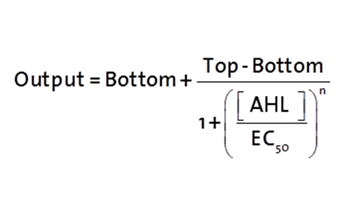Team:ETH Zurich/Experiments 5
From 2013.igem.org
Contents |
High pass filters
The detection of different OHHL levels depending on the number of mines needs to have filters in our detection system. We decided to create a high pass filter library by doing site directed mutagenesis of the wild type [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_R0062 BBa_R0062 PLuxR] promoter. The sites for mutagenisis were chosen from literature (2) (see Figure 1).
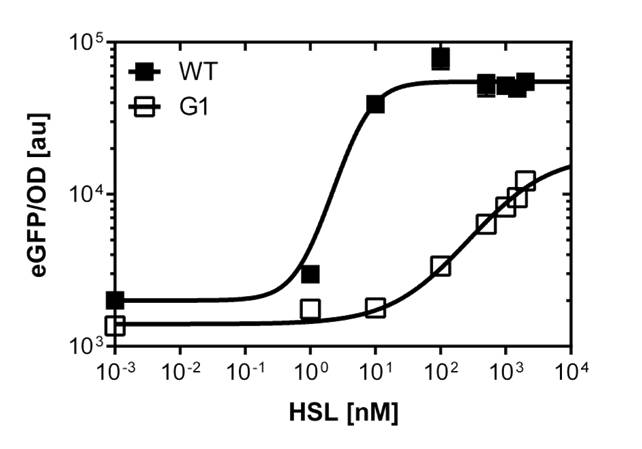
We were able to isolate a promoter having a lower expression level and being less sensitive than the wild type promoter (Figure 2). The promoter is called [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1216007?title=Part:BBa_K1216007 PluxR1 BBa_K1216007] (G1, according to its initial position in the deep well plate.
Those two different promoters are used to created two different high pass filter to detect the different OHHL concentrations. The two promoters were analyzed not only by 96-well plate assay and single cell analysis (FACS) but also for E.coli grown in liquid culture and on agar plate. Interestingly the EC50 sensitivity (half maximal effective concentration, EC50) is different between cells in liquid culture and cells in agar plates.
Site directed saturation mutagenesis PCR of the BBa_R0062 PluxR

We did site directed saturation mutagenisis of specific sites of the lux box according to the results taken from literature (2)(see Figure 2).
We mutated the promoter directly in the BBa_J09855 construct and cloned into a eGFP gene as a reporter to be able to screen for differences in the dose response curves. In the end we isolated one mutated promoter which shows a shift in sensitivity (see section below)
Fluorescence data analysis
The fitting of the following graphs was performed using this equation :
Output = eGFP levels [au]
Top = maximal eGFP level [au]("full induction")
Bottom = minimal eGFP level [au](“leakiness”)
n = Hill coefficient (“cooperativity”)
EC50 = Half-maximal effective concentration (“sensitivity”)
[AHL]=OHHL concentration [nM]
Native OHHL tests using microtiter plates
In order to select mutated luxR promoters we need to know about the sensitivity.Thus, we carried out dose response cruves using the Tecan Infinite M200 plate reader. The test range was inspired form literature (1).
The results are shown in Figure 2. The experimental set-up included a 96-well plate filled with 180 μL LB media , 10uμ of receiver cells and 10μL of different OHHL concentrations, everything in triplicates. (+ blank and negative control). The experiment runs for 16 hours in order to monitor the evolution of fluorescence and later choose the steady state to create the sensitivity curve.
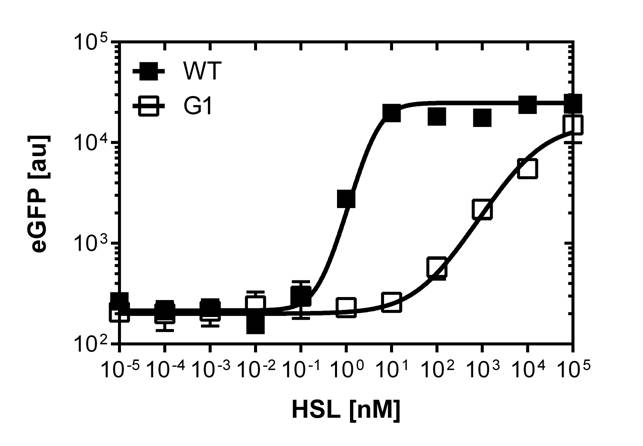
Dose response curves of luxR promoters under single cell analysis
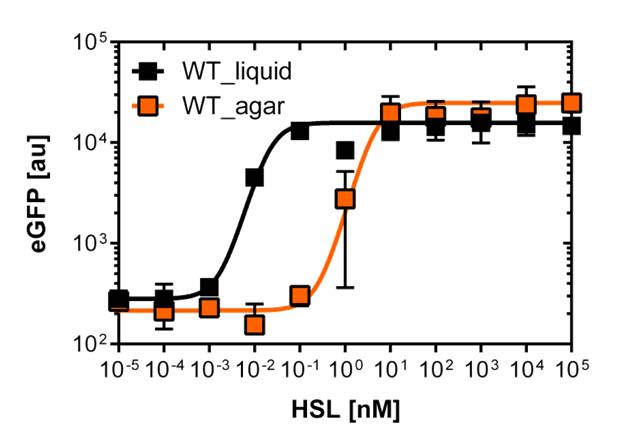
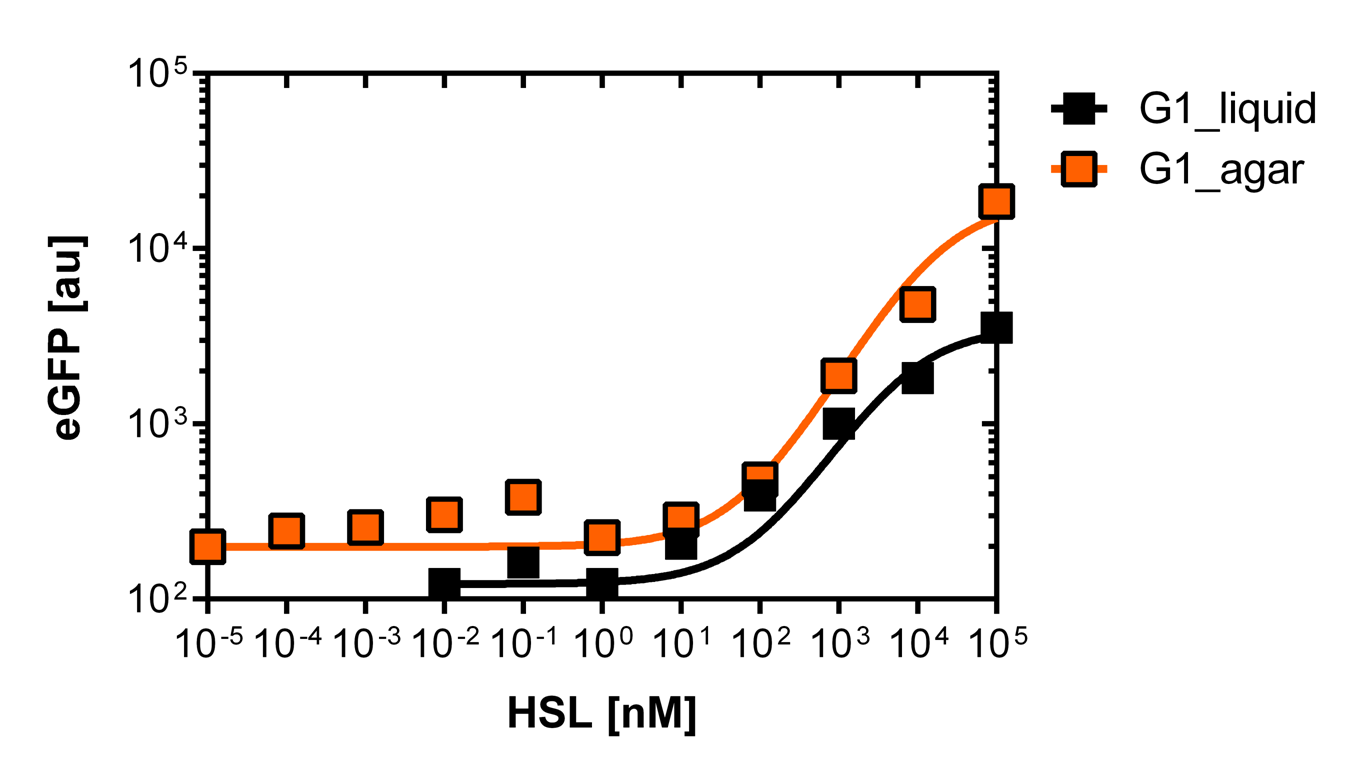
Liquid culture and agar plate OHHL detection comparison
To gain precise data out of our fluorescence analysis, to better characterize the different promoters, we use the single analysis to obtain data.
The protocol was the following :
From overnight cultures we inoculate 50 mL Falcon™ tubes containing 5mL LB media, 5 μL OHHL and the antibiotic. We evaluate a range of 10 different concentrations from
10-4nM OHHL to 105nM OHHL by a 10 fold increase, according to the results of the plate reader analysis. The measurements were done in duplicates.
Here we employed single cell flow cytometry to obtain high quality fluorescence data of each promoter under different OHHL concentrations.we started by analyzing cells grown in liquid culture, then we shifted to agar plate format in order to fit to our project. We obtained different EC50 values between cells in liquid culture and in agar plates for each luxR promoter (see Figure 3, 4 and 5).

In liquid culture
The direct plot of both sensitivity curves shows the clearly shifted sensivity of the pLuxR1 promoter in comparison to the wild type BBa_R0062 promoter. The EC50 shifted from 0.02nM for the wild type BBA_R0062 to 6'250 nM for the luxR variant promoter which is equal to a 312'500 fold increase.
The wild type promoter [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_R0062 BBa_R0062 PLuxR] is used for the detection of low OHHL concentrations and therefore be almost activated when one mine cell is in the vincinity of the receiver cell. The wild type promoter induces the expression of GusA, a hydrolase able to convert a specific substrate to a visible red output.The mutated promoter [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1216007?title=Part:BBa_K1216007 PluxR1 BBa_K1216007] will be used in our final set-up to only respond to high concentrations of OHHL and therefore be activated, when two sender cells are surrounding the receiver cell, and expressing the AES hydrolase responsible for the colorimetric conversion of the specific substrate to a visible purple output.
On agar plates
For the real colisweeper game we need to know about the behavior of the promoters on agar plates.
We set-up an experiment which consists in pooring agar plates containing different OHHL concentration going form 10-5nM to 105nM by 10 fold increase. The wild type and the pLuxR1 promoter were streaked onto those plates to analyze the sensivity to OHHL of the wild type and the promoter on an agar plate. After 15hours of incubation at 37 degree celsius some colonies were picked and resuspended in Phosphate Buffered Solution (PBS) for the single cell analysis , using again the BD LSRFortessa™ Flow Cytometer System.
References
(1) Geske G.D.,Evaluation of a focused library of N-aryl L-homoserine lactones reveals a new set of potent quorum sensing modulators.
 "
"