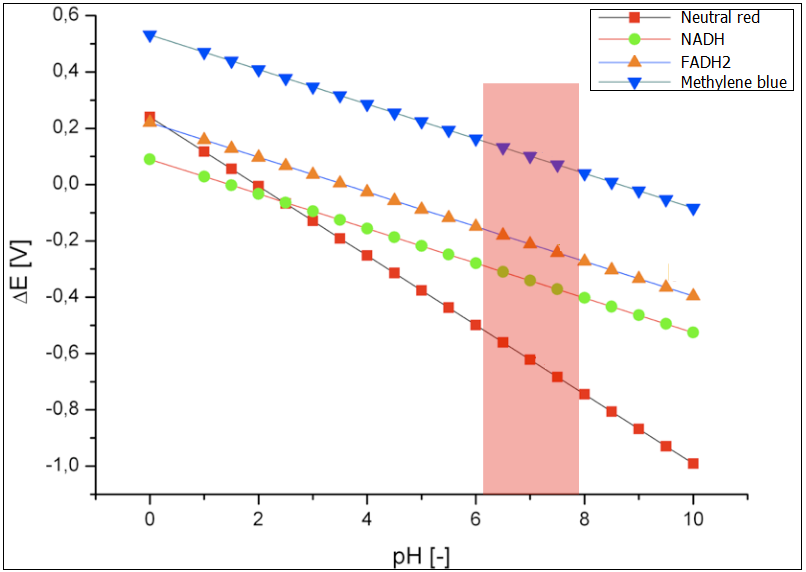
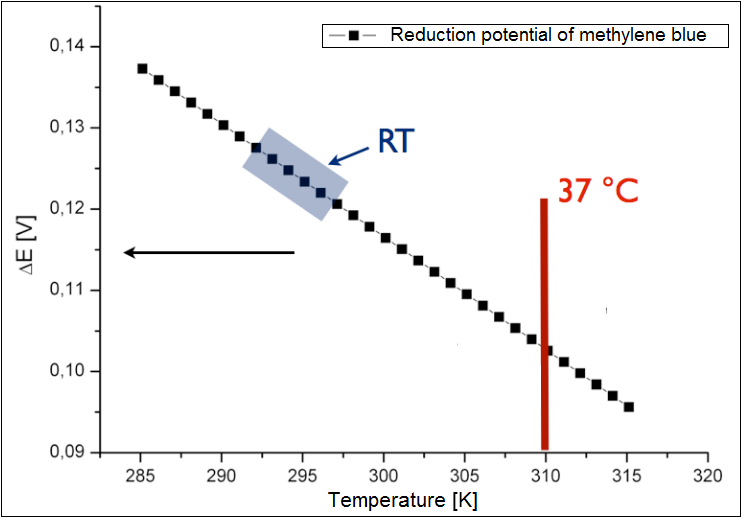
The microbial fuel cell will be subjected to numerous parameters, which will heavily influence its performance. Therefore, there is a need to inquiry the impact of those parameters on the efficiency of the system. In our approach we focused on how the reduction potential of the given mediators depends on two most significant parameters, namely the pH value and the temperature. | The microbial fuel cell will be subjected to numerous parameters, which will heavily influence its performance. Therefore, there is a need to inquiry the impact of those parameters on the efficiency of the system. In our approach we focused on how the reduction potential of the given mediators depends on two most significant parameters, namely the pH value and the temperature. | ||
| - | All values were calculated based on the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nernst_equation Nernst equation] , which describes the relation between the electromotive force of the full cell and the temperature or the pH-value. | + | All values were calculated based on the[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nernst_equation Nernst equation], which describes the relation between the electromotive force of the full cell and the temperature or the pH-value. |
</p> | </p> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
Revision as of 22:33, 4 October 2013
Modeling
Overview
The microbial fuel cell will be subjected to numerous parameters, which will heavily influence its performance. Therefore, there is a need to inquiry the impact of those parameters on the efficiency of the system. In our approach we focused on how the reduction potential of the given mediators depends on two most significant parameters, namely the pH value and the temperature. All values were calculated based on the[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nernst_equation Nernst equation], which describes the relation between the electromotive force of the full cell and the temperature or the pH-value.
Optimal pH value
Optimal temperature
References
 "
"