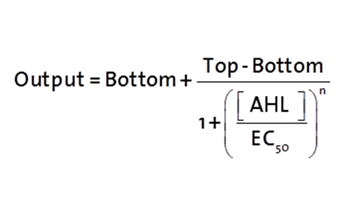Team:ETH Zurich/Experiments 5
From 2013.igem.org
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
<h1>High pass filters</h1> | <h1>High pass filters</h1> | ||
[[File:promotercomparisonfinal.png|left|400px|thumb|<b>Dose response curve of the promoter library.</b><br>7 different promoter were created by partial sensitivity recovery of the P<sub>LuxR</sub> variant.The colonies have the [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_R0062 BBa_J09855] construct with the different mutated promoter as well as a RFP reporter to analyze the dose response in the flow cytometer. The colonies were grown on 11 different plates with 11 different concentrtions as explained in Figure 9. Please see table 1 for the characteristics of the promoter library.]] | [[File:promotercomparisonfinal.png|left|400px|thumb|<b>Dose response curve of the promoter library.</b><br>7 different promoter were created by partial sensitivity recovery of the P<sub>LuxR</sub> variant.The colonies have the [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_R0062 BBa_J09855] construct with the different mutated promoter as well as a RFP reporter to analyze the dose response in the flow cytometer. The colonies were grown on 11 different plates with 11 different concentrtions as explained in Figure 9. Please see table 1 for the characteristics of the promoter library.]] | ||
| - | <p align="justify">The detection of different AHL levels depending on the number of mines requires filters in our detection system. We decided to create a high pass filter library by doing site directed mutagenesis of the wild type [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_R0062 BBa_R0062]P<sub>LuxR</sub>. The sites for mutagenesis were chosen from literature ([https://2013.igem.org/Team:ETH_Zurich/Experiments_5#referencespromoter 2]) (see <i>Figure 1</i>).<br> | + | <p align="justify">The detection of different AHL levels depending on the number of mines requires filters in our detection system. We decided to create a high pass filter library by doing site directed mutagenesis of the wild type [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_R0062 BBa_R0062] P<sub>LuxR</sub>. The sites for mutagenesis were chosen from literature ([https://2013.igem.org/Team:ETH_Zurich/Experiments_5#referencespromoter 2]) (see <i>Figure 1</i>).<br> |
| - | We were able to isolate a promoter having a lower expression level and being less sensitive than the wild type promoter (<i>Figure 2</i>). The promoter is called [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1216007 | + | We were able to isolate a promoter having a lower expression level and being less sensitive than the wild type promoter (<i>Figure 2</i>). The promoter is called P<sub>LuxR</sub> variant[http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1216007 BBa_K1216007] (G1, according to its initial position in the deep well plate).<br> Those two different promoters were used to create two high pass filter to detect different AHL concentrations. The two promoters were analyzed not only in liquid culture by 96-well plate assays and single cell analysis (FACS) but also for'' E.coli'' on agar plate. Interestingly the EC<sub>50</sub> sensitivity (half maximal effective concentration, EC<sub>50</sub>) is different between cells in liquid culture and cells on agar plates. After We then used the P<sub>LuxR</sub> variant (G1) to do partial sensitivity recovery by backmutating the two mutated nucleotides of the variant. Rational design and oligomers allow us to create a library of 7 different sensitive promoters. See the figure on the left, and the full results in the <i>second library</i> part below.</p> |
<br clear="all"/> | <br clear="all"/> | ||
Revision as of 16:06, 28 October 2013
High pass filters
7 different promoter were created by partial sensitivity recovery of the PLuxR variant.The colonies have the [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_R0062 BBa_J09855] construct with the different mutated promoter as well as a RFP reporter to analyze the dose response in the flow cytometer. The colonies were grown on 11 different plates with 11 different concentrtions as explained in Figure 9. Please see table 1 for the characteristics of the promoter library.
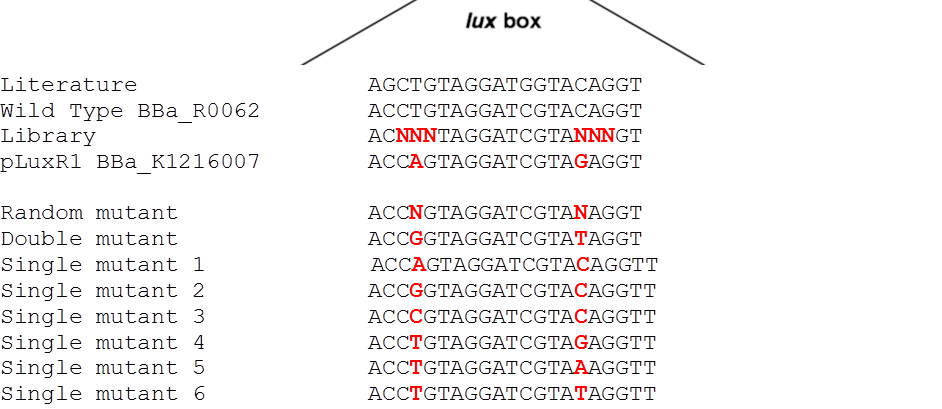
The detection of different AHL levels depending on the number of mines requires filters in our detection system. We decided to create a high pass filter library by doing site directed mutagenesis of the wild type [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_R0062 BBa_R0062] PLuxR. The sites for mutagenesis were chosen from literature (2) (see Figure 1).
We were able to isolate a promoter having a lower expression level and being less sensitive than the wild type promoter (Figure 2). The promoter is called PLuxR variant[http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1216007 BBa_K1216007] (G1, according to its initial position in the deep well plate).
Those two different promoters were used to create two high pass filter to detect different AHL concentrations. The two promoters were analyzed not only in liquid culture by 96-well plate assays and single cell analysis (FACS) but also for E.coli on agar plate. Interestingly the EC50 sensitivity (half maximal effective concentration, EC50) is different between cells in liquid culture and cells on agar plates. After We then used the PLuxR variant (G1) to do partial sensitivity recovery by backmutating the two mutated nucleotides of the variant. Rational design and oligomers allow us to create a library of 7 different sensitive promoters. See the figure on the left, and the full results in the second library part below.
First library: Preliminary tests and dose response curve single cell analysis of the wild-type PLuxR and PLuxR varaint (G1)
Positive and negative selection of the cells transformed with mutated PLuxR</br>
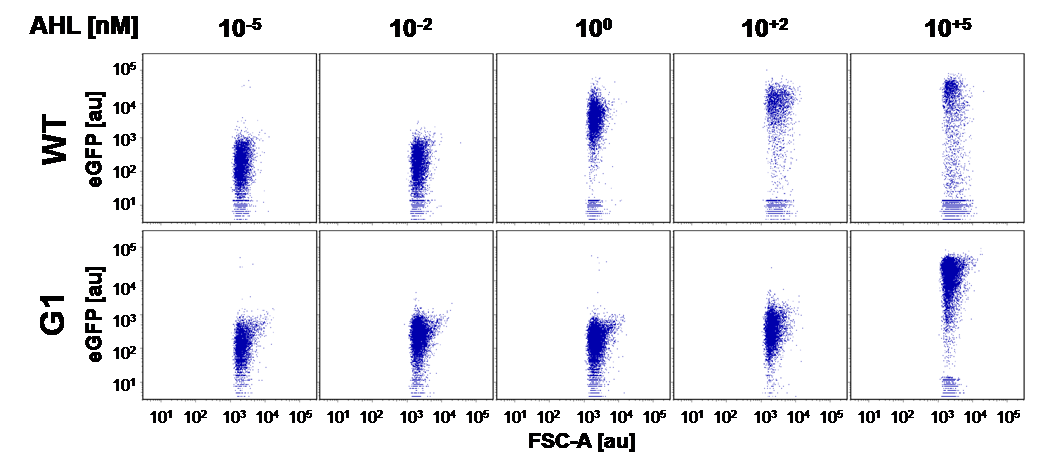
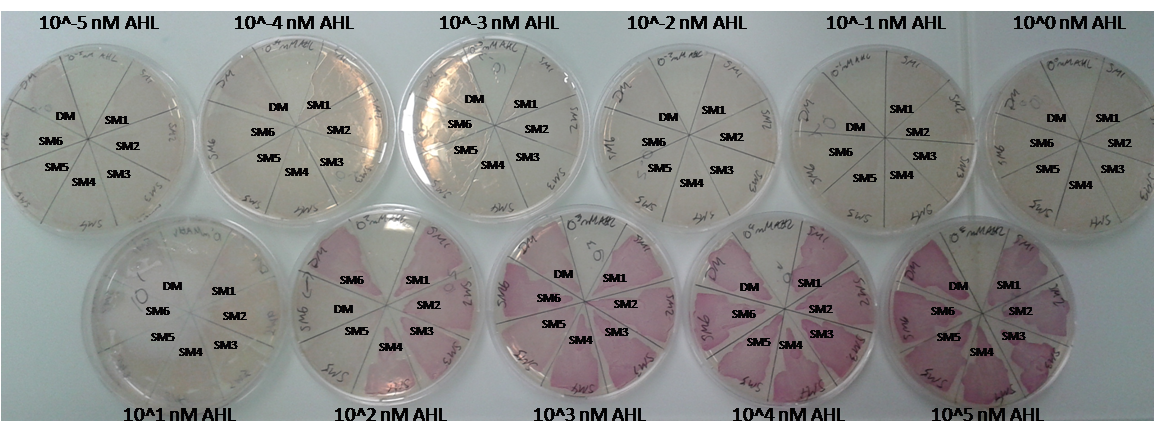
At first we incubated the transformed cells on an AHL containing plate to rule out all AHL-insensitive mutations. All colonies expressing GFP were then restreaked on a plate which contained no AHL, thus allowing us to rule out constitutive promoters. The remaining clones were then grown in luquid cultures on 96-well plates and tested for sensitivity over a broad range of AHL concentrations. Promising candidates were then measured in a flow cytometer to check for bistable promoters.
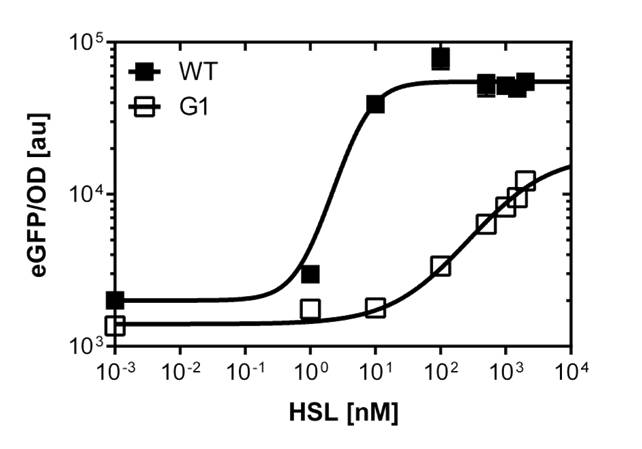
For the wild type: EC50=5.86 nM, R2= 0.87,n=1.7
Fore the G1 mutant: EC50=1'341 nM, R2= 0.98,n=0.8. All assays were carried out in triplicates, results are presented as mean ± standard deviation.
Preliminary tests on microtiter plate reader screening
First of all we did a fast and preliminary screening of the mutated PluxR promoters with the microtiter plate reader. Thus, we carried out dose response curves using the Tecan Infinite M200 plate reader. The test range was inspired from literature (1). Afterwards we did flow cytometry of the most promissing promoters to have high quality data and exclude bistable promoters.
The results are shown in Figure 2.
Dose response curve single cell analysis of the wild-type PLuxR and the first PLuxR variant(G1)
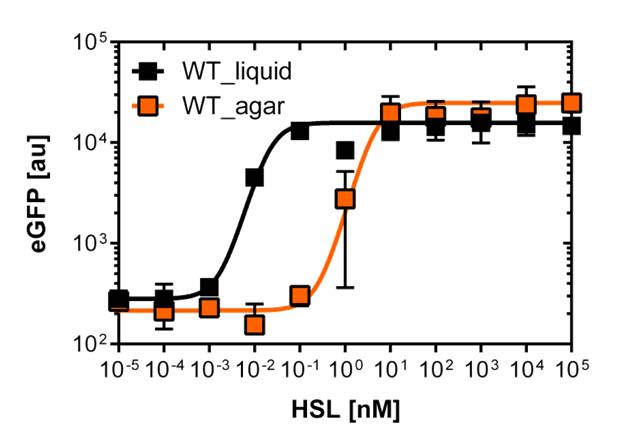
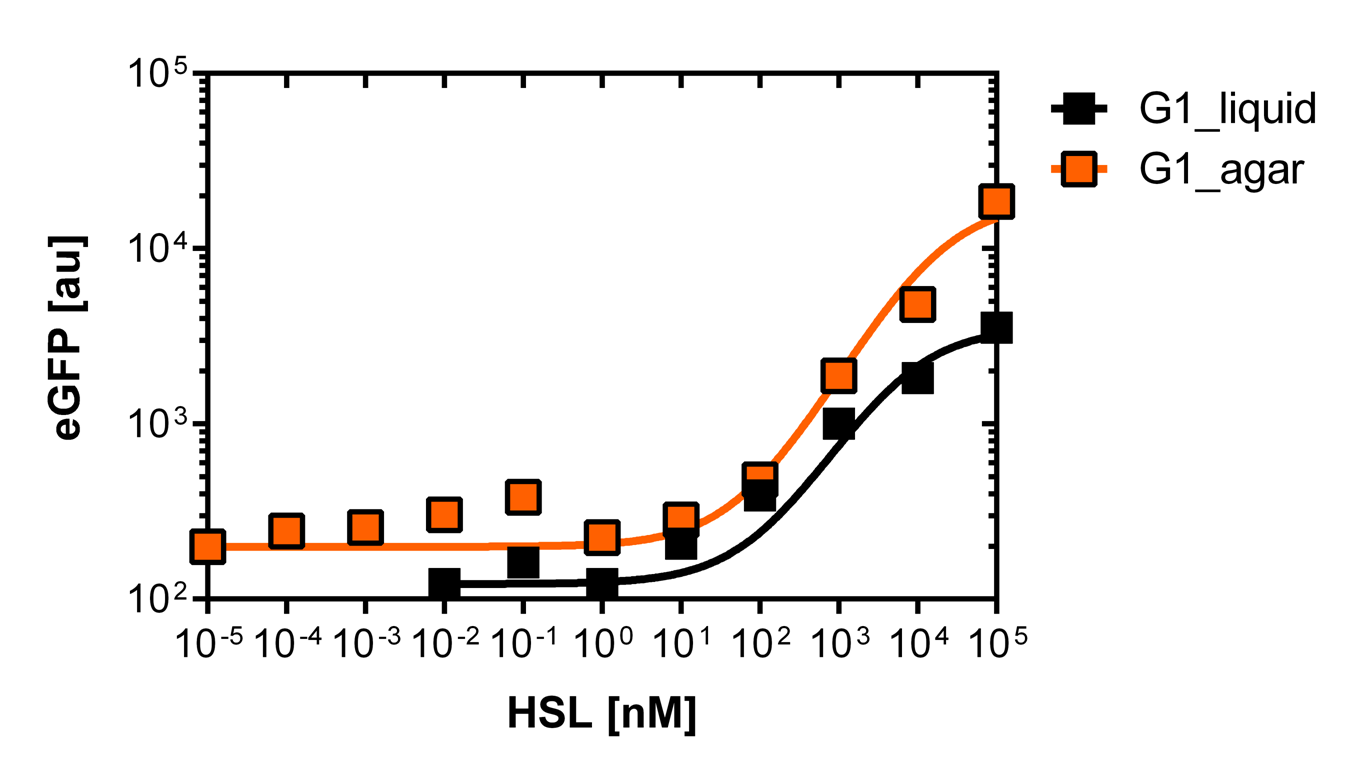
Liquid culture and agar plate AHL detection comparison
Here we employed single cell flow cytometry to obtain high quality fluorescence data of each promoter under different AHL concentrations.we started by analyzing cells grown in liquid culture, then we shifted to agar plate format in order to fit to our project. We obtained different EC50 values between cells in liquid culture and in agar plates for each luxR promoter (see Figure 3, 4 and 5). See methods for the protocol
For the liquid culture we got: EC50=6482 nM, R2=0.97, n=0.8;
For the agar plates we got :EC50=12'555nM, R2=0.93, n=0.8. All assays were carried out in duplicates, results are presented as mean ± standard deviation.
In liquid culture
The direct plot of both sensitivity curves (Figure 6) shows the shifted sensitivity of the luxR promoter in comparison to the wild type BBa_R0062 promoter. The EC50 shifted from 0.02nM for the wild type BBA_R0062 to 6'250 nM for the luxR variant promoter which is equal to a 300'000 fold increase.

For the wild type :EC50=0.02nM, R2=0.84, n=1.7
For G1 we got :EC50=6482nM, R2=0.97, n=0.8. All assays were carried out in duplicates, results are presented as mean ± standard deviation.
On agar plates
The direct plot of both sensitivity curves (Figure 6) shows the shifted sensitivity of the PluxR promoter in comparison to the wild type BBa_R0062 promoter. The EC50 shifted from 4.45 nM for the wild type BBA_R0062 to 12'555 nM for the luxR variant promoter which is equal to a 2800 fold increase. Therefore, comparing with the results from cells growing in liquid culture an increase of 220 and 2 times for wild type BBa_R0062 and pluxR variant respectively. If you want to know more about the methods please click here
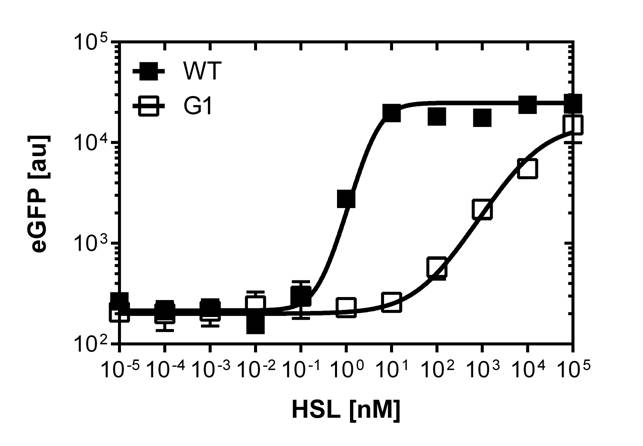
For the wild type we got :EC50=4.45 nM, R2=0.80, n=1.7
For the pLuxR variant we got :EC50=12'555 nM, R2=0.93, n=0.8. All assays were carried out in duplicates, results are presented as mean ± standard deviation.
Second library : Back mutation and single cell analysis of the first PLuxR varaint (G1) by rational design and partial sensitivity recovery.
Rational design and single cell analysis of additional PLuxR variants with partial sensitivity recovery based on the first PLuxR variant (G1)
According to initial model predictions confirmed by successive experimental validation the G1 promoter sensitivity is too low to drive a significant response in the concentration gradient established by our sender cells.
We need a collection of promoters with a set of EC50 values between the wild type and G1 itself.
Since G1 has been obtained through two random mutations: 4T>A and 16C>G reverting one of the two, we reasoned, should result in a LuxR binding strength closer to the wild type.
To test this hypothesis we ordered oligos encompassing all the possible combination of single position mutants (See list) and plan to experimentally characterize, and eventually deposit in the registry, all the resulting pLux variants. In parallel we used degenerate oligos to generate a small library (16 members) containing all the combination of double mutants for the two G1 key position to verify if all the double mutants show similar EC50.
Finally characterized promoter library
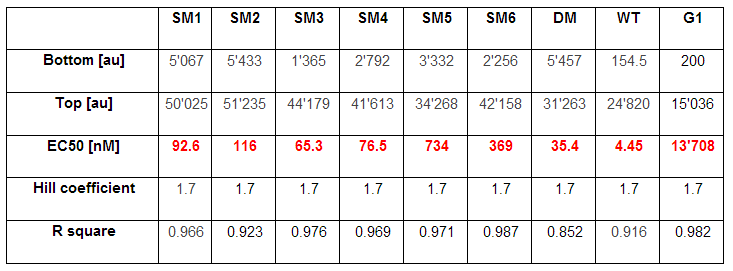
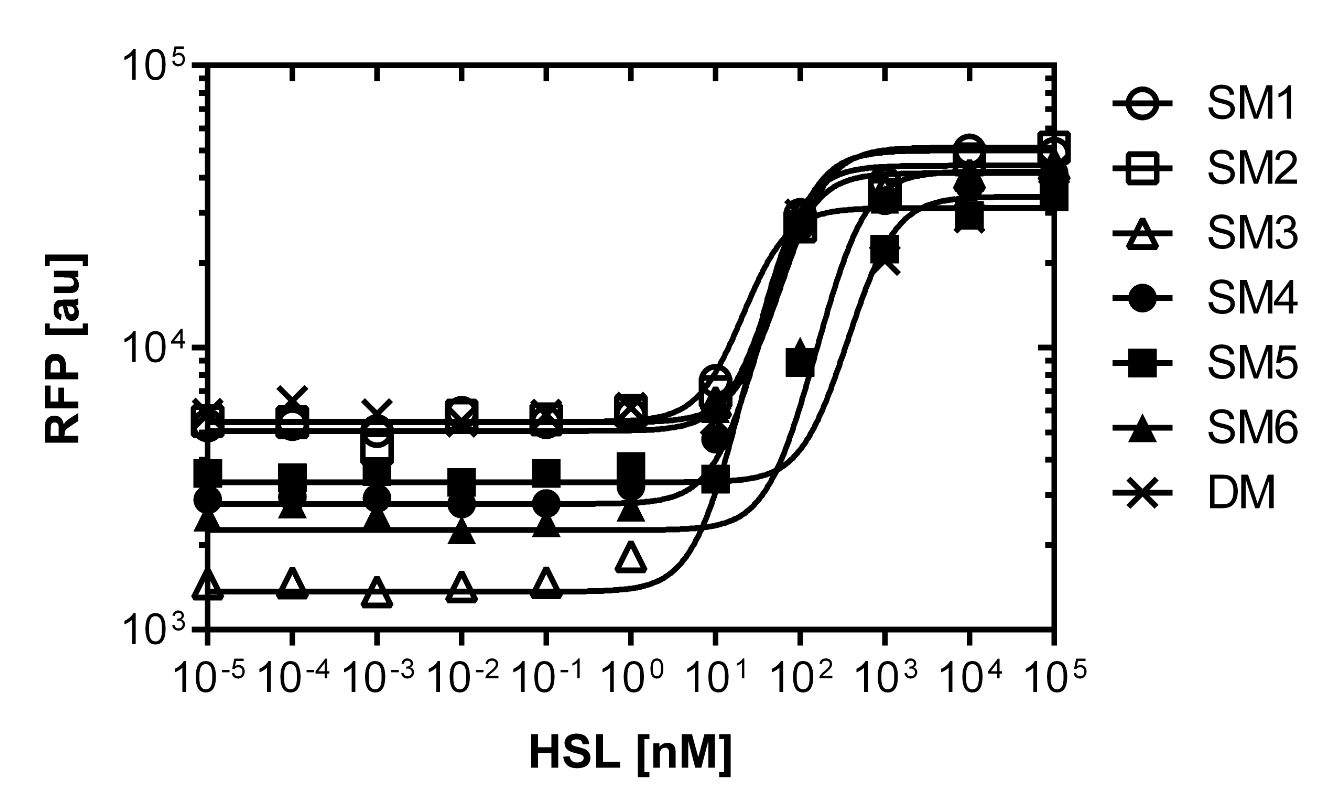
As explained above we created a library of promoters originating from PLuxR variant(G1). We characterized the dose response curve to AHL on agar plates of all 7 promoters by following the same protocol as for the PLuxR variant characterization. See the different shifted dose response curves in Figure 10. and the characteristics of the library in Table 1.

Fluorescence data analysis
The fitting of the following graphs was performed using this equation :
Output = eGFP levels [au]
Top = maximal eGFP level [au]("full induction")
Bottom = minimal eGFP level [au](“leakiness”)
n = Hill coefficient (“cooperativity”)
EC50 = Half-maximal effective concentration (“sensitivity”)
[AHL]=AHL concentration [nM]
References
(1) M Geske G.D.,Evaluation of a focused library of N-aryl L-homoserine lactones reveals a new set of potent quorum sensing modulators.
(2) Luis Caetano A Mutational Analysis Defines Vibrio fischeri LuxR Binding Sites
 "
"