Team:NTU-Taida/Project/Target
From 2013.igem.org
(→Acyl-homoserine lactone) |
(→Acyl-homoserine lactone (AHL) and quorum sensing transcriptional regulator) |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
[[File:NTU-Taida-target-1.jpg|600px|thumb|center|Figure.1]] | [[File:NTU-Taida-target-1.jpg|600px|thumb|center|Figure.1]] | ||
| - | ==Acyl-homoserine lactone | + | ==Acyl-homoserine lactone and quorum sensing transcriptional regulator== |
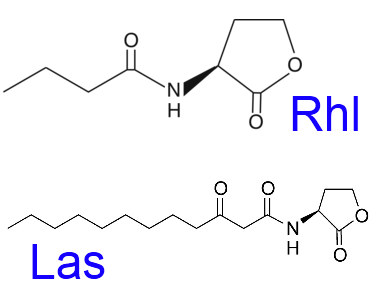
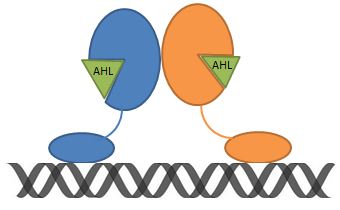
| - | For gram negative bacteria, AHLs are used as quorum sensing signals. AHL consists of a five-member homoserine lactone ring and an acyl side chain. The length and the substitution group of the side chain determine the specificity of AHL-receptor binding. On the other hand, the transcriptional regulator consists of an N-terminal ligand-binding domain (to bind AHL) and a C-terminal DNA binding domain. | + | For gram negative bacteria, Acyl-homoserine lactones (AHLs) are used as quorum sensing signals. AHL consists of a five-member homoserine lactone ring and an acyl side chain. The length and the substitution group of the side chain determine the specificity of AHL-receptor binding. On the other hand, the transcriptional regulator consists of an N-terminal ligand-binding domain (to bind AHL) and a C-terminal DNA binding domain. |
[[File:NTU-Taida-target-2.jpg|700px|thumb|center|Figure.2]] | [[File:NTU-Taida-target-2.jpg|700px|thumb|center|Figure.2]] | ||
Revision as of 15:46, 27 September 2013
Contents |
Project Target Molecules
Quorum sensing (QS) signals can be transmitted through several types of molecules. In our project, we used Rhl, Las and PQS quorum sensing signals as our target. Both Rhl and Las systems use acyl homoserine lactones (AHLs) as quorum sensing targets, while PQS uses 2-heptyl-3-hydroxy-4-quinolone as its QS target.
Acyl-homoserine lactone and quorum sensing transcriptional regulator
For gram negative bacteria, Acyl-homoserine lactones (AHLs) are used as quorum sensing signals. AHL consists of a five-member homoserine lactone ring and an acyl side chain. The length and the substitution group of the side chain determine the specificity of AHL-receptor binding. On the other hand, the transcriptional regulator consists of an N-terminal ligand-binding domain (to bind AHL) and a C-terminal DNA binding domain.
AHL binding and quorum sensing transcriptional regulator
Rhl transcriptional regulator senses C-12 acyl homoserine lactone. The structure of the transcriptional regulator consists of an N-terminal ligand-binding domain and a C-terminal DNA binding domain. The length of the AHL acyl group plays a critical role in quorum sensing specificity. Las transcriptional regulator has similar characteristics.
Due to the fact that quorum sensing genes are highly related to bacterial resistant factors, we want to sense the expression of AHL of resistant bacteria and create novel data for further bacterial identification. Our final goal is to collect enough data to create a quorum sensing array that provides instant identification of bacterial species.
 "
"